Middle cerebellar peduncle
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Callum Smith had no recorded disclosures.
View Callum Smith's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Rohit Sharma had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Rohit Sharma's current disclosures- Middle cerebellar peduncles
- Brachium pontis
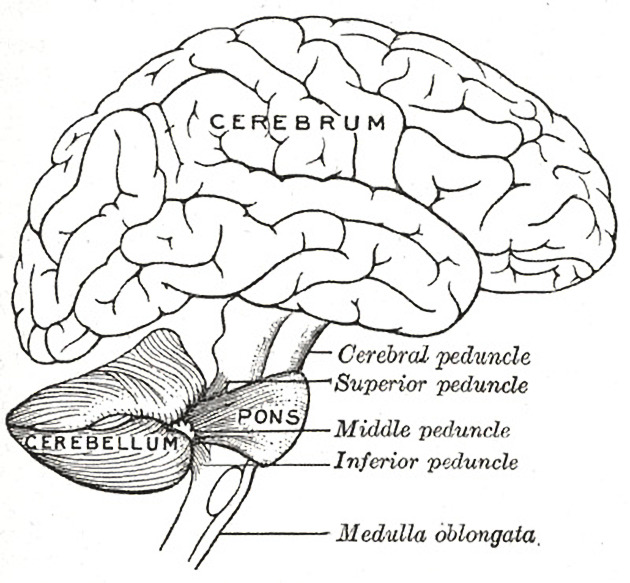
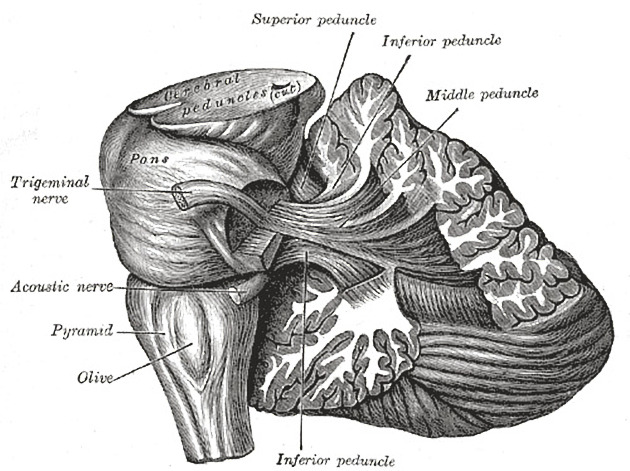
The middle cerebellar peduncles (MCP), also known as the brachium pontis, are paired structures connecting the cerebellum to the pons.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The middle cerebellar peduncles contain afferent white matter projection fibers which originate in contralateral pontine nuclei. The corticopontocerebellar pathway is the predominant afferent fiber pathway that passes through the middle cerebellar peduncles. The corticopontocerebellar pathway itself is involved in the communication between the cerebellum and the prefrontal cortex for the coordination and planning of motor tasks.
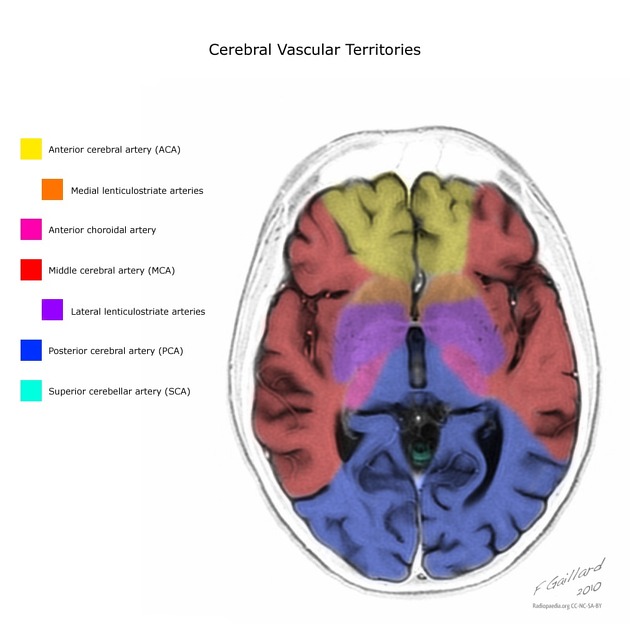
Arterial supply
The middle cerebellar peduncles receive their arterial blood supply through branches of the anterior inferior cerebellar artery and the superior cerebellar artery.
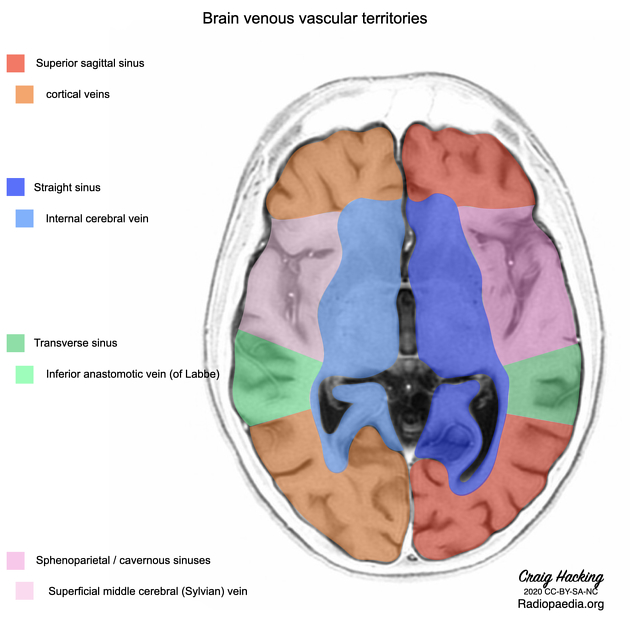
Venous drainage
Venous drainage occurs mainly through veins of the anterior (petrosal) posterior fossa group which empty into the sigmoid and inferior petrosal sinuses.
Radiographic features
See below articles for further discussion of radiographic features of pathologies and signs affecting the middle cerebellar peduncles:
Clinical importance
Diseases affecting the middle cerebellar peduncles present with clinical signs ipsilateral to the middle cerebellar peduncle lesion. This is a result of the dual decussation of cerebellar pathways 1-4.
References
- 1. Morales H, Tomsick T. Middle cerebellar peduncles: Magnetic resonance imaging and pathophysiologic correlate. World journal of radiology. 7 (12): 438-47. doi:10.4329/wjr.v7.i12.438 - Pubmed
- 2. Kouichirou Okamoto, Susumu Tokiguchi, Tetsuya Furusawa, Kazuhiro Ishikawa, Akther F. Quardery, Satoru Shinbo, Keisuke Sasai. MR Features of Diseases Involving Bilateral Middle Cerebellar Peduncles. American Journal of Neuroradiology. 24 (10): 1946. Pubmed
- 3. Mcminn. Last's Anatomy. ISBN: 9780729537520
- 4. Toshio Matsushima. Microsurgical Anatomy and Surgery of the Posterior Cranial Fossa. ISBN: 9784431541837
Incoming Links
- Superior cerebellar artery
- Inferior medullary velum
- Fourth ventricle
- CLCN2-related leukoencephalopathy
- Pontine haemorrhage
- Anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- Inferior medial pontine syndrome
- JC virus granule cell neuronopathy
- Superior petrosal vein
- Bilateral middle cerebellar peduncle lesions
- Pons
- Facial nucleus
- Spetzler-Martin arteriovenous malformation grading system
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (M)
- Hot cross bun sign (pons)
- Multiple system atrophy
- Cerebellum
- Guineafowl (Rorschach radiology)
- Susac syndrome
- Pontocerebellar hypoplasia
- Incidentally discovered metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- Pontocerebellar hypoplasia
- Cerebellar peduncles (Gray's illustration)
- Cerebellar peduncles (Gray's illustration)
- Cavernoma - middle cerebellar peduncle
- Acoustic neuroma with obstructive hydrocephalus
- Meningioma of the cerebellopontine angle
- Cerebral metastases from lung cancer with amyloid angiopathy and cerebellopontine angle meningioma
- Epidermoid cyst compressing the trigeminal nerve
- Maple syrup urine disease
- Meningioma - cerebellopontine angle
- Neurofibromatosis type 2
- Olivopontocerebellar atrophy
- Decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle on diffusion tensor imaging
- Malignant degeneration of low grade glioma
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum [+][+]
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem [+][+]
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere[+][+]
- cerebellar peduncles
- superior cerebellar peduncle
- middle cerebellar peduncle
- inferior cerebellar peduncle
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)[+][+]
- CSF spaces[+][+]
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)[+][+]
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy[+][+]
- CNS development[+][+]
- cerebral vascular supply[+][+]
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.