Cystitis cystica
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created The Radswiki had no recorded disclosures.
View The Radswiki's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosuresCystitis cystica is the same condition as ureteritis cystica and is closely related to cystitis glandularis. It is a relatively common chronic reactive inflammatory disorder that occurs in the setting of chronic irritation of the bladder mucosa.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Cystitis cystica is seen in various patients with chronic bladder inflammation as a uniting feature.
Pathology
Chronic irritation from infection, calculi, or even the presence of tumors results in metaplasia of the urothelium. The urothelium proliferates into buds, which grow down into the connective tissue beneath the epithelium in the lamina propria. In the case of cystitis cystica, the buds then differentiate into cystic deposits (whereas in cystitis glandularis, they differentiate into goblet cells). Indeed, in most cases, both conditions can be shown to co-exist histologically.
Etiology
The underlying causes include:
-
chronic bladder outlet obstruction
chronic infection
Radiographic features
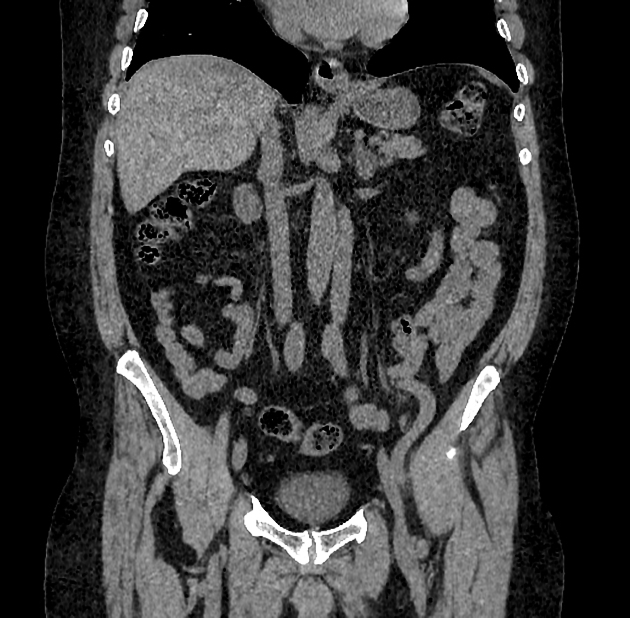
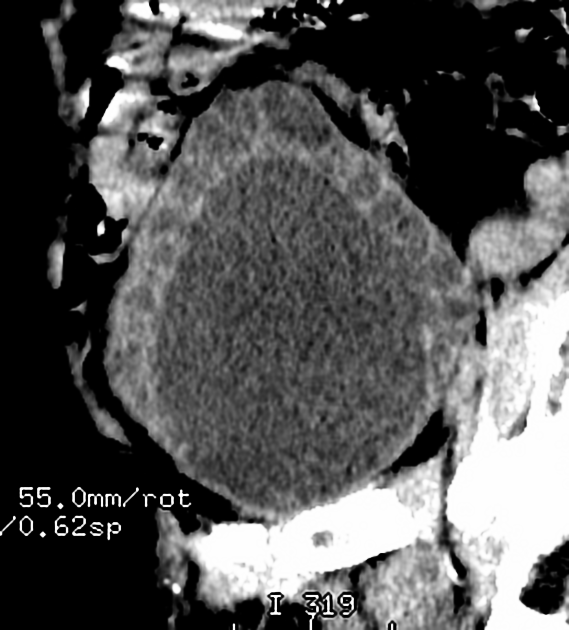
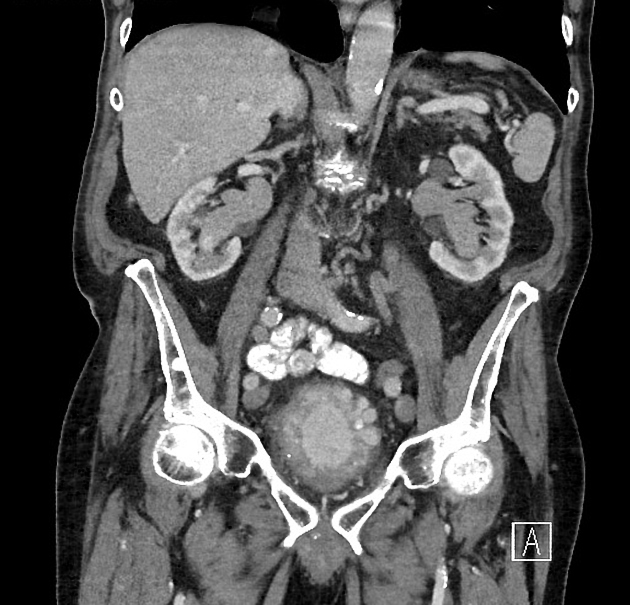
Whether imaged with conventional intravenous excretory urography or with a CT urogram, the appearance is that of multiple, small (2-5 mm) smooth walled, rounded, lucent filling defects projecting into the lumen. Rarely, they can reach 2-3 cm in size 2-3.
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment consists of removing the source of irritation and surgical excision of the area of inflammation or, in rare severe cases, cystectomy. An association with adenocarcinoma of the bladder has been described; thus, these patients should be monitored.
References
- 1. Wong-You-Cheong J, Woodward P, Manning M, Davis C. From the Archives of the AFIP: Inflammatory and Nonneoplastic Bladder Masses: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation. Radiographics. 2006;26(6):1847-68. doi:10.1148/rg.266065126 - Pubmed
- 2. James M. Provenzale, Rendon C. Nelson. Duke Radiology Case Review. (1998) ISBN: 9780397516131 - Google Books
- 3. Francis Joffre. Radiological Imaging of the Ureter. (2003) ISBN: 9783540655213 - Google Books
Incoming Links
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta previa
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumors
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumors of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumors
- mixed germ cell tumor
- yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumor
- sex cord / stromal tumors of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumor of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumors (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumors
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.