Fetal tachycardia
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures- Fetal sinus tachycardia
- Fetal tachycardias
Fetal tachycardia is an abnormal increase in the fetal heart rate. It is variably defined as a heart rate above 160-180 beats per minute (bpm) and typically ranges between 170-220 bpm (higher rates can occur with tachyarrhythmias).
On this page:
Epidemiology
The estimated prevalence is ~0.4-1% of pregnancies 3,7.
Pathology
In the majority of cases, the abnormal electrical impulses originate from the atria. A fetal tachycardia can range from simple sinus tachycardia to various fetal tachyarrhythmias. In sinus tachycardia, there is a 1:1 conduction from the atria through to the ventricles.
Associations
A fetal tachycardia can be associated with many maternal, as well as fetal conditions, which include:
-
maternal
maternal hyperthyroidism
maternal medications
maternal tachycardia (e.g. systemic infection)
-
fetal
-
chromosomal anomalies
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Radiographic features
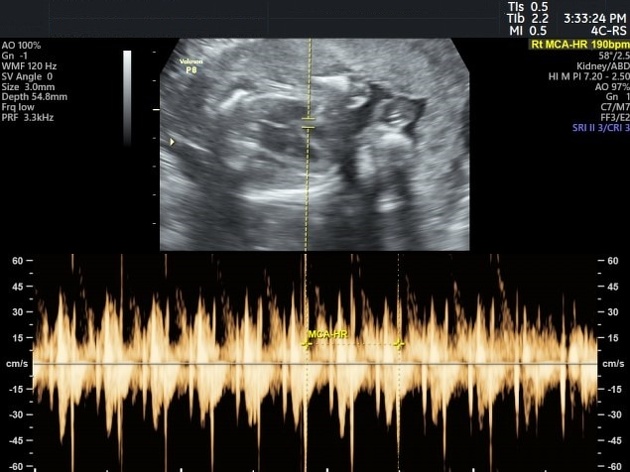
Ultrasound
Fetal echocardiography
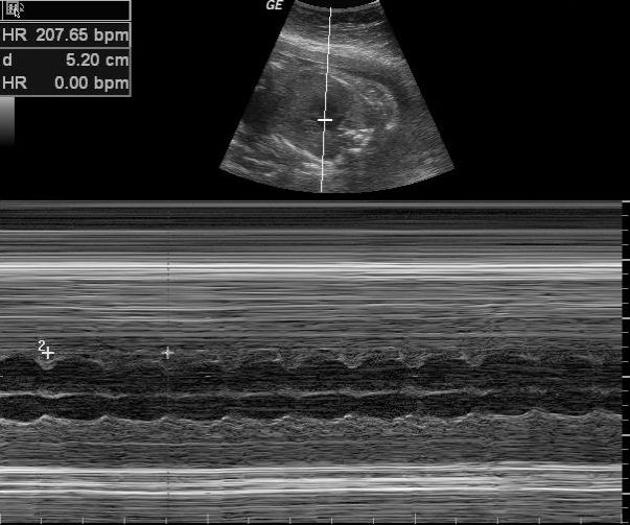
An M-mode Doppler study is best for assessment of heart rate. It is recommended that the sampling line intercepts both the atrial and ventricular walls, thereby allowing simultaneous assessment of both ventricular and atrial contractility.
Ancillary features
Ultrasound may also show evidence of associated complications, such as signs of hydrops fetalis.
Treatment and prognosis
The long-term prognosis for most fetuses diagnosed with sinus tachycardia is generally good, with the abnormal rhythm resolving spontaneously during the first year of life in the majority of cases 5. Treatment options (if required) include transplacental administration of antiarrhythmic drugs.
History and etymology
It was first recognized by A S Hyman in 1930 2.
Differential diagnosis
Considerations include:
fetal premature atrial contraction(s): transient and not sustained
fetal premature ventricular contraction(s): transient and not sustained
References
- 1. Oudijk MA, Visser GH, Meijboom EJ. Fetal tachyarrhythmia--part I: Diagnosis. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J. 2004;4 (3): 104-13. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J (link) - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 2. Hyman AS. Irregularities of the fetal heart: a phonocardiographic study of the fetal heart sounds from the fifth to eighth months of pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1930;20:332–347.
- 3. Bergmans M, Jonker G, Kock H. Fetal Supraventricular Tachycardia. Review of the Literature. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1985;40(2):61-8. doi:10.1097/00006254-198502000-00002 - Pubmed
- 4. Kothari DS, Skinner JR. Neonatal tachycardias: an update. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2006;91 (2): F136-44. doi:10.1136/adc.2004.049049 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 5. Lulić Jurjević R, Podnar T, Vesel S. Diagnosis, Clinical Features, Management, and Post-Natal Follow-Up of Fetal Tachycardias. Cardiol Young. 2009;19(5):486-93. doi:10.1017/S1047951109990497 - Pubmed
- 6. Brown DL. Sonographic assessment of fetal arrhythmias. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997;169 (4): 1029-33. AJR Am J Roentgenol (citation) - Pubmed citation
- 7. Michael Entezami. Ultrasound Diagnosis of Fetal Anomalies. (2004) ISBN: 9781588902122 - Google Books
Incoming Links
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta previa
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumors
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumors of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumors
- mixed germ cell tumor
- yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumor
- sex cord / stromal tumors of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumor of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumors (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumors
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.