Ovarian fibrothecoma
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created The Radswiki had no recorded disclosures.
View The Radswiki's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosures- Ovarian fibrothecomas
- Fibrothecoma of the ovary
Ovarian fibrothecomas comprise tumors in the spectrum of ovarian sex cord / stromal tumors where there are components of both an ovarian fibroma and an ovarian thecoma.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Most occur in adult women, with ~66% in postmenopausal women. Although they account for ~1% of all ovarian tumors 5, they are the most common benign solid ovarian tumor. It represents <2% of pediatric ovarian tumors.
Clinical presentation
The thecoma component of a fibrothecoma can secrete estrogen, and the patient may present with abnormal vaginal bleeding and endometrial hyperplasia.
Pathology
These tumors have a variable amount of both fibrous tissue (see ovarian fibroma) and thecal cells (see ovarian thecoma).
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
They may be seen as a homogeneous hypoechoic mass with posterior acoustic shadowing, although in most cases the sonographic appearance is nonspecific.
CT
The vast majority (~80%) of ovarian fibrothecomas appear as solid masses with a delayed accumulation of contrast medium. On dynamic CT, there is an absence of arterial vessels and absence or slight early uptake of contrast enhancement 3. Calcification may be present and, as these tumors enlarge, myxoid or cystic degeneration may occur, resulting in a heterogeneous pattern 4.
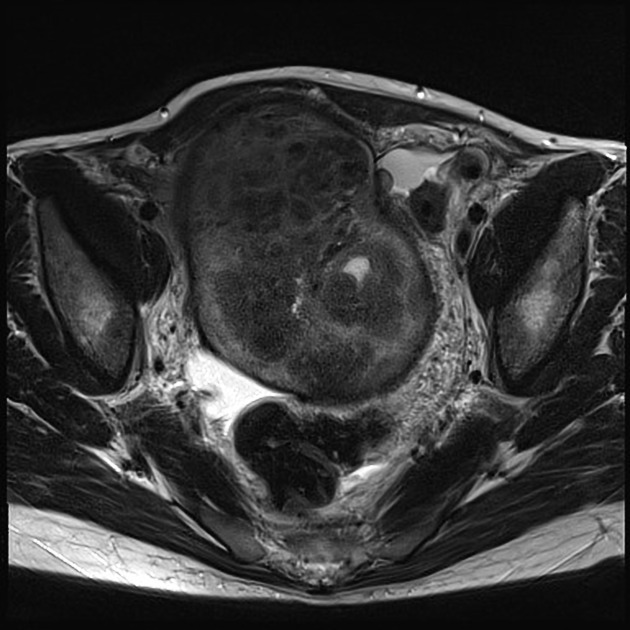
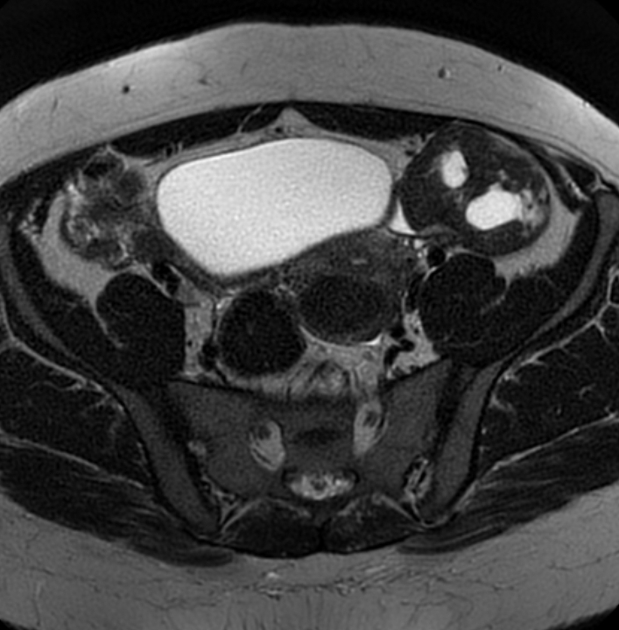
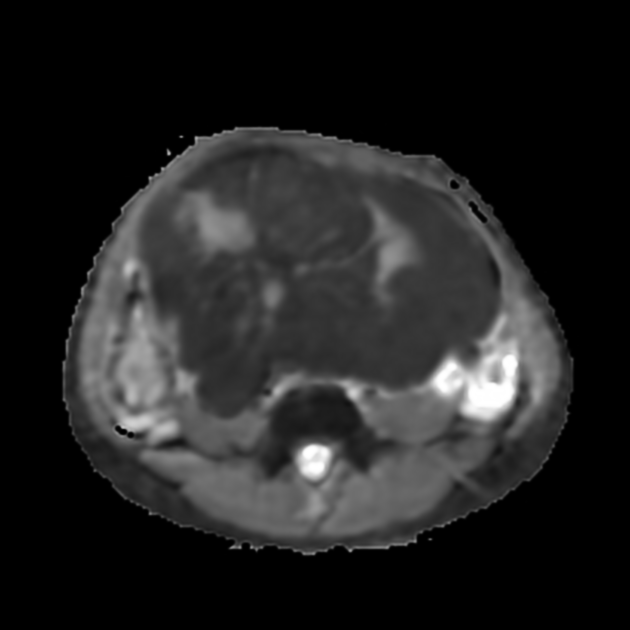
MRI
Reported signal characteristics include 1:
T1: typically shows homogeneous low signal intensity
-
T2
lesions show predominantly homogeneous low signal intensity (from fibrous components)
scattered high signal areas may be present, representing areas of cystic degeneration +/- edema
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Treatment and prognosis
Most cases are benign and surgical resection is curative.
Fibrothecomas are at risk for adnexal torsion, particularly with large tumors 4. As with pure ovarian fibromas, Meigs syndrome may complicate ~1% of cases.
Differential diagnosis
Consider other forms of ovarian tumors (especially fibrous components such as ovarian fibroma).
References
- 1. Troiano RN, Lazzarini KM, Scoutt LM et-al. Fibroma and fibrothecoma of the ovary: MR imaging findings. Radiology. 1997;204 (3): 795-8. Radiology (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- 2. Jung SE, Lee JM, Rha SE et-al. CT and MR imaging of ovarian tumors with emphasis on differential diagnosis. Radiographics. 22 (6): 1305-25. doi:10.1148/rg.226025033 - Pubmed citation
- 3. Bazot M, Ghossain MA, Buy JN et-al. Fibrothecomas of the ovary: CT and US findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 17 (5): 754-9. - Pubmed citation
- 4. Mak CW, Tzeng WS, Chen CY. Computed tomography appearance of ovarian fibrothecomas with and without torsion. Acta Radiol. 2009;50 (5): 570-5. doi:10.1080/02841850902896163 - Pubmed citation
- 5. Hodler J, Schulthess GK, Zollikofer CL. Diseases of the Abdomen and Pelvis 2010-2013, Diagnostic Imaging and Interventional Techniques. Springer. (2010) ISBN:8847016363. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 6. Outwater EK, Wagner BJ, Mannion C et-al. Sex cord-stromal and steroid cell tumors of the ovary. Radiographics. 18 (6): 1523-46. Radiographics (abstract) - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
- Ovarian fibroma
- Ovarian lesions with T2 hypointensity
- Ovarian hyperthecosis
- Broad ligament leiomyoma
- Ovarian thecoma
- Ovarian fibromatosis
- Brenner tumour
- Ovarian tumours
- Ovarian tumours associated with endometrial thickening
- Predominantly solid ovarian neoplasms
- Sex cord / stromal ovarian tumours
- Meigs syndrome
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics[+][+]
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta previa
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus[+][+]
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle[+][+]
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease[+][+]
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix[+][+]
- fallopian tube[+][+]
- other[+][+]
- male genital tract[+][+]
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumors
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumors of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumors
- mixed germ cell tumor
- yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumor
- sex cord / stromal tumors of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumor of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumors (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB[+][+]
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumors
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.