Arcuate uterus
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Natalie Yang had no recorded disclosures.
View Natalie Yang's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosures- Arcuate Womb
An arcuate uterus is a mildly variant shape of the uterus. It is technically one of the Müllerian duct anomalies, but is often classified as a normal variant. It is the uterine anomaly that is least commonly associated with reproductive failure. Arcuate uterus can be characterized with ultrasound or MRI.
On this page:
Pathology
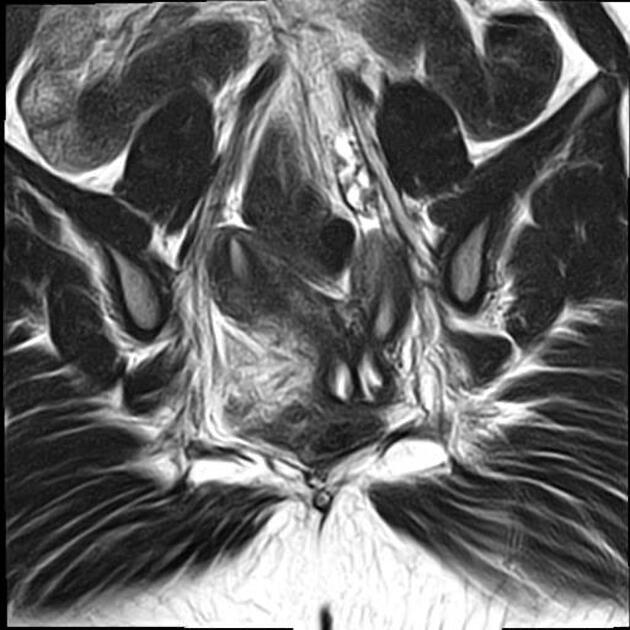
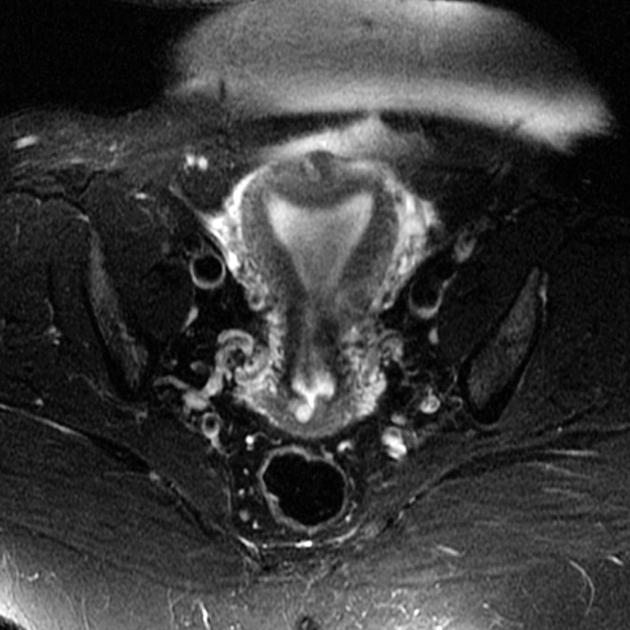
An arcuate uterus is characterized by a mild indentation of the endometrium at the uterine fundus. It occurs due to a failure of complete resorption of the uterovaginal septum, and is the most common Mullerian duct anomaly, affecting 3.9% of the general population 7.
Radiographic features
General features include:
normal fundal contour
no division of uterine horns
smooth indentation of fundal endometrial canal: the depth of indentation is usually considered to be <1 cm
increased transverse diameter of uterine cavity
Fluoroscopy
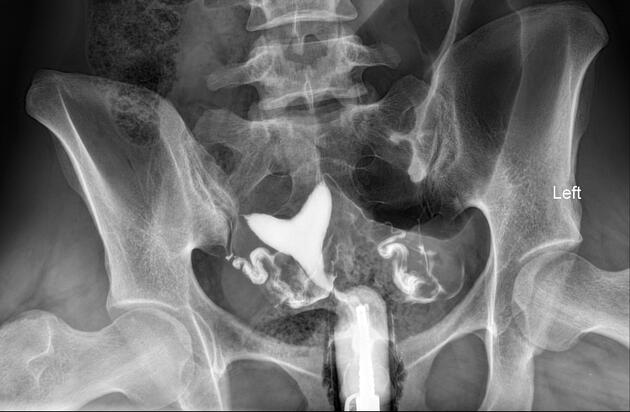
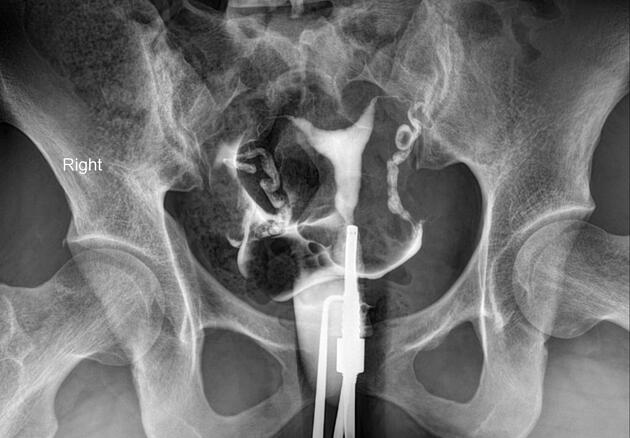
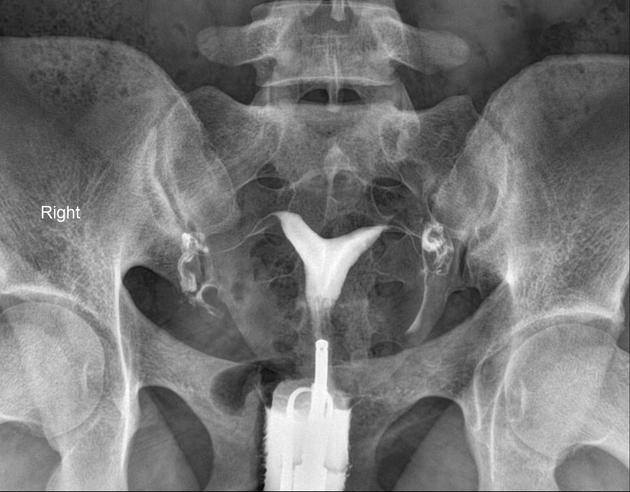
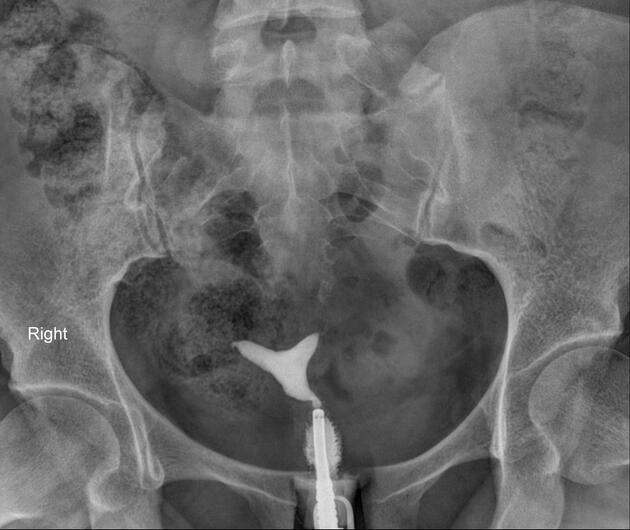
On hysterosalpingograms there is opacification of the endometrial cavity demonstrates a single uterine canal with a broad saddle-shaped indentation of the uterine fundus.
Pelvic ultrasound
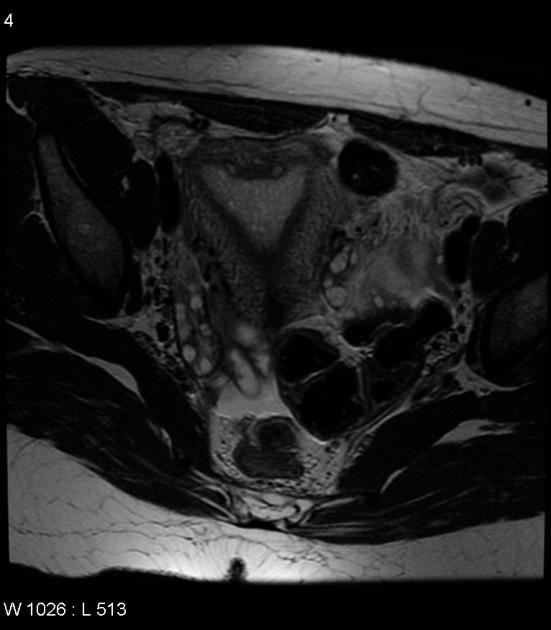
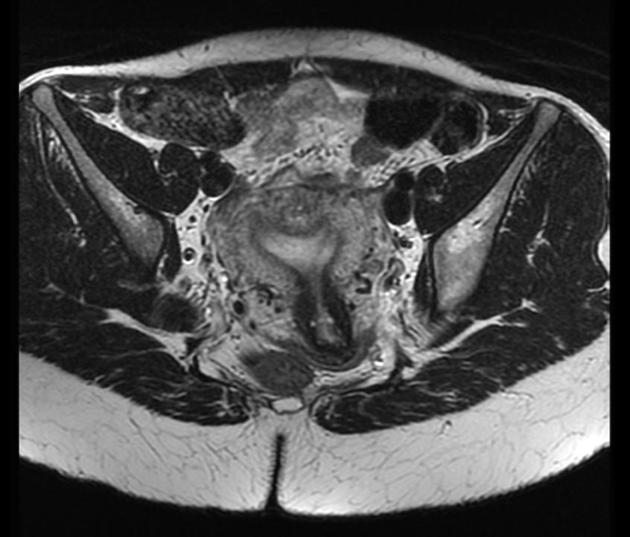
A normal external uterine contour is noted, with a broad smooth indentation on the fundal segment of the endometrium. There should not be division of the uterine horns.
MRI
A normal external uterine contour is maintained. The myometrial fundal indentation is smooth and broad, and the signal intensity of this region is isointense to normal myometrium.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Differential diagnosis
-
arcuate uterus and septate uterus exist on a spectrum from most to least resorption of the uterovaginal septum, respectively
-
arcuate uterus can be distinguished from a bicornuate uterus on the basis of its complete fundal unification (i.e. an arcuate uterus has a normal or slightly indented external fundal contour, whereas a bicornuate uterus has a more marked fundal indentation, ≤5 mm above the level of the uterine horns)
fundal fibroid: on hysterosalpingography can exert smooth indentation of fundal endometrium giving similar appearance to arcuate uterus 8
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Ubeda B, Paraira M, Alert E et-al. Hysterosalpingography: spectrum of normal variants and nonpathologic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177 (1): 131-5. AJR Am J Roentgenol (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 2. Chaudhry S. AJR Teaching File: infertility in a young woman. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189 (3): S11-2. doi:10.2214/AJR.07.7019 - Pubmed citation
- 3. Dykes, Thomas M.; Siegel, Cary; Dodson, William. American Journal of Roentgenology. doi:10.2214/AJR.06.0821
- 4. Troiano RN, Mccarthy SM. Mullerian duct anomalies: imaging and clinical issues. Radiology. 2004;233 (1): 19-34. doi:10.1148/radiol.2331020777 - Pubmed citation
- 5. Imaoka I, Wada A, Matsuo M et-al. MR imaging of disorders associated with female infertility: use in diagnosis, treatment, and management. Radiographics. 23 (6): 1401-21. doi:10.1148/rg.236025115 - Pubmed citation
- 6. Mucowski SJ, Herndon CN, Rosen MP. The arcuate uterine anomaly: a critical appraisal of its diagnostic and clinical relevance. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2010;65 (7): 449-54. doi:10.1097/OGX.0b013e3181efb0db - Pubmed citation
- 7. Behr SC, Courtier JL, Qayyum A. Imaging of müllerian duct anomalies. Radiographics. 2012;32 (6): E233-50. doi:10.1148/rg.326125515 - Pubmed citation
- 8. Panchal S & Nagori C. Chapter-03 Abnormal Uterus. A Complete Textbook for GNM Internship. 2015;:41-76. doi:10.5005/jp/books/12608_4
Incoming Links
- Interstitial ectopic pregnancy
- Undescended fallopian tubes
- Hydrosalpinx
- Arcuate uterus
- Arcuate uterus
- Arcuate uterus
- Arcuate uterus
- Arcuate uterus
- Subseptate uterus
- Arcuate uterus
- Arcuate uterus
- Arcuate uterus
- Subseptate uterus
- Hydrocele of the canal of Nuck
- Subseptate uterus
- Arcuate uterus
- Arcuate uterus
- Mullerian duct anomalies - AFS classification (illustrations)
- Adenomyosis of the uterus
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta previa
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumors
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumors of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumors
- mixed germ cell tumor
- yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumor
- sex cord / stromal tumors of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumor of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumors (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumors
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.