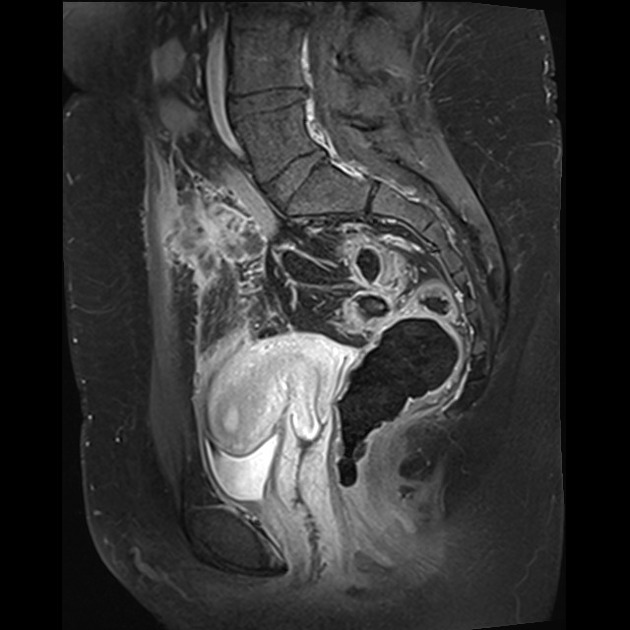
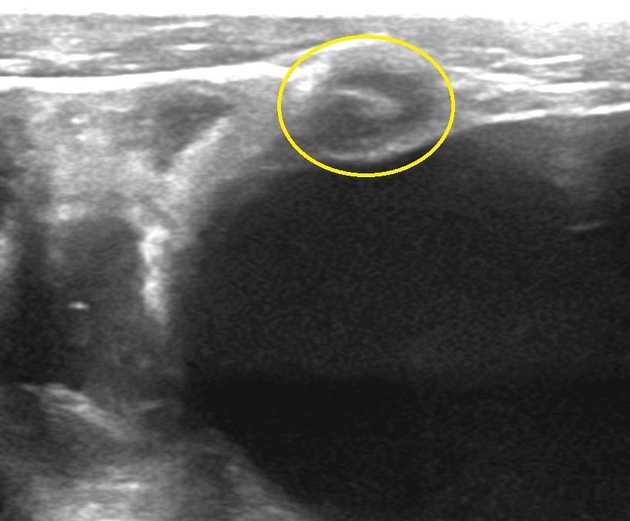
Urachal cyst
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created The Radswiki had no recorded disclosures.
View The Radswiki's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Mohammad Taghi Niknejad had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Mohammad Taghi Niknejad's current disclosures- Urachal cysts
Urachal cysts are one of the manifestations of the spectrum of congenital urachal remnant abnormalities.
On this page:
Epidemiology
An infected urachal cyst can occur at any age.
Clinical presentation
Urachal cysts usually remain asymptomatic until complicated by infection or bleeding.
Pathology
Urachal cysts form when both the umbilical and vesical ends of the urachal lumen close while an intervening portion remains patent and fluid-filled. The cyst can drain through the umbilicus, bladder, or through the peritoneum and into intraperitoneal organs. Rarely it can cause peritonitis and abdominal symptoms.
The most common pathogens of urachal abscess are Staphylococcus, E. coli, Pseudomonas, and Streptococcus.
Radiographic features
An uncomplicated urachal cyst appears as a collection of simple fluid localized in the midline of the anterior abdominal wall, between the umbilicus and the pubis and often contiguous with the bladder dome.
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment of a urachal cyst may involve IV antibiotic therapy and/or surgical excision. Drainage is usually associated with a high rate of relapse. Sometimes it is advisable to drain the cyst contents before its excision.
Differential diagnosis
For an infected urachal cyst, bladder adenocarcinoma should be considered. For a non-infected urachal cyst general imaging differential considerations include
References
- 1. Berrocal T, López-pereira P, Arjonilla A et-al. Anomalies of the distal ureter, bladder, and urethra in children: embryologic, radiologic, and pathologic features. Radiographics. 22 (5): 1139-64. Radiographics (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 2. Yu JS, Kim KW, Lee HJ et-al. Urachal remnant diseases: spectrum of CT and US findings. Radiographics. 21 (2): 451-61. Radiographics (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 3. Pesce C, Costa L, Musi L, Campobasso P, Zimbardo L. Relevance of infection in children with urachal cysts. (2000) European urology. 38 (4): 457-60. doi:10.1159/000020324 - Pubmed
- 4. Navarrete S, Sánchez Ismayel A, Sánchez Salas R, Sánchez R, Navarrete Llopis S. Treatment of urachal anomalies: a minimally invasive surgery technique. (2005) JSLS : Journal of the Society of Laparoendoscopic Surgeons. 9 (4): 422-5. Pubmed
- 5. Chauvin N, Domachowske JB. Infected urachal cyst presenting as fever of unknown origin. (2005) Clinical pediatrics. 44 (1): 85-7. doi:10.1177/000992280504400111 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Intravesical urachal cyst
- Umbilical granuloma
- Vesicourachal diverticulum and calculus
- Infected urachal cyst
- Infected urachal cyst with urachal-sigmoid fistula
- Urachal cyst
- Urachal cyst
- Intravesical urachal cyst
- Urachus (illustration)
- Infected urachal cyst
- Infected vesicourachal diverticulum
- Urachal cyst
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta previa
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumors
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumors of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumors
- mixed germ cell tumor
- yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumor
- sex cord / stromal tumors of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumor of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumors (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumors
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys














 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.