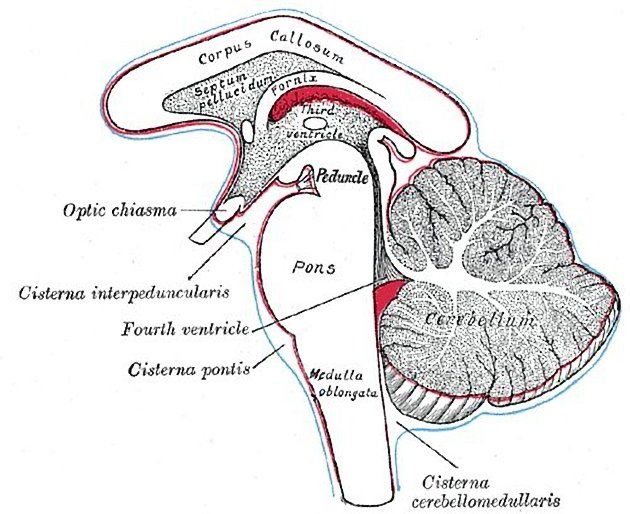
Subarachnoid cisterns
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Kajanan Nithiyananthan had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Kajanan Nithiyananthan's current disclosures- Basal CSF cisterns
- Basal cisterns
The subarachnoid cisterns, or basal cisterns, are compartments within the subarachnoid space where the pia mater and arachnoid membrane are not in close approximation and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) forms pools or cisterns (Latin: "box"). As they are interconnected, their patency is essential for CSF circulation. Cisterns may have vessels and/or cranial nerves passing through them.
The named subarachnoid cisterns are (roughly from superior to inferior):
pericallosal cistern (unpaired): superior to the cistern of the lamina terminalis, superior to the corpus callosum
cistern of the lamina terminalis (unpaired): superior to the suprasellar cistern, anterior to the anterior wall of the third ventricle
Sylvian cistern (paired): deep part of the Sylvian fissure
cistern of the velum interpositum (unpaired): between the layers of tela choroidea in the roof of the third ventricle
suprasellar (chiasmatic) cistern (unpaired): anterior to the interpeduncular cistern, surrounds the pituitary infundibulum and optic chiasm
carotid cistern (paired): lateral to the suprasellar cistern, surrounds the supraclinoid internal carotid artery
-
perimesencephalic cisterns
interpeduncular cistern (unpaired): between the cerebral crura
crural cisterns (paired): between the cerebral crus and uncus of the temporal lobe
ambient cisterns (paired): posterolateral to the midbrain
quadrigeminal cistern (unpaired): between colliculi, splenium of the corpus callosum, and superior surface of the cerebellum
superior cerebellar cistern (unpaired): posterior to the quadrigeminal cistern, between the superior surface of cerebellum and tentorium
prepontine cistern (unpaired): anterior to the pons
cerebellopontine (cerebellopontine angle) cisterns (paired): lateral to the pons, at the cerebellopontine angle
cerebellomedullary (lateral cerebellomedullary) cisterns (paired): lateral to the medulla oblongata
premedullary cistern (unpaired): anterior to the medulla
cisterna magna (unpaired): posterior to the medulla, the largest of the subarachnoid cisterns
The cisterns are, in some instances, separated from each other by arachnoid membranes.
Related pathology
mass effect and increased intracranial pressure, effacing one or more of the cisterns
subarachnoid haemorrhage, including perimesencephalic subarachnoid haemorrhage, filling one or more of the cisterns with blood
References
- 1. Standring S (editor). Gray's Anatomy (39th edition). Churchill Livingstone. (2011) ISBN:0443066841. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Ross LMMP. Atlas of anatomy. George Thieme Verlag. (2007) ISBN:3131421215. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Butler P, Mitchell A, Healy JC. Applied Radiological Anatomy. Cambridge University Press. (2012) ISBN:0521766664. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Altafulla J, Bordes S, Jenkins S, Litvack Z, Iwanaga J, Loukas M, Tubbs RS. The Basal Subarachnoid Cisterns: Surgical and Anatomical Considerations. (2019) World neurosurgery. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2019.05.087 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27-altered
- Cerebellomedullary cisterns
- Arachnoid membranes
- Extra-axial
- Transcranial Doppler sonography (ultrasound)
- Suprasellar cistern
- Diffuse brainstem glioma (historical)
- Frontotemporal brain sagging syndrome
- Prepontine cistern
- Sylvian cistern
- Cistern of the lamina terminalis
- Cerebellopontine angle cistern
- Cisterna magna
- Midline shift
- CT head (an approach)
- Pericallosal cistern
- Traumatic subarachnoid haemorrhage
- Quadrigeminal cistern
- Subarachnoid space
- Interpeduncular cistern
- Subarachnoid haemorrhage
- Aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage
- Ruptured basilar tip aneurysm
- Congenital cytomegalovirus brain infection
- Anterior communicating artery aneurysm with subarachnoid haemorrhage
- White cerebellum sign
- Progressive postnatal pansynostosis
- Non-aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrage with right A1 hypoplasia of the circle of Willis
- Right-sided aortic arch with mirror image branching
- Atlanto-occipital dissociation with vertebral artery transection
- Arterial tortuosity syndrome
- Quadrigeminal cistern lipoma
- Subarachnoid haemorrhage
- Epidermoid cyst - posterior cranial fossa
- Intracranial epidermoid cyst
- Anoxic brain injury secondary to cardiac arrest
- Neurovascular conflict in the CPA cistern
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum [+][+]
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem [+][+]
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)[+][+]
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)[+][+]
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)[+][+]
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy[+][+]
- CNS development[+][+]
- cerebral vascular supply[+][+]
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.