Portal hypertension is defined as a hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) >5 mmHg, which is a surrogate for the portosystemic pressure gradient. Clinically significant portal hypertension is defined as a gradient >10 mmHg, and variceal bleeding may occur at a gradient >12 mmHg.
On this page:
Pathology
Etiology
Causes can be split by their relation to the hepatic sinusoids 7:
Prehepatic causes
extrinsic compression of portal vein
arteriovenous fistula
SVC obstruction (downhill varices)
Hepatic/sinusoidal causes
schistosomiasis (S. mansoni or S. japonicum)
Posthepatic causes
Subtypes
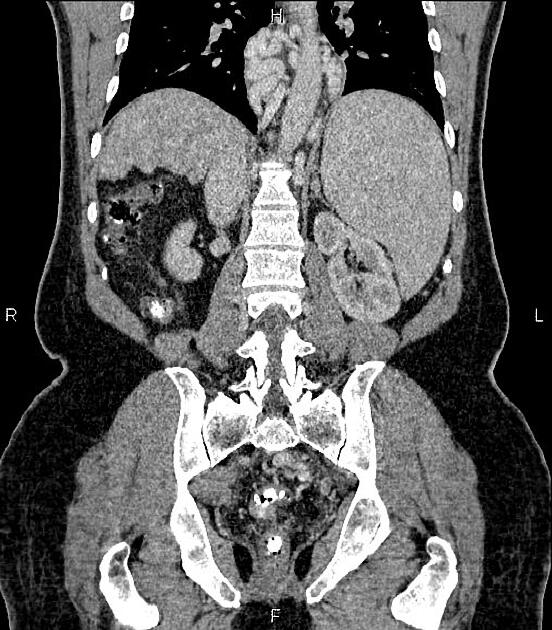
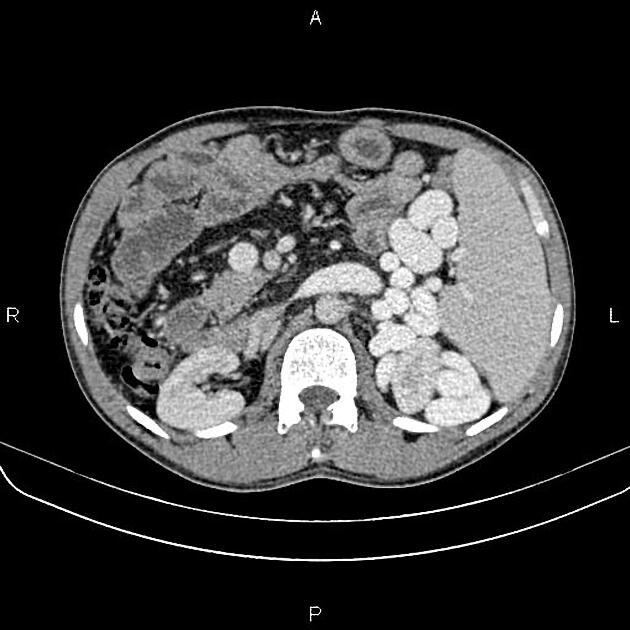
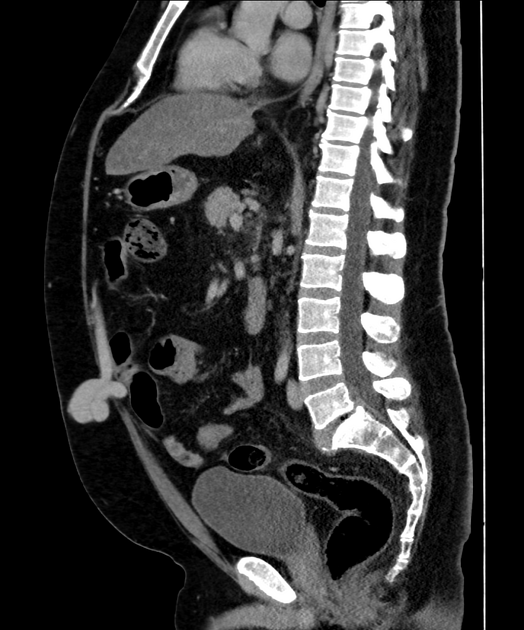
Radiographic features
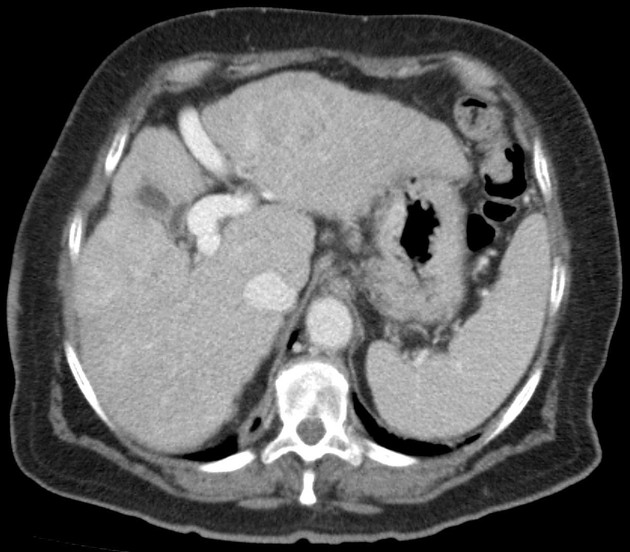
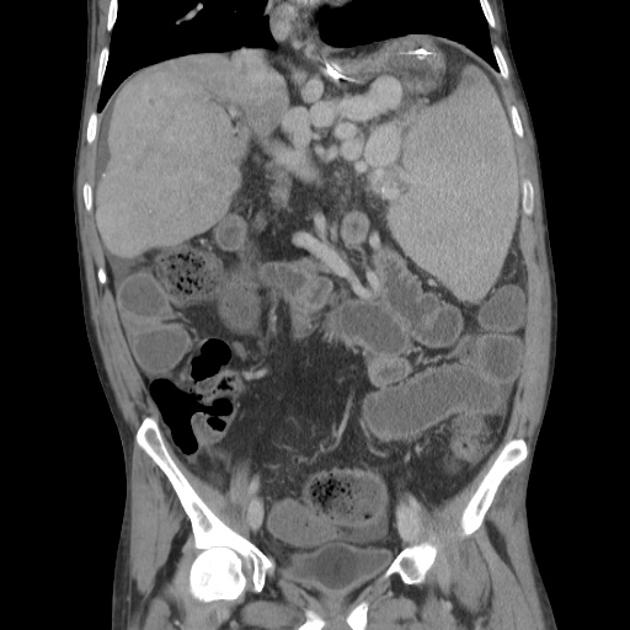
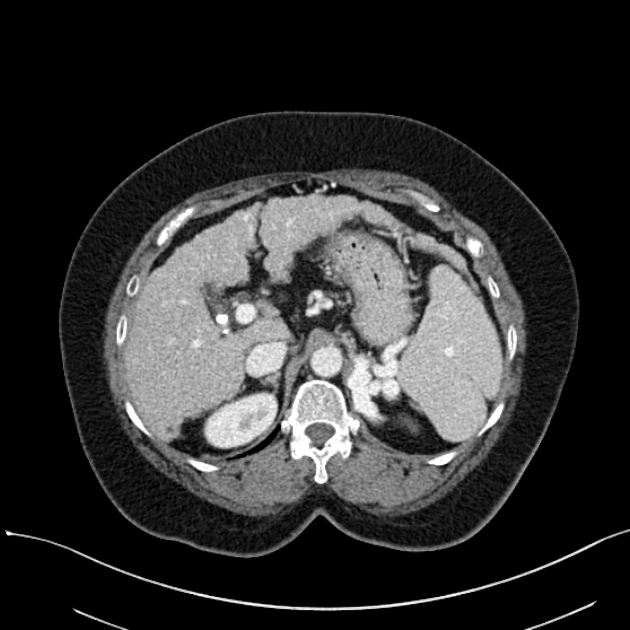
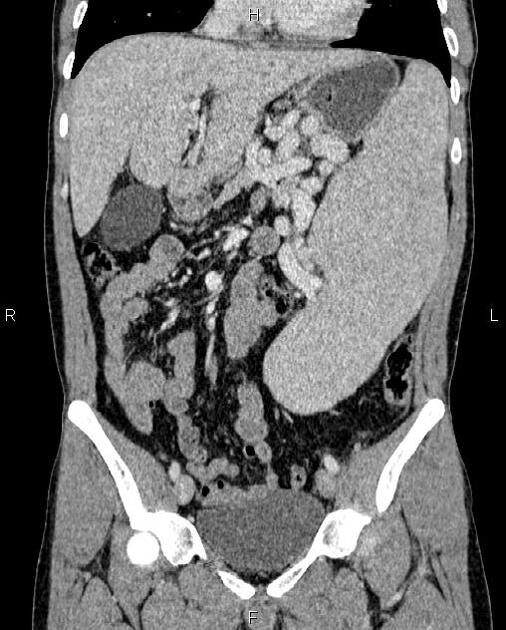
Ultrasound
dilated portal vein (>13 mm): non-specific as an isolated finding 10
-
decreased portal vein velocity <16 cm/sec 10
if recanalized paraumbilical vein, velocity may be increased 9
pulsatile portal waveform as pressure increases 9,10
biphasic or reverse flow in the portal vein (late stage): pathognomonic 11
portal-systemic collateral pathways: varices (e.g. paraumbilical, splenorenal) are considered pathognomonic 11
cause of portal hypertension often identified, most commonly cirrhosis
CT and MRI
dilated portal vein +/- mesenteric veins
contrast enhancement of the paraumbilical vein: pathognomonic ref
cause of portal hypertension can often be identified
Treatment and prognosis
Management ultimately depends on the underlying etiology and the associated complications. Generally, management options include:
lifestyle modifications: dietary sodium restriction (e.g. for ascites)
medications: propranolol (e.g. for varices), diuretics (e.g. for ascites)
-
interventional procedures
creation of shunts: transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS), surgical portosystemic shunt, surgical splenorenal shunt
balloon dilatation of hepatic vein (e.g. for thrombosis/web in hepatic vein)
transhepatic clot thrombolysis (e.g. for portal vein thrombosis)
liver transplantation
Complications
-
esophageal varices and gastric varices
variceal bleeding (30-50% mortality with each bleed)
congestive splenomegaly and hypersplenism
Differential diagnosis
Dilatation of splenic veins at the splenic hilum without splenomegaly may occur in situations such as a state of increased perfusion of splenic tissue associated with an immune response 6.









 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.