Prostatic utricle cyst
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created The Radswiki had no recorded disclosures.
View The Radswiki's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Ammar Ashraf had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Ammar Ashraf's current disclosures- Prostatic utricle cyst (PUC)
- Utricle cyst
- Utricle cysts
- Prostatic utricle cysts
- Utricle cyst of prostate
- Utricular cyst of the prostate
- Prostate utricular cyst
- Prostatic utricular cyst
A prostatic utricle cyst, also known as a utricular cyst, is an area of focal dilatation that occurs within the prostatic utricle.
They are midline cystic masses in the male pelvis and can be very difficult or impossible to distinguish from a Müllerian duct cyst.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Utricle cysts are most often detected in the 1st and 2nd decades of life (Müllerian duct cysts usually occur in the 3rd and 4th decades).
The incidence of prostatic utricle cysts ranges around 11-14% in association with hypospadias or intersex anomalies and up to 50% in the presence of perineal hypospadias 3.
Associations
Prostatic utricle cysts are associated with a variety of genitourinary abnormalities including:
unilateral renal agenesis
anorectal malformations e.g. imperforate anus
Müllerian duct cysts have no such associations 1.
Clinical presentation
The clinical presentation of utricular cysts is variable and includes pelvic mass, obstructive and irritative urinary tract symptoms, hematuria, and suprapubic or rectal pain.
Urine may pool in utricle cysts, since they communicate with the urethra, occasionally resulting in post-void dribbling. Some patients may be asymptomatic.
Pathology
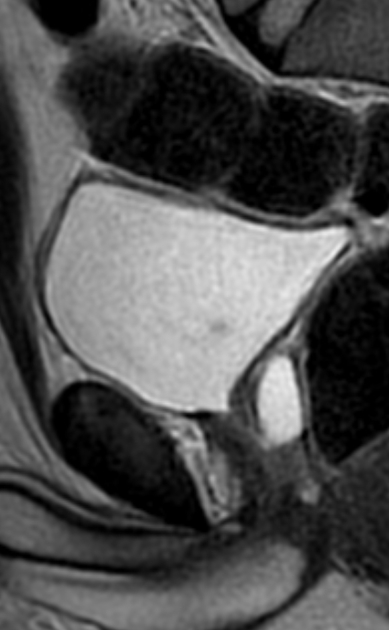
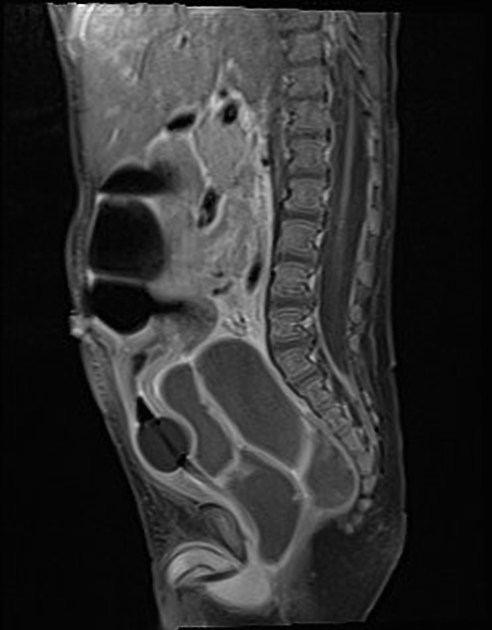
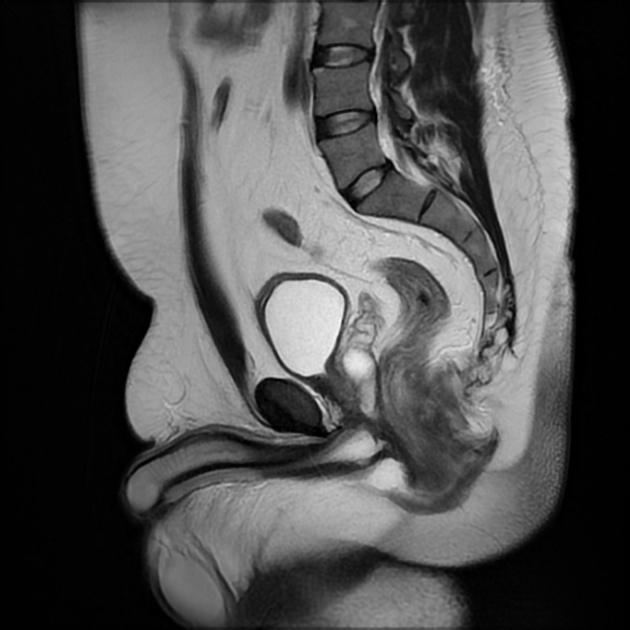
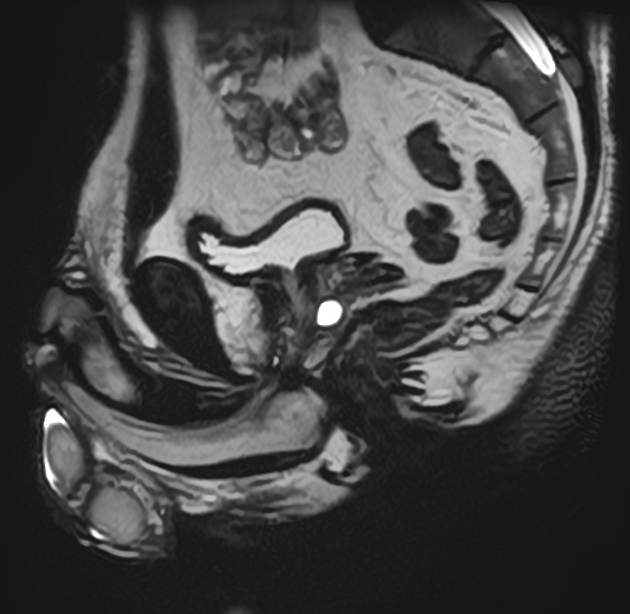
Prostatic utricle cysts always arise from the level of the verumontanum and are always in the midline. Müllerian duct cysts can arise anywhere along the path of Müllerian duct regression, from the scrotum to the utricle.
Utricle cysts are variable in size but are usually smaller (commonly <10 mm) than Müllerian duct cysts and usually do not extend above the prostate gland (Müllerian duct cysts typically extend above the prostate gland).
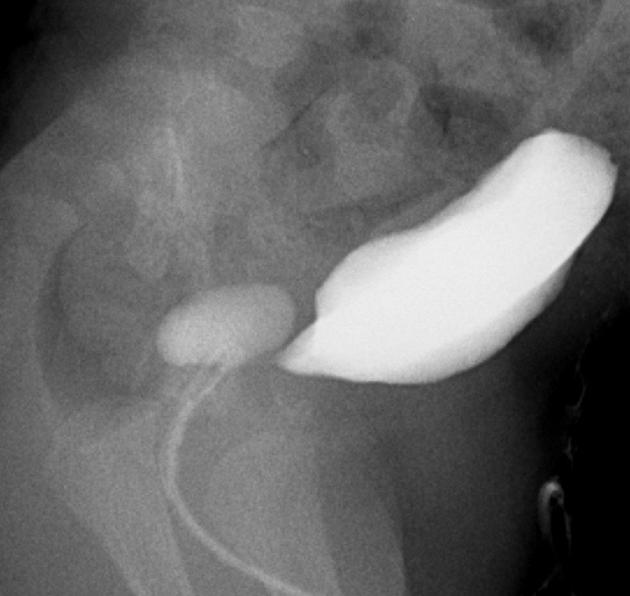
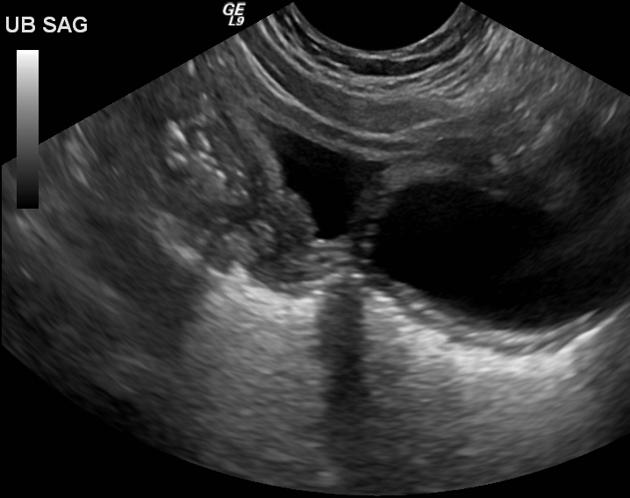
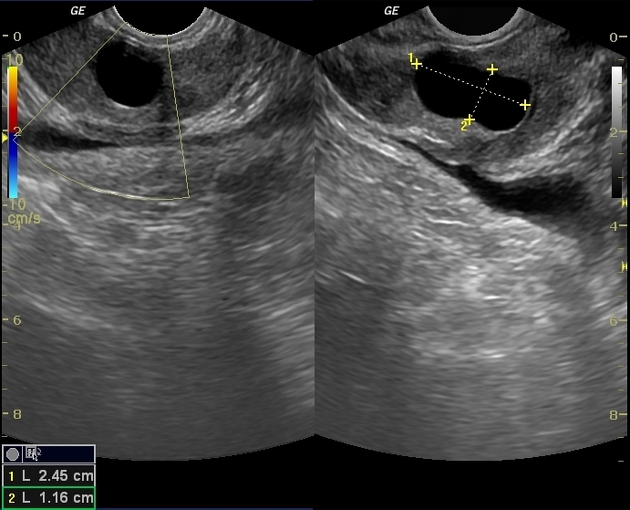
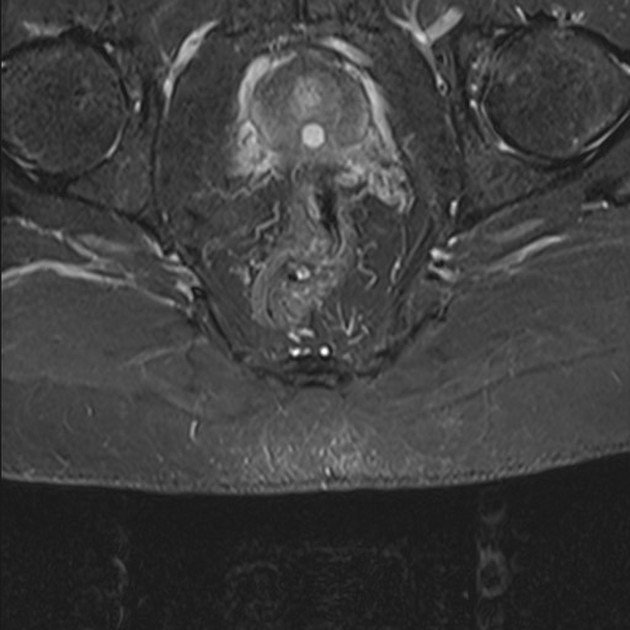
Radiographic features
MRI
Seen as a midline prostatic cyst.
Treatment and prognosis
Complications
utricle cysts may contain pus or hemorrhage if infected
utricle cysts may contain cancer (e.g. clear cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma) with a reported prevalence as high as 3% 5
Differential diagnosis
-
older age (second or third decade of life)
usually large and tear drop shape
may extend above base of prostate
See also
References
- 1. Curran S, Akin O, Agildere AM et-al. Endorectal MRI of prostatic and periprostatic cystic lesions and their mimics. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188 (5): 1373-9. doi:10.2214/AJR.06.0759 - Pubmed citation
- 2. Mcdermott VG, Meakem TJ, Stolpen AH et-al. Prostatic and periprostatic cysts: findings on MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995;164 (1): 123-7. AJR Am J Roentgenol (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- 3. Priyadarshi V, Singh JP, Mishra S, Vijay MK, Pal DK, Kundu AK. Prostatic utricle cyst: a clinical dilemma. APSP journal of case reports. 4 (2): 16. Pubmed
- 4. Shebel HM, Farg HM, Kolokythas O, El-Diasty T. Cysts of the lower male genitourinary tract: embryologic and anatomic considerations and differential diagnosis. (2013) Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 33 (4): 1125-43. doi:10.1148/rg.334125129 - Pubmed
- 5. Linda C. Chu, Hillary M. Ross, Tamara L. Lotan, Katarzyna J. Macura. Prostatic Stromal Neoplasms: Differential Diagnosis of Cystic and Solid Prostatic and Periprostatic Masses. (2013) American Journal of Roentgenology. doi:10.2214/AJR.12.9741
Incoming Links
- Prostatic urticle cyst
- Midline prostatic cyst
- Concomitant double urethra and utricular cyst
- Prostate cyst
- Prostatic utricle cyst causing ejaculatory duct obstruction and persistent haemtospermia
- Neonatal prostatic utricle abscess / cyst
- Prostatic utricle cyst
- Prostatic utricle cyst (on MRI)
- Prostatic abscess (TRUS)
- Midline prostatic cyst
- Prostatic utricle cyst
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta previa
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumors
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumors of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumors
- mixed germ cell tumor
- yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumor
- sex cord / stromal tumors of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumor of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumors (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumors
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.