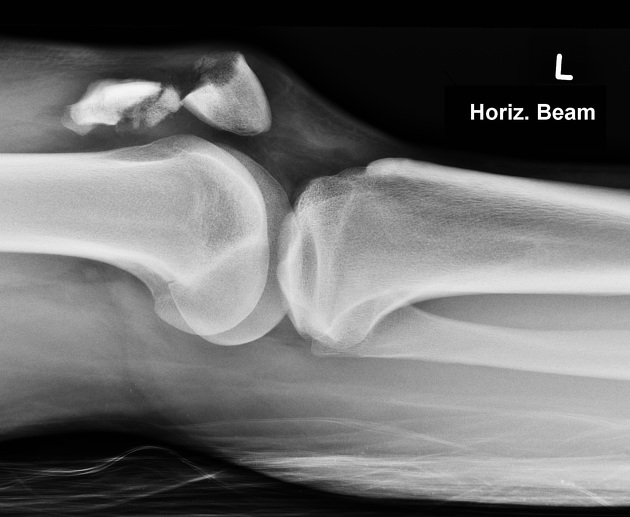
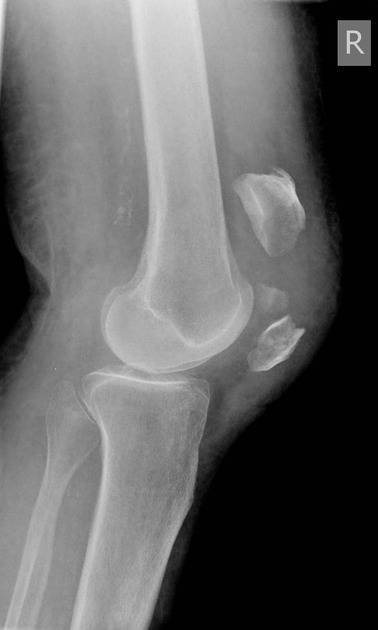
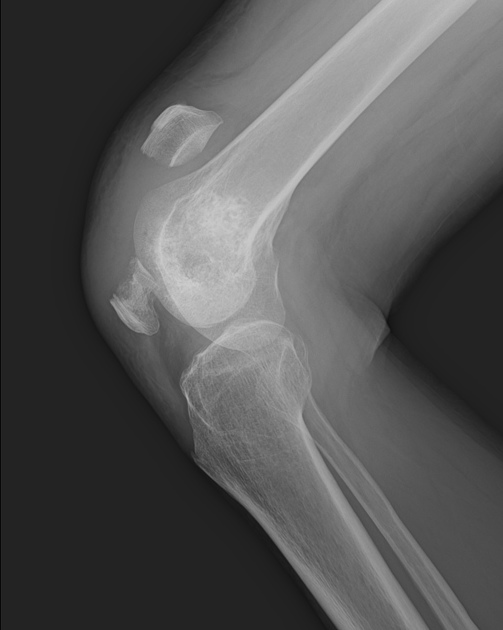
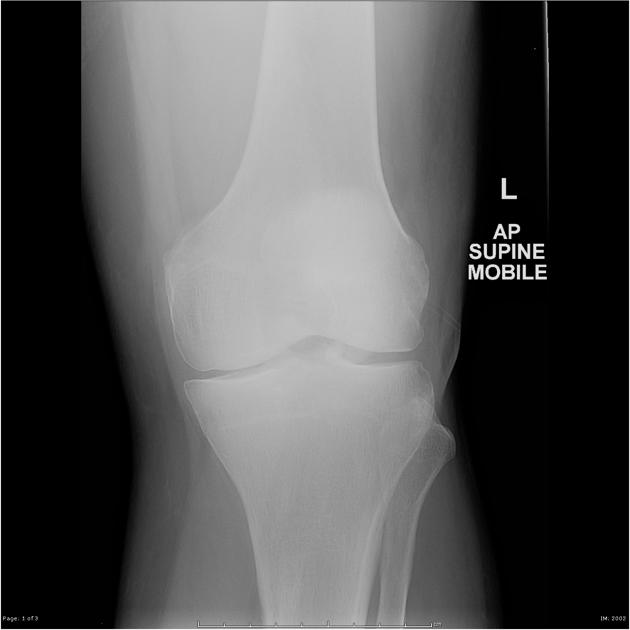
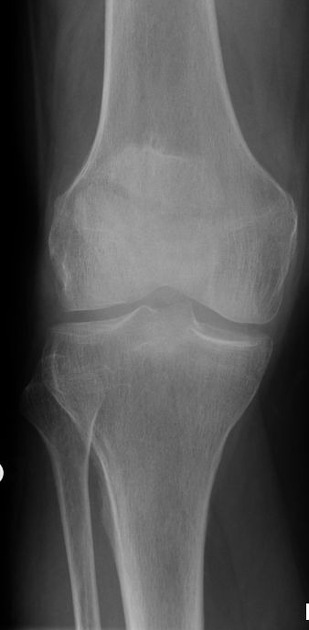
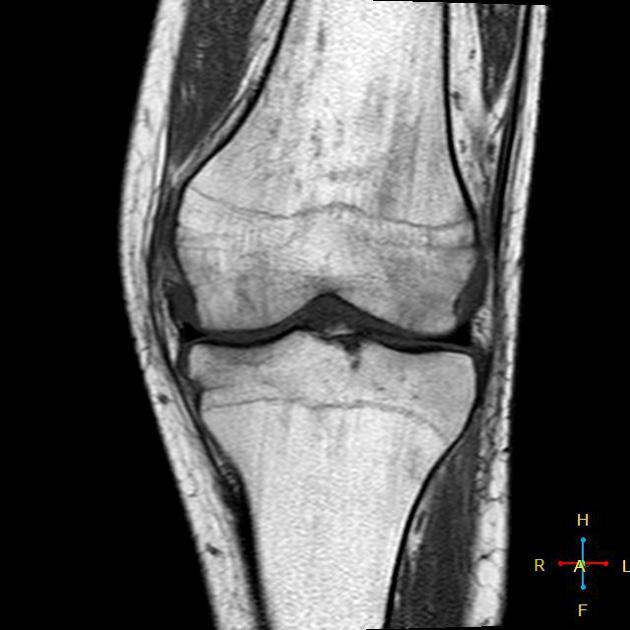
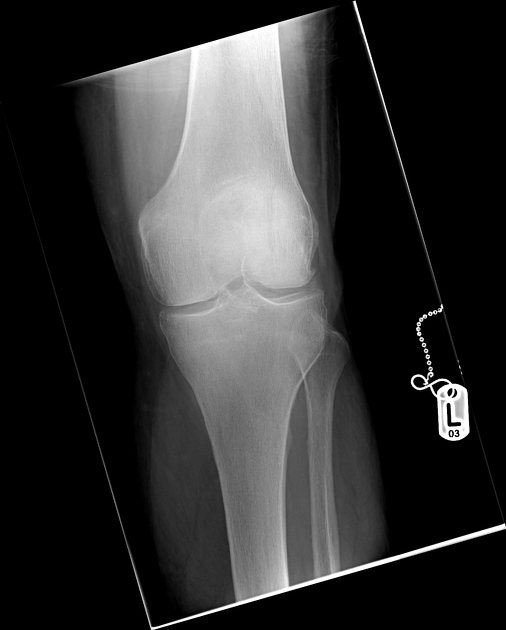
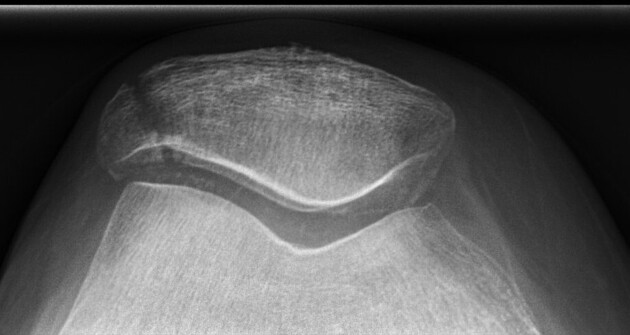
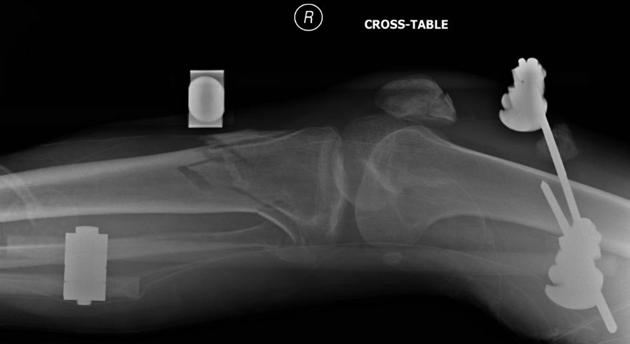
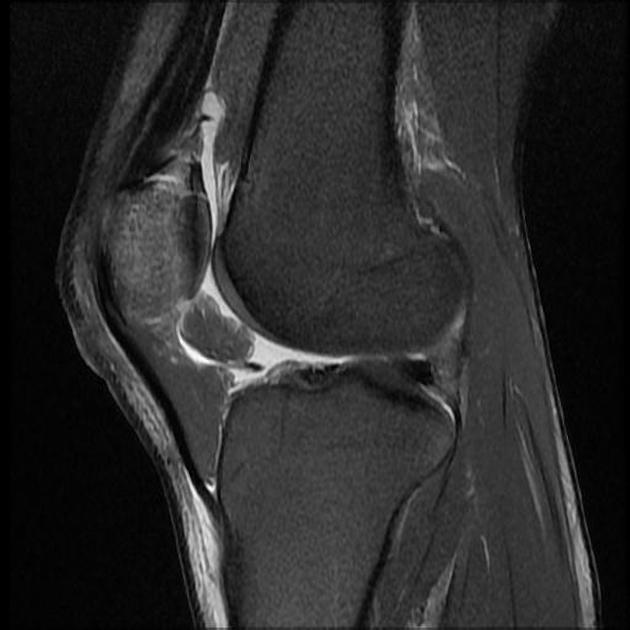
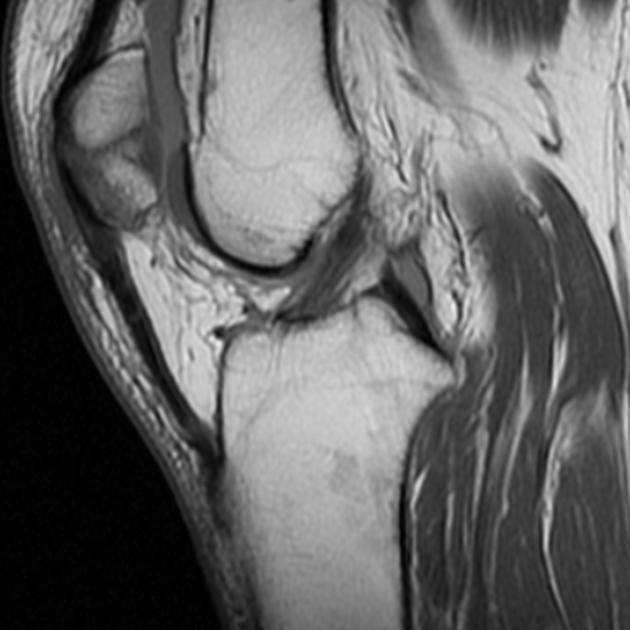
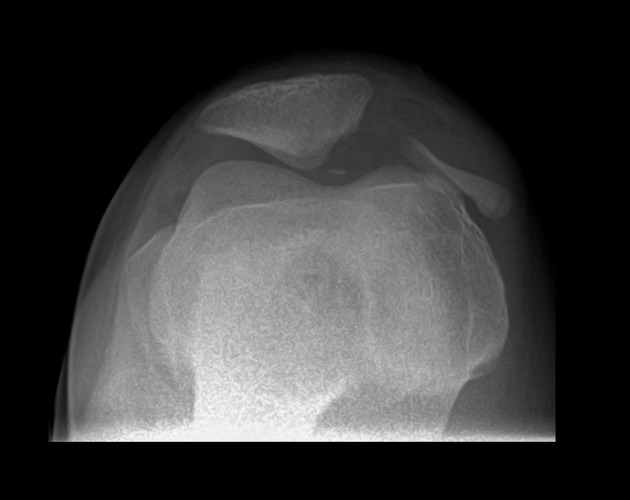
Patellar fracture
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Anon Ny Mous had no recorded disclosures.
View Anon Ny Mous's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Karen Machang'a had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Karen Machang'a's current disclosures- Fracture of patella
- Patella fractures
- Fracture of the patella
- Fractured patella
- Patella fracture
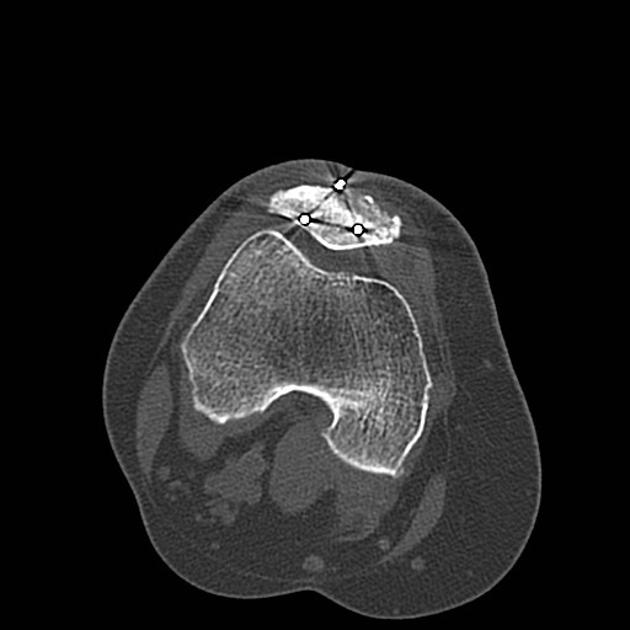
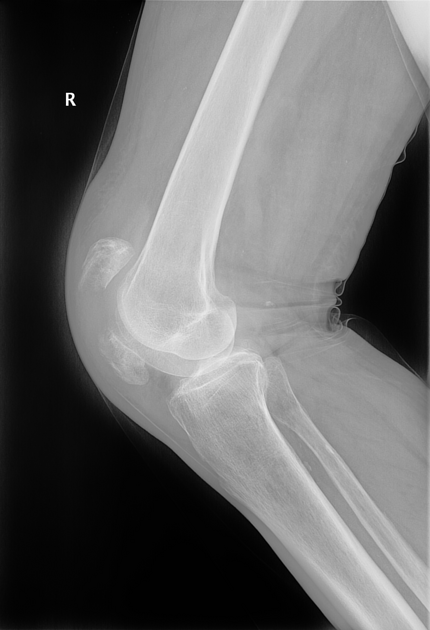
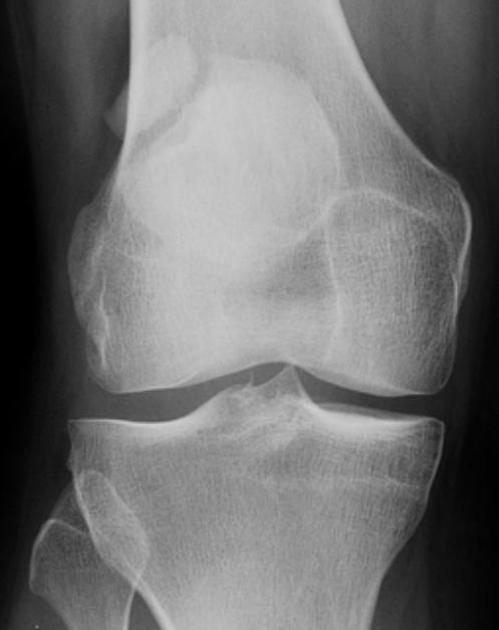
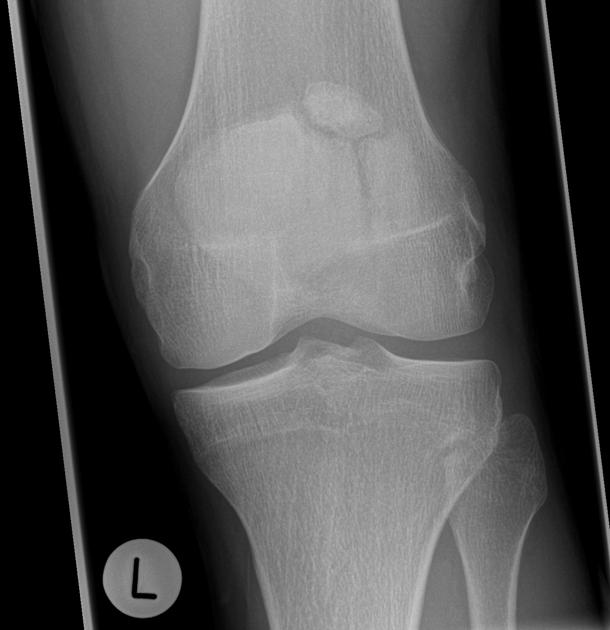
Patellar fracture is one of the common knee injuries usually post direct trauma to the patella or sudden forceful contraction of the quadriceps muscles in the context of a sports injury.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Fractures of the patella represent ~1% of all fractures and are most common in those aged 20-50 years. Two-thirds of cases are in males 7.
Clinical presentation
Patients present with marked swelling and pain over the patella with point tenderness and marked reduction in extension strength. Usually, there is a large joint effusion or hemarthrosis.
Complications
- stiffness
- weak extensor mechanism
- degenerative disease of the patellofemoral joint
Pathology
Etiology
There are different causes of patella fracture:
- direct blow to the patella, e.g. dashboard injury (high energy) or fall onto the patella (low energy)
- severe forces by the extensor mechanism
- after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
- after total knee reconstruction
- pathological fracture
In practice, often both direct and indirect mechanisms are important, e.g. a direct trauma coupled with a forceful contraction of the quadriceps 7.
Morphology
- transverse fracture of mid patella (most common)
- comminuted fracture
- vertical fracture (least common)
- osteochondral defect usually from medial facet
- patellar sleeve fracture in children
Some fractures are more subtle and need to be differentiated from normal variants.
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment is determined by the amount of displacement of the fracture and whether the extensor mechanism of the knee is intact or disrupted.
For patients with a nondisplaced or minimally displaced fracture and an intact extensor mechanism, nonoperative treatment may be suitable. This usually involved a Zimmer knee splint for 4-6 weeks. The patient is usually allowed to weight bear in the splint during this period 6.
In the case of displaced fractures or disrupted extensor mechanism, surgical management is usually required 6. The surgical treatment of these fractures usually involves tension band wiring (K wire technique).
Differential diagnosis
The main differential is of multipartite patella, where there is a failure of fusion of secondary ossification centers. The unfused fragments are almost always in the superolateral quadrant of the patella. With a multipartite patella, the volume of the true patella plus that of the smaller ossification centers is greater than that expected of a normal patella. With a patellar fracture, the volume of the fractured components is equivalent to that of a normal patella.
Rarely a traumatic separation of a multipartite patella may occur 7.
References
- 1. Bates D, Hresko M, Jaramillo D. Patellar Sleeve Fracture: Demonstration with MR Imaging. Radiology. 1994;193(3):825-7. doi:10.1148/radiology.193.3.7972832
- 2. Chun K, Ohashi K, Bennett D, El-Khoury G. Patellar Fractures After Total Knee Replacement. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;185(3):655-60. doi:10.2214/ajr.185.3.01850655
- 3. Lazaro L, Wellman D, Pardee N et al. Effect of Computerized Tomography on Classification and Treatment Plan for Patellar Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(6):336-44. doi:10.1097/bot.0b013e318270dfe7
- 4. Lee B, Christino M, Daniels A, Hulstyn M, Eberson C. Adolescent Patellar Osteochondral Fracture Following Patellar Dislocation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;21(8):1856-61. doi:10.1007/s00167-012-2179-z
- 5. Scolaro J, Bernstein J, Ahn J. In Brief: Patellar Fractures. Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research. 2011;469(4):1213-5. doi:10.1007/s11999-010-1537-8
- 6. Gwinner C, Märdian S, Schwabe P, Schaser KD, Krapohl BD, Jung TM. Current concepts review: Fractures of the patella. (2016) GMS Interdisciplinary plastic and reconstructive surgery DGPW. 5: Doc01. doi:10.3205/iprs000080 - Pubmed
- 7. Jarraya M, Diaz L, Arndt W, Roemer F, Guermazi A. Imaging of Patellar Fractures. Insights Imaging. 2016;8(1):49-57. doi:10.1007/s13244-016-0535-0
Incoming Links
- Knee radiograph (checklist)
- Quadriceps tendon rupture
- Patella
- Total knee arthroplasty
- Multipartite patella
- Musculoskeletal curriculum
- Extensor mechanism of the knee injuries
- Anterior knee pain
- Patellar sleeve fracture
- Knee joint
- Avulsion fractures of the knee
- Bipartite patella
- Knee radiograph (an approach)
- Lower extremity fractures
- Lipohaemarthrosis
- Patellar tendon rupture
- Sinding-Larsen- Johansson disease
- Patellar fracture
- Patellar fracture (MRI)
- Bilateral bipartite patella
- Tibial plateau fracture
- Patellar fracture
- Patellar fracture (MRI)
- Tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture
- Patellar fracture
- Osteochondral fracture - patella
- Patellar fracture
- Patellar fracture
- Patellar sleeve avulsion
- Patellar fracture
- Non-displaced patellar fracture - MRI
- Patella fracture
- Patella fracture
- Patellar chondral avulsion fracture
- Sinding-Larsen-Johansson disease
- Bipartite patella
Related articles: Fractures
-
fracture
- terminology[+][+]
- fracture location
- diaphyseal fracture
- metaphyseal fracture
- physeal fracture
- epiphyseal fracture
- fracture types
- avulsion fracture
- articular surface injuries
- complete fracture
- incomplete fracture
- infraction
- compound fracture
- pathological fracture
- stress fracture
- fracture displacement
- fracture location
- fracture healing[+][+]
- skull fractures[+][+]
-
facial fractures[+][+]
- fractures involving a single facial buttress
- alveolar process fractures
- frontal sinus fracture
- isolated zygomatic arch fractures
- mandibular fracture
- nasal bone fracture
- orbital blow-out fracture
- paranasal sinus fractures
- complex fractures
- dental fractures
- fractures involving a single facial buttress
-
spinal fractures[+][+]
- classification (AO Spine classification systems)
-
cervical spine fracture classification systems
- AO classification of upper cervical injuries
- AO classification of subaxial injuries
- Anderson and D'Alonzo classification (odontoid fracture)
- Roy-Camille classification (odontoid process fracture)
- Gehweiler classifcation (atlas fractures)
- Levine and Edwards classification (hangman fracture)
- Allen and Ferguson classification (subaxial spine injuries)
- subaxial cervical spine injury classification (SLIC)
- thoracolumbar spinal fracture classification systems
- three column concept of spinal fractures (Denis classification)
- classification of sacral fractures
-
cervical spine fracture classification systems
- spinal fractures by region
- spinal fracture types
- classification (AO Spine classification systems)
- rib fractures[+][+]
- sternal fractures
-
upper limb fractures[+][+]
- classification
- Rockwood classification (acromioclavicular joint injury)
- AO classification (clavicle fracture)
- Neer classification (clavicle fracture)
- Neer classification (proximal humeral fracture)
- AO classification (proximal humeral fracture)
- AO/OTA classification of distal humeral fractures
- Milch classification (lateral humeral condyle fracture)
- Weiss classification (lateral humeral condyle fracture)
- Bado classification of Monteggia fracture-dislocations (radius-ulna)
- Mason classification (radial head fracture)
- Frykman classification (distal radial fracture)
- Mayo classification (scaphoid fracture)
- Hintermann classification (gamekeeper's thumb)
- Eaton classification (volar plate avulsion injury)
- Keifhaber-Stern classification (volar plate avulsion injury)
- upper limb fractures by region
- shoulder
- clavicular fracture
-
scapular fracture
- acromion fracture
- coracoid process fracture
- glenoid fracture
- humeral head fracture
- proximal humeral fracture
- humeral neck fracture
- arm
- elbow
- forearm
- wrist
-
carpal bones
- scaphoid fracture
- lunate fracture
- capitate fracture
- triquetral fracture
- pisiform fracture
- hamate fracture
- trapezoid fracture
- trapezium fracture
- hand
- shoulder
- classification
- lower limb fractures
- classification by region[+][+]
- pelvic fractures
- hip fractures
- Pipkin classification (femoral head fracture)
- Garden classification (hip fracture)
- American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Cooke and Newman classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Johansson classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Vancouver classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- femoral
- knee
- Schatzker classification (tibial plateau fracture)
- AO classification of distal femur fractures
- Meyers and McKeevers classification (anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture)
- tibia/fibula
- Watson-Jones classification (tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture)
- ankle
- foot
- Berndt and Harty classification (osteochondral lesions of the talus)
- Sanders CT classification (calcaneal fracture)
- Hawkins classification (talar neck fracture)
- Myerson classification (Lisfranc injury)
- Nunley-Vertullo classification (Lisfranc injury)
- pelvis and lower limb fractures by region
- pelvic fracture[+][+]
- sacral fracture[+][+]
- coccygeal fracture
-
hip[+][+]
- acetabular fracture
- femoral head fracture
-
femoral neck fracture
- subcapital fracture
- transcervical fracture
- basicervical fracture
-
trochanteric fracture
- pertrochanteric fracture
- intertrochanteric fracture
- subtrochanteric fracture
- femur[+][+]
- mid-shaft fracture
- bisphosphonate-related fracture
- distal femoral fracture
- knee
- avulsion fractures[+][+]
- Segond fracture
- reverse Segond fracture
- anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture
- posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture
- arcuate complex avulsion fracture (arcuate sign)
- biceps femoris avulsion fracture
- iliotibial band avulsion fracture
- semimembranosus tendon avulsion fracture
- Stieda fracture (MCL avulsion fracture)
- patellar fracture
- tibial plateau fracture
- avulsion fractures[+][+]
- leg[+][+]
- tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture
- tibial shaft fracture
- fibular shaft fracture
- Maisonneuve fracture
- ankle[+][+]
- foot[+][+]
- tarsal bones
- metatarsal bones
- phalanges
- classification by region[+][+]
- terminology[+][+]
Related articles: Knee pathology
The knee is a complex synovial joint that can be affected by a range of pathologies:
- bone and cartilage
-
knee fractures
- distal femoral condyle fracture
- tibial plateau fracture (classification)
- patella fracture
-
avulsion fractures of the knee[+][+]
- arcuate complex avulsion fracture (arcuate sign)
- anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture
- biceps femoris avulsion fracture
- iliotibial band avulsion fracture
- quadriceps tendon avulsion fracture
- patellar sleeve fracture
- posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture
- reverse Segond fracture
- Segond fracture
- semimembranosus tendon avulsion fracture
- Stieda fracture chronic avulsion injuries
- dislocation[+][+]
- chondromalacia patellae
- osteoarthritis of the knee[+][+]
- osteochondral[+][+]
- patterns of bone bruise in knee injury[+][+]
-
knee fractures
- ligaments[+][+]
- anterior cruciate ligament tear
- anterior cruciate ligament ganglion cyst
- anterior cruciate ligament mucoid degeneration
- posterior cruciate ligament tear
- medial collateral ligament tear
- lateral collateral ligament tear
- medial patellofemoral ligament tear
- posterolateral corner injury
- posteromedial corner injury
- tendons[+][+]
- meniscal lesions[+][+]
- bursosynovial lesions[+][+]
- fat pad[+][+]
- popliteal fossa[+][+]
- fascia[+][+]
- alignment[+][+]
- knee
- patellofemoral
- gamut[+][+]





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.