Posterior inferior cerebellar artery
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Mostafa Elfeky had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Mostafa Elfeky's current disclosures- Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA)
- PICA
Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) is one of the three vessels that provide arterial supply to the cerebellum. It is the most variable and tortuous cerebellar artery.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Origin
The PICA is a paired artery that originates from the vertebral artery V4 segment.
However, its origin is highly variable:
~20% arise extracranially, inferior to the foramen magnum
10% arise from the basilar rather than vertebral artery
2% bilaterally absent
occasionally arises from a common origin with the anterior inferior cerebellar artery
Segments
The segmental anatomy was defined microsurgically by Lister et al. 6,7:
-
anterior medullary (p1) segment
courses along the front of the medulla at the level of the inferior olive
-
lateral medullary (p2) segment
-
tonsillomedullary (p3; TM) segment
courses along the posterolateral surface of the medulla and inferior cerebellar tonsil
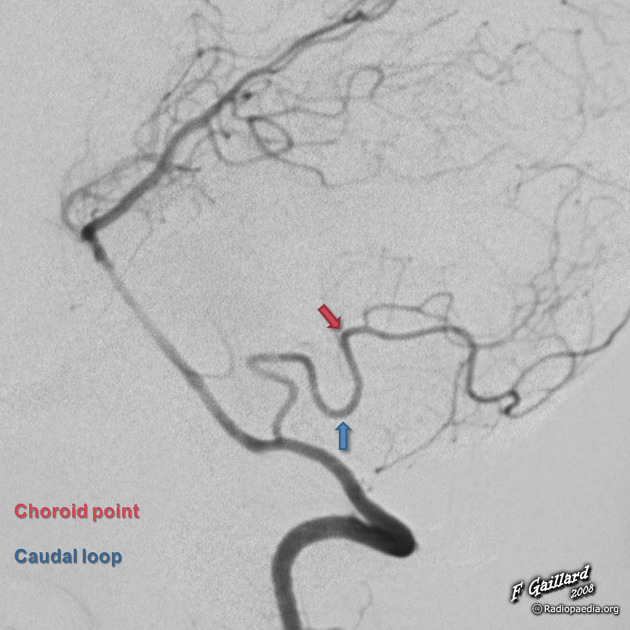
contains the caudal loop, a downward convex loop that mostly remain superior to the foramen magnum but occasionally extend below it
marks the transition between the proximal (medulla-supplying) and distal (cerebellum-supplying) parts of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery
-
telovelotonsillar (p4; TVT) segment
courses in the cleft between the tela choroidea, inferior medullary velum rostrally, and superior pole of the cerebellar tonsil caudally
contains the cranial loop, also known as the choroid point or choroid arch, an upward convex loop that has a constant relation to the 4th ventricle and gives rise to choroidal arteries
-
cortical (p5) segment
supplies branches to the cerebellar surface
Branches
The main trunk of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery usually bifurcates somewhere along the margin of the cerebellar tonsil into
-
medial trunk
supplies the vermis and adjacent hemisphere
-
lateral trunk
supplies the tonsil and hemisphere
The posterior inferior cerebellar artery gives off the following arteries:
perforating (medullary) arteries
choroidal arteries
cortical arteries
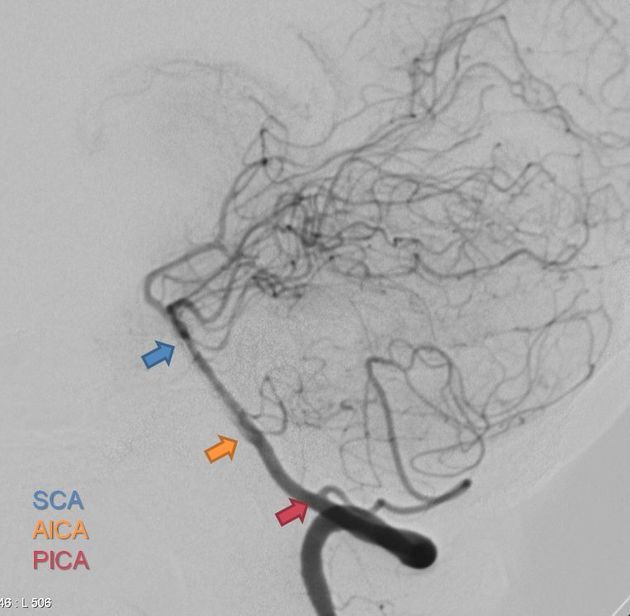
Note: occasionally, a small vertebral artery will terminate into a common AICA-PICA complex.
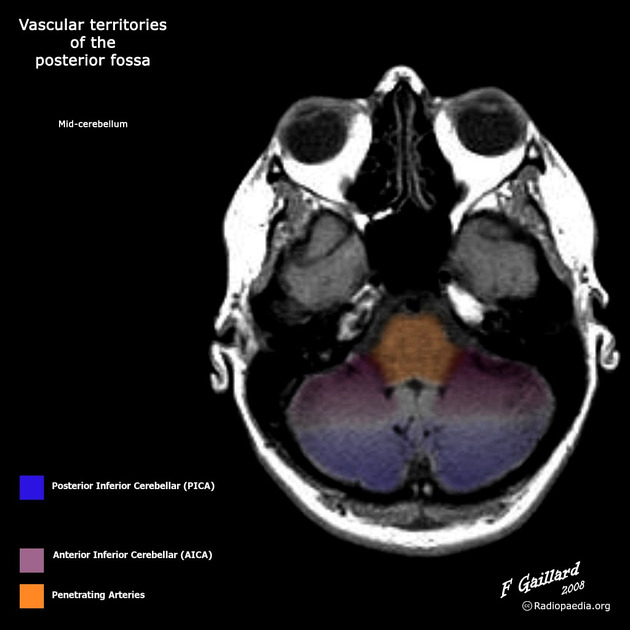
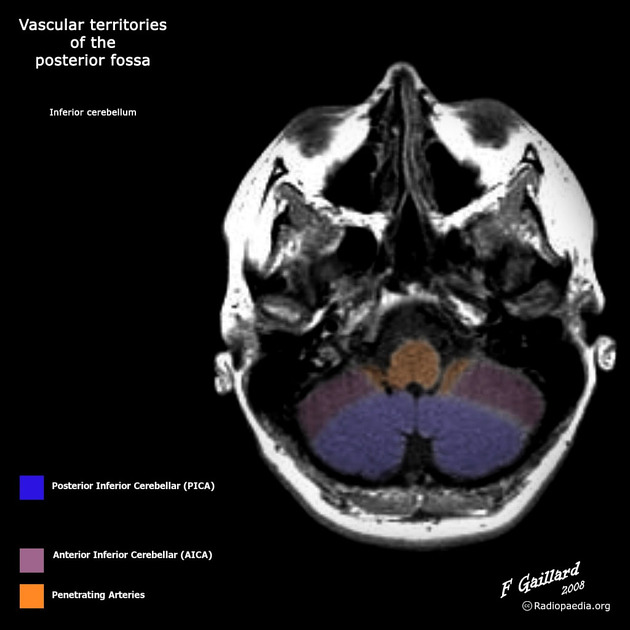
Supply
It has a variable territory depending on the size of the AICA (AICA-PICA dominance). Typically it supplies:
-
posteroinferior cerebellar hemispheres (up to the great horizontal fissure)
cerebellar tonsils: 85% of the time
biventral lobule: 80%
nucleus gracilis: 85%
superior semilunar lobule: 50%
inferior portion of the vermis
lower part of the medulla: 50%
Variant anatomy
course may loop around the cerebellar tonsil
rarely a single unpaired PICA will supply the PICA territory bilaterally 8
Related pathology
References
- 1. Morris P. Practical neuroangiography. (2007) ISBN:0781765153. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Lasjaunias P, Brugge KT, Berenstein A. Surgical Neuroangiography, Vol. 3: Clinical and Interventional Aspects in Children. Springer. (2007) ISBN:3540416811. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Uflacker R. Atlas of vascular anatomy, an angiographic approach. (2007) ISBN:078176081X. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Krayenbühl H, Yaşargil MG, Huber P. Cerebral angiography. Thieme Medical Publishers. (1982) ISBN:0865770670. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 5. Last's anatomy, regional and applied. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN:044304662X. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 6. Lister JR, Rhoton AL, Matsushima T, Peace DA. Microsurgical anatomy of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. (1982) Neurosurgery. 10 (2): 170-99. Pubmed
- 7. Macchi V, Porzionato A, Parenti A, De Caro R. The course of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery may be related to its level of origin. (2004) Surgical and radiologic anatomy : SRA. 26 (1): 60-5. doi:10.1007/s00276-003-0190-2 - Pubmed
- 8. Gaida-Hommernick B, von Smekal U, Kirsch M, Schminke U, Machetanz J, Kessler C. Bilateral Cerebellar Infarctions Caused by a Stenosis of a Congenitally Unpaired Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery. J Neuroimaging. 2001;11(4):435-7. doi:10.1111/j.1552-6569.2001.tb00075.x - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (P)
- Olive
- Babinski-Nageotte syndrome
- Medulla oblongata
- Central nervous system curriculum
- Primitive arteries in the brain (mnemonic)
- Superior cerebellar artery
- Cerebellar tonsils
- Brain arterial vascular territories
- Hemifacial spasm
- Lateral medullary syndrome
- Hemimedullary syndrome
- AICA-PICA dominance
- Cisterna magna
- Medium vessel occlusion
- Cerebellum
- Posterior cerebral circulation
- Vertebral artery dissection
- Premedullary cistern
- Posterior spinal arteries
- Anterior inferior cerebellar artery infarct
- Persistent primitive trigeminal artery
- Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
- Early hyperacute ischemic stroke
- Vertebrobasilar artery occlusion - diagnosis and treatment
- Lateral medullary (Wallenberg) syndrome
- Vermian infarct
- Bilateral cerebellar tonsil infarction
- Posterior inferior cerebellar arterial infarct
- Cerebellar infarcts
- Right-sided aortic arch with mirror image branching
- Intracranial neurenteric cyst
- Vertebral artery hypoplasia
- Subacute posterior inferior cerebellar artery infarct
- Bilateral cerebellar infarction
- Basilar artery stroke
- Lateral medullary syndrome
- Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) infarct
- Absent right PICA
- Brainstem arterial territories (diagrams)
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway
Related articles: Anatomy: Spine
-
osteology[+][+]
- vertebrae
- spinal canal
- cervical spine
- thoracic spine
- lumbar spine
- sacrum
- coccyx
-
anatomical variants
- vertebral body
- neural arch
- transitional vertebrae
- ossicles
- ossification centers
- intervertebral disc[+][+]
- articulations[+][+]
- ligaments[+][+]
- musculature of the vertebral column[+][+]
- muscles of the neck
- muscles of the back
-
suboccipital muscle group
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- splenius capitis muscle
- splenius cervicis muscle
- erector spinae group
- transversospinalis group
- quadratus lumborum muscle
-
suboccipital muscle group
- spinal meninges and spaces[+][+]
-
spinal cord
- gross anatomy[+][+]
-
white matter tracts (white matter)[+][+]
- corticospinal tract
- anterolateral columns
- lateral columns
-
dorsal columns
- fasiculus gracilis (column of Goll)
- fasiculus cuneatus (column of Burdach)
- grey matter[+][+]
- nerve root[+][+]
- central canal
- functional anatomy[+][+]
-
spinal cord blood supply
- arteries
-
vertebral artery
- anterior spinal artery[+][+]
- posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA)
- segmental arteries[+][+]
-
vertebral artery
- veins[+][+]
- arteries
- sympathetic chain[+][+]





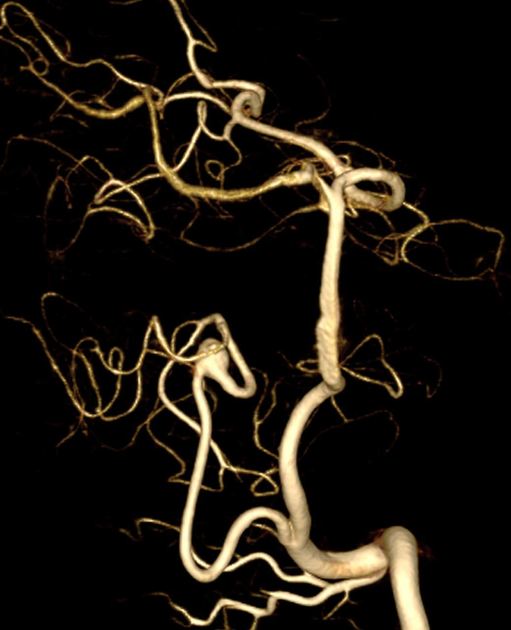


 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.