Strain elastography
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Matt A. Morgan had no recorded disclosures.
View Matt A. Morgan's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures- Tissue strain imaging
- Static elastography
- Compression elastography
Strain elastography (also known as tissue strain elastography/static elastography/compression elastography) is a developing form of ultrasound that assesses tissues' macroscopic structure through the strain modulus. This is different from normal B-mode grayscale ultrasound which characterizes a tissue's elasticity but at a microscopic level.
Strain elastography relies on Young's modulus to detect strain in the axial dimension. The characteristics of an ultrasound beam through tissue before and after compression are compared. In some systems, the strain of tissues is measured in a semi-quantitative way, relying on Young's modulus, but not directly calculating it.
Applications of strain elastography are being developed for:
breast ultrasound
-
liver ultrasound
detection of small lesions
evaluation of diffuse liver disease
prostate ultrasound
thyroid nodule ultrasound
musculoskeletal ultrasound
obstetric ultrasound for preterm labor 2
There may also be some applications in echocardiography.
The technique is still being developed for clinical use. There are a number of different ways to perform strain elastography and continued improvement in differentiation between the lesion and background tissue is necessary for reliable clinical diagnosis.
Breast
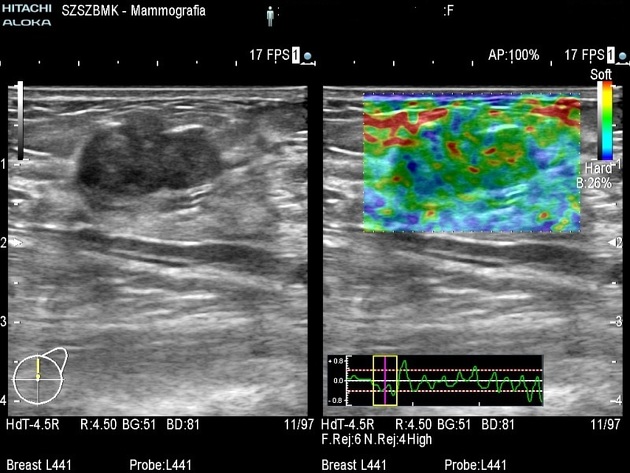
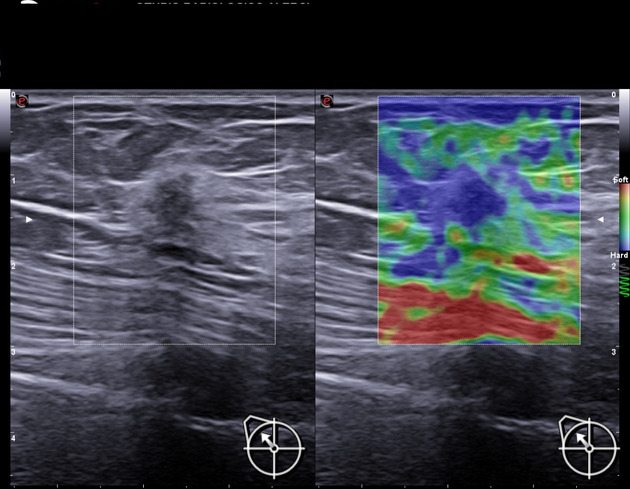
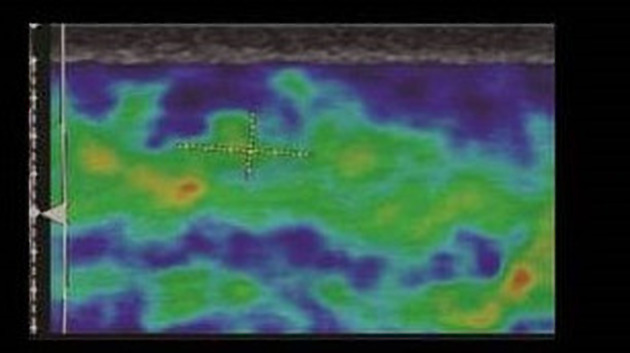
Malignant breast lesion generally has higher stiffness and appears larger on elastography when compared to usual ultrasound B-mode images. There are three methods used in strain elastography of the breast 3.
First method is to use a 5-point color scale to determine the stiffness of a lesion. Color blue is rated as stiff while color red is rated as soft 3.
The second method is to calculate the strain ratio, which is comparing the strain of the surrounding fat tissue with the strain of the breast lesion. The cut-off point of strain ratio, however, is vendor dependent 3.
The third method is to calculate the E/B ratio, which is comparing the diameter of the lesion on elastography with the diameter of the same lesion on B-mode ultrasound. E/B ratio less than 1 is considered as benign. E/B ratio is more sensitive and specific than other two methods 3.
References
- 1. Sigrist R, Liau J, Kaffas A, Chammas M, Willmann J. Ultrasound Elastography: Review of Techniques and Clinical Applications. Theranostics. 2017;7(5):1303-29. doi:10.7150/thno.18650 - Pubmed
- 2. Gesthuysen A, Gesthuysen HK, Gesthuysen MlM, Gesthuysen BJ, Gesthuysen OdMK, Gesthuysen FM, Gesthuysen KsH, Gesthuysen MlU, Gesthuysen FA, Gesthuysen BE, Gesthuysen KW, Gesthuysen SR, Gesthuysen. Evaluation of Cervical Elastography Strain Pattern to Predict Preterm Birth. (2020) Ultraschall in der Medizin (Stuttgart, Germany : 1980). doi:10.1055/a-0865-1711 - Pubmed
- 3. Barr R. Breast Elastography: How to Perform and Integrate Into a "Best-Practice" Patient Treatment Algorithm. J Ultrasound Med. 2020;39(1):7-17. doi:10.1002/jum.15137 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Imaging technology
- imaging technology
- imaging physics[+][+]
- imaging in practice
-
x-rays[+][+]
- x-ray physics
- x-ray in practice
- x-ray production
- x-ray tube
- filters
- automatic exposure control (AEC)
- beam collimators
- grids
- air gap technique
- cassette
- intensifying screen
- x-ray film
- image intensifier
- digital radiography
- digital image
- mammography
- x-ray artifacts
- radiation units
- radiation safety
- radiation detectors
- fluoroscopy[+][+]
-
computed tomography (CT)[+][+]
- CT physics
- CT in practice
- CT technology
- CT image reconstruction
- CT image quality
- CT dose
-
CT contrast media
-
iodinated contrast media
- agents
- water soluble
- water insoluble
- vicarious contrast material excretion
- iodinated contrast media adverse reactions
- agents
- non-iodinated contrast media
-
iodinated contrast media
-
CT artifacts
- patient-based artifacts
- physics-based artifacts
- hardware-based artifacts
- ring artifact
- tube arcing
- out of field artifact
- air bubble artifact
- helical and multichannel artifacts
- CT safety
- history of CT
-
MRI [+][+]
- MRI physics
- MRI in practice
- MRI hardware
- signal processing
-
MRI pulse sequences (basics | abbreviations | parameters)
- T1 weighted image
- T2 weighted image
- proton density weighted image
- chemical exchange saturation transfer
- CSF flow studies
- diffusion weighted imaging (DWI)
- echo-planar pulse sequences
- fat-suppressed imaging sequences
- gradient echo sequences
- inversion recovery sequences
- metal artifact reduction sequence (MARS)
-
perfusion-weighted imaging
- techniques
- derived values
- saturation recovery sequences
- spin echo sequences
- spiral pulse sequences
- susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI)
- T1 rho
- MR angiography (and venography)
-
MR spectroscopy (MRS)
- 2-hydroxyglutarate peak: resonates at 2.25 ppm
- alanine peak: resonates at 1.48 ppm
- choline peak: resonates at 3.2 ppm
- citrate peak: resonates at 2.6 ppm
- creatine peak: resonates at 3.0 ppm
- functional MRI (fMRI)
- gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) peak: resonates at 2.2-2.4 ppm
- glutamine-glutamate peak: resonates at 2.2-2.4 ppm
- Hunter's angle
- lactate peak: resonates at 1.3 ppm
- lipids peak: resonates at 1.3 ppm
- myoinositol peak: resonates at 3.5 ppm
- MR fingerprinting
- N-acetylaspartate (NAA) peak: resonates at 2.0 ppm
- propylene glycol peak: resonates at 1.13 ppm
-
MRI artifacts
- MRI hardware and room shielding
- MRI software
- patient and physiologic motion
- tissue heterogeneity and foreign bodies
- Fourier transform and Nyquist sampling theorem
- MRI contrast agents
- MRI safety
-
ultrasound
- ultrasound physics
-
transducers[+][+]
- linear array
- convex array
- phased array
- frame averaging (frame persistence)
- ultrasound image resolution
- imaging modes and display
- pulse-echo imaging[+][+]
- real-time imaging
-
Doppler imaging[+][+]
- Doppler effect
- color Doppler
- power Doppler
- B flow
- color box
- Doppler angle
- pulse repetition frequency and scale
- wall filter
- color write priority
- packet size (dwell time)
- peak systolic velocity
- end-diastolic velocity
- resistive index
- pulsatility index
- Reynolds number
- panoramic imaging
- compound imaging
- harmonic imaging
-
elastography
- transient elastography
- shear wave elastography
- strain elastography
- Young's modulus
- scanning modes[+][+]
- 2D ultrasound
- 3D ultrasound
- 4D ultrasound
- M-mode
-
ultrasound artifacts[+][+]
- acoustic shadowing
- acoustic enhancement
- beam width artifact
- reverberation artifact
- ring down artifact
- mirror image artifact
- side lobe artifact
- speckle artifact
- speed displacement artifact
- refraction artifact
- multipath artifact
- anisotropy
- electrical interference artifact
- hardware-related artifacts
- Doppler artifacts
- aliasing
- tissue vibration
- spectral broadening
- blooming
- motion (flash) artifact
- twinkling artifact
- acoustic streaming
- biological effects of ultrasound[+][+]
- history of ultrasound
-
nuclear medicine [+][+]
- nuclear medicine physics
- detectors
- tissue to background ratio
-
radiopharmaceuticals
- fundamentals of radiopharmaceuticals
- radiopharmaceutical labeling
- radiopharmaceutical production
- nuclear reactor produced radionuclides
- cyclotron produced radionuclides
- radiation detection
- dosimetry
- specific agents
- carbon-11
- chromium-51
- fluorine agents
- gallium agents
- Ga-67 citrate
- Ga-68
- iodine agents
-
I-123
- I-123 iodide
- I-123 ioflupane (DaTSCAN)
- I-123 ortho-iodohippurate
- I-131
-
MIBG scans
- I-123 MIBG
- I-131 MIBG
-
I-123
- indium agents
- In-111 Octreoscan
- In-111 OncoScint
- In-111 Prostascint
- In-111 oxine labeled WBC
- krypton-81m
- nitrogen-13
- oxygen-15
- phosphorus-32
- selenium-75
-
technetium agents
- Tc-99m DMSA
- Tc-99m DTPA
- Tc-99m DTPA aerosol
- Tc-99m HMPAO
- Tc-99m HMPAO labeled WBC
- Tc-99m MAA
- Tc-99m MAG3
- Tc-99m MDP
- Tc-99m mercaptoacetyltriglycine
- Tc-99m pertechnetate
- Tc-99m labeled RBC
- Tc-99m sestamibi
- Tc-99m sulfur colloid
- Tc-99m sulfur colloid (oral)
- thallium-201 chloride
- xenon agents
- in vivo therapeutic agents
- pharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine
-
emerging methods in medical imaging[+][+]
- radiography
- phase-contrast imaging
- CT
- deep-learning reconstruction
- photon counting CT
- virtual non-contrast imaging
- ultrasound
- magnetomotive ultrasound (MMUS)
- superb microvascular imaging
- ultrafast Doppler imaging
- ultrasound localization microscopy
- MRI
- nuclear medicine
- total body PET system
- immuno-PET
- miscellaneous
- radiography





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.