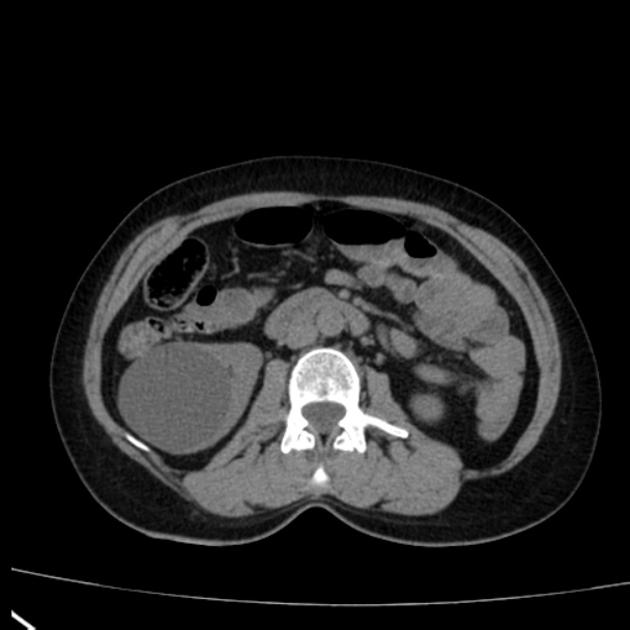
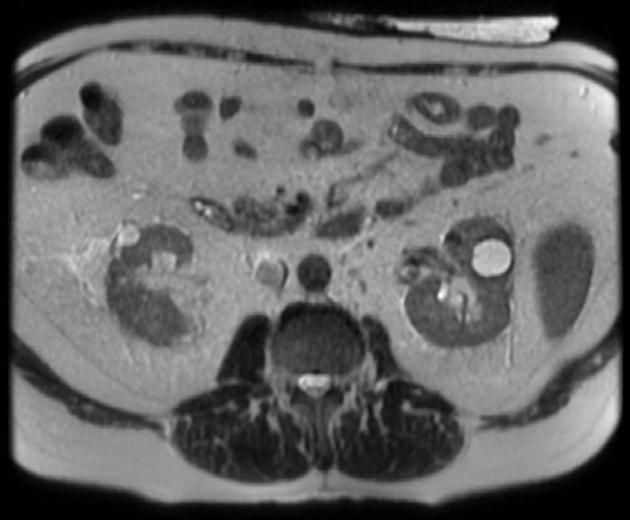
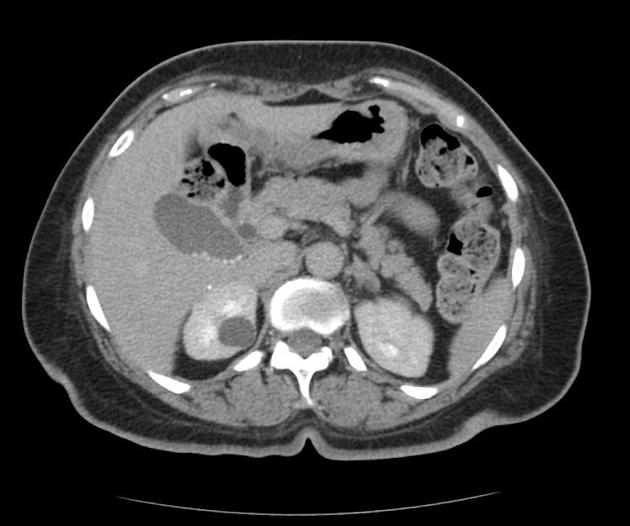
Renal cyst is a generic term commonly used to describe any predominantly cystic renal lesion. Most parenchymal cystic lesions represent benign epithelial cysts; however, malignancies, such as renal cell carcinoma (RCC), may also present as cystic lesions 8.
On this page:
Terminology
Renal cyst is a catch-all term for epithelial cysts, renal sinus (parapelvic/peripelvic) cysts, or calyceal diverticula. This is likely because these have similar appearances on imaging, and distinguishing them is often clinically inconsequential.
Bosniak v2019 recommends that "cyst" be used to describe Bosniak class I cysts and proven Bosniak class II cysts and that "cystic mass" be used to describe other Bosniak class II lesions and Bosniak class III-V lesions 10.
Various terms have been used to describe renal cysts:
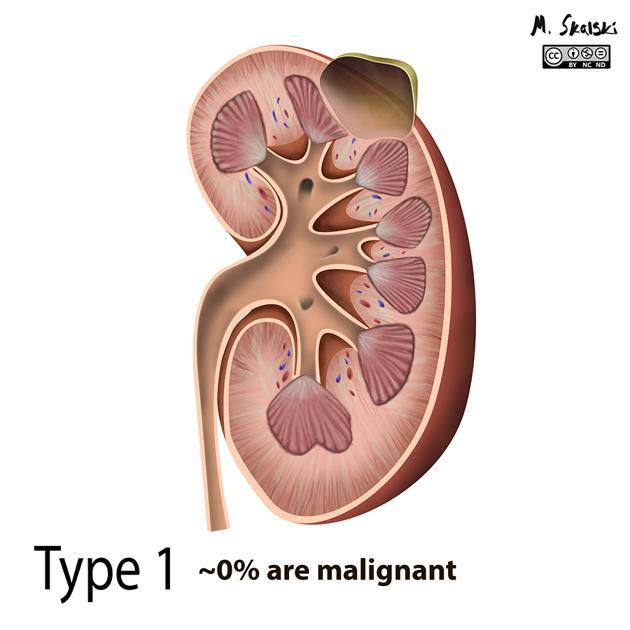
simple: benign, round, thin-walled, homogeneous, fluid-filled cysts without septations or calcifications (equivalent to Bosniak class I cysts) 10-12
complex: any cyst that is not simple 11
-
complicated
cysts that have ruptured, bled or become infected 13
both simple and complex cysts can be "complicated renal cysts"
However, the distinction between complex and complicated cysts has blurred over time, and Bosniak v2019 recommends these terms should be avoided 10.
Epidemiology
The frequency of renal cysts increases with age, and they are present in approximately ~40% of all individuals receiving a CT scan 3. Incidental renal cysts are present in ~0.2% of pediatric patients 4.
Radiographic features
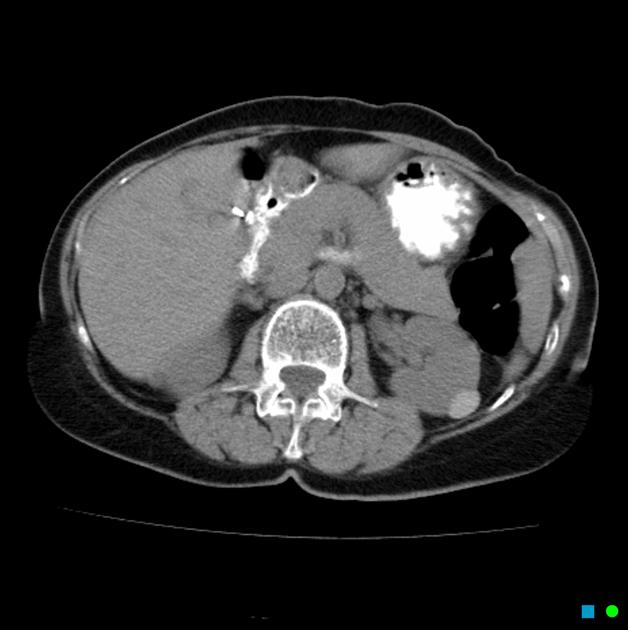
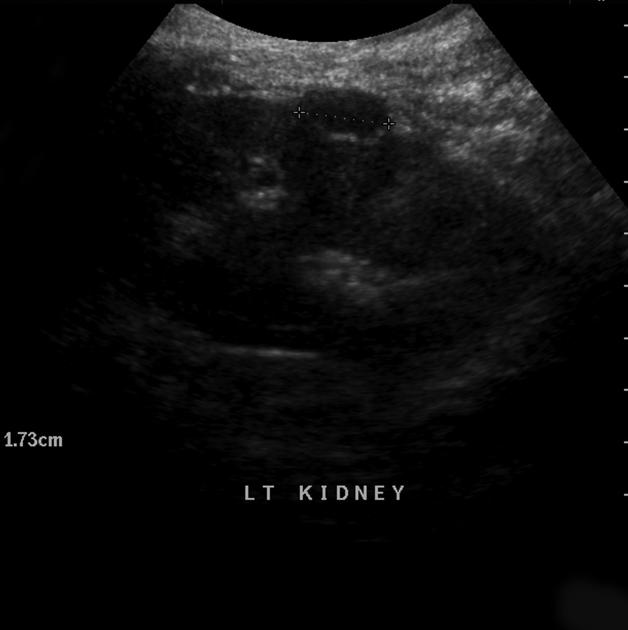
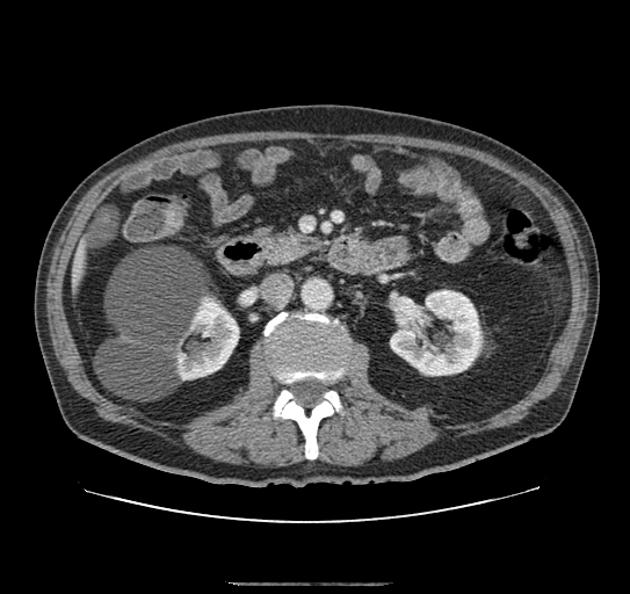
Ultrasound
Simple renal cysts are commonly defined as having all of the following features:
round or oval with smooth, well-marginated, thin walls 11,12
-
anechoic contents 11
anechoic cysts may show some artifactual internal low-level echoes, which may be improved with harmonic imaging 13
no calcifications 11,12
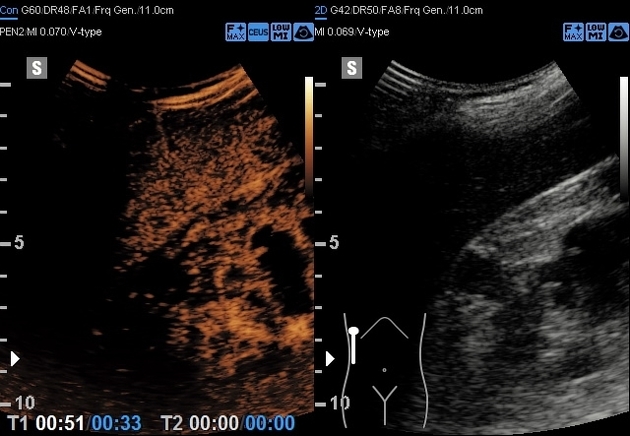
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound may be useful to show vascularity of septa or nodular protuberances in a renal cyst and can help differentiate a benign cyst from an indeterminate cyst or a malignant-appearing cyst 7.
CT/MRI
See article: Bosniak classification of cystic renal masses (version 2019).
Treatment and prognosis
Simple renal cysts are overwhelmingly asymptomatic, although there have been occasional reports of symptomatic giant cysts causing pain from mass effect on adjacent structures. Cysts may occasionally rupture, causing pain.
A symptomatic renal cyst can be aspirated, but cysts have a high rate of recurrence. Percutaneous alcohol ablation has been practised with some success in selected cases of symptomatic cysts 5.
In a pediatric patient with normal renal function, no follow up is necessary for an incidentally-discovered renal cyst 4.
Differential diagnosis
Single cyst
Multiple cysts
cystic change of dialysis
lithium-related cysts: multiple tiny cysts
-
some multisystem disorders include multiple renal cysts




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.