Renal abscess is a collection of infective fluid in the kidney. It is usually a sequela of acute pyelonephritis, where severe vasospasm and inflammation may occasionally result in liquefactive necrosis and abscess formation.
On this page:
Epidemiology
It can affect all ages and has no recognized gender predilection.
Risk factors
The predisposing factors include 4:
ureteral obstruction
Clinical presentation
The most common signs or symptoms are:
fever
flank/abdominal pain
chills
dysuria
Radiographic features
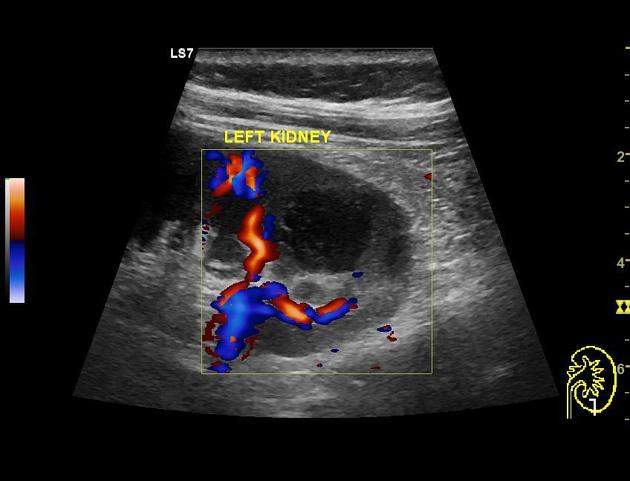
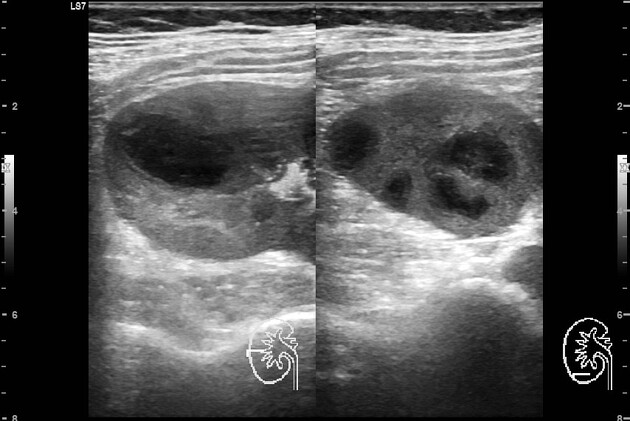
Ultrasound
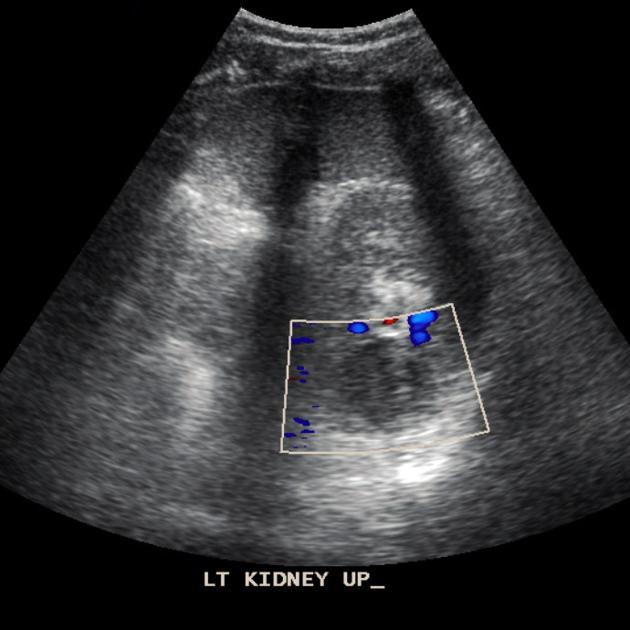
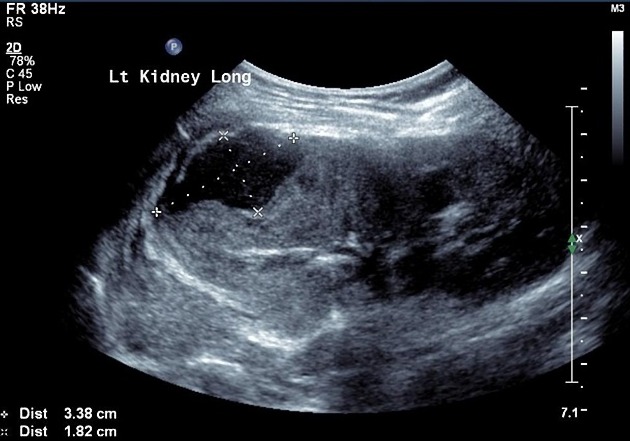
A renal abscess typically appears as a well-defined hypoechoic area within the cortex or the corticomedullary parenchyma. It demonstrates internal echoes within, and an associated diffusely hypoechoic kidney due to acute pyelonephritis may be seen. Perinephric collection may also be seen.
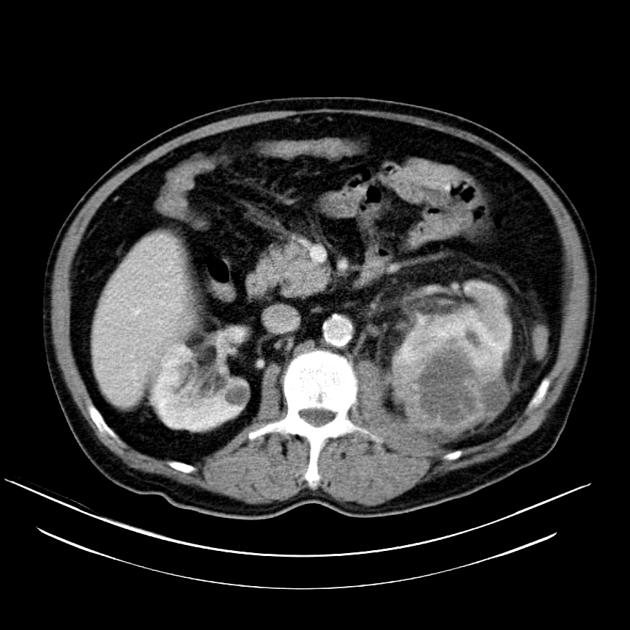
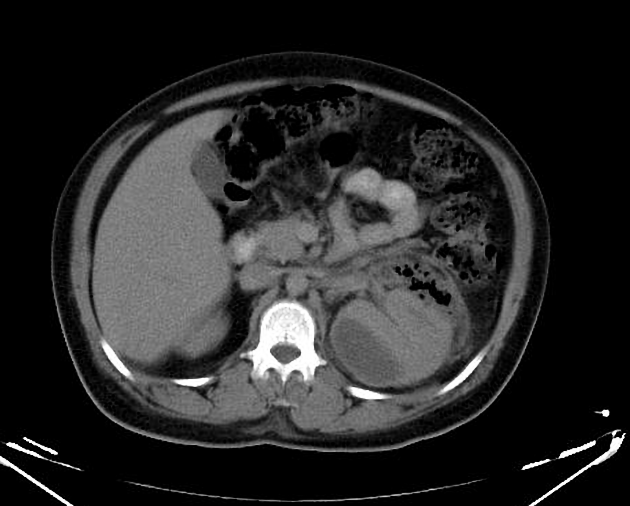
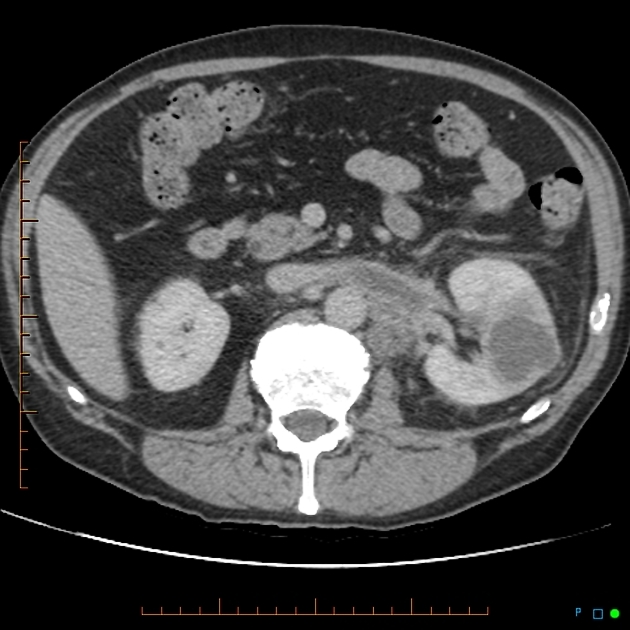
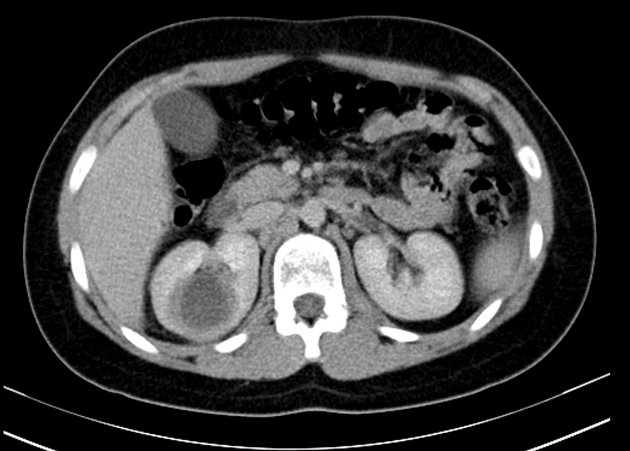
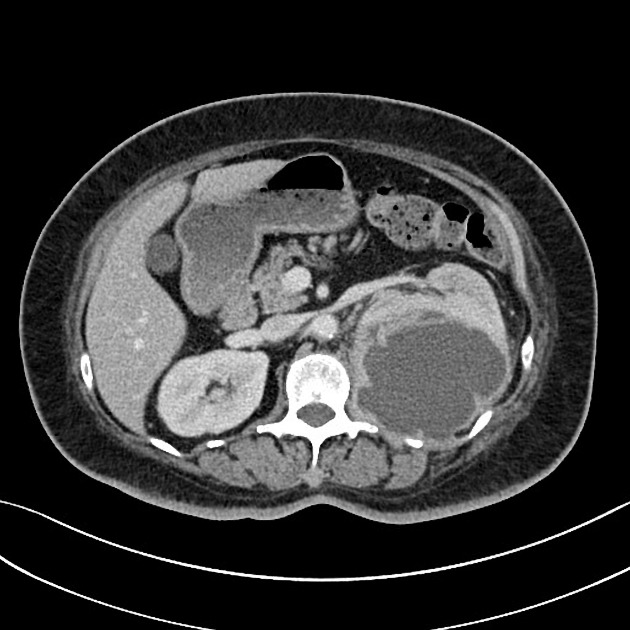
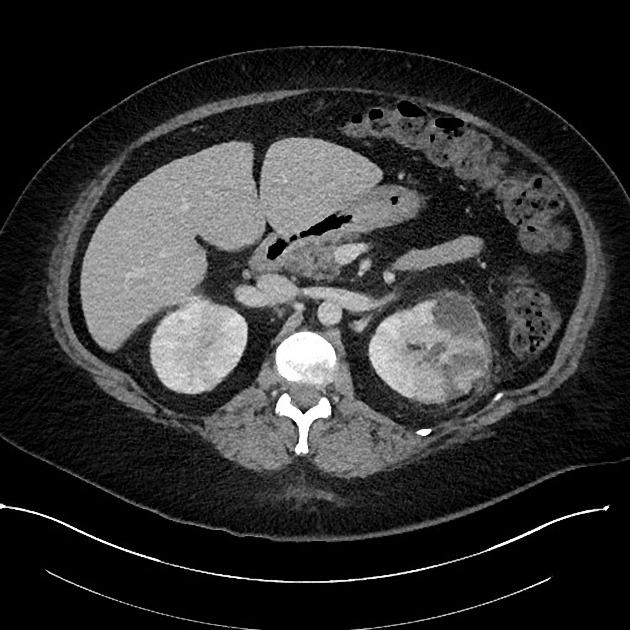
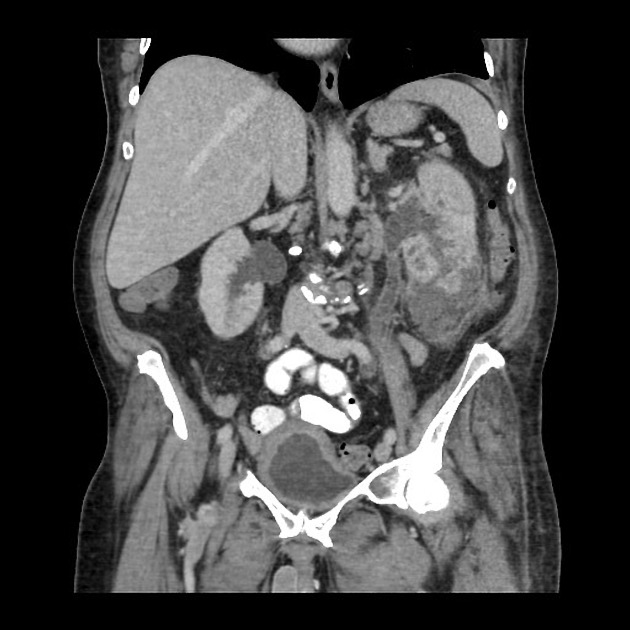
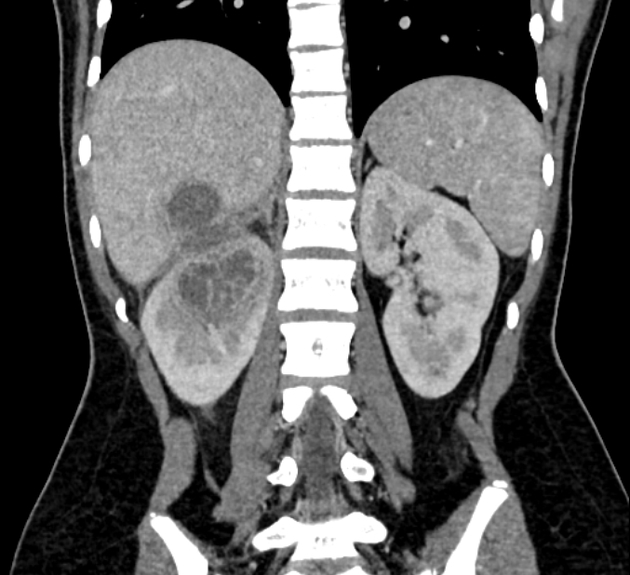
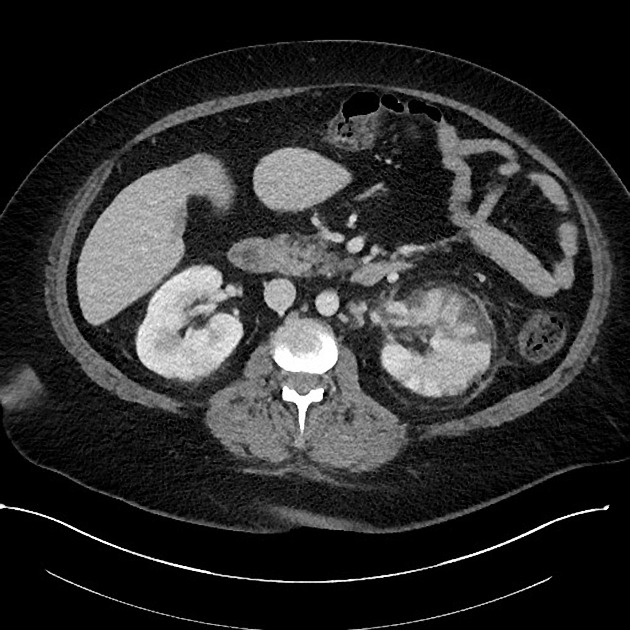
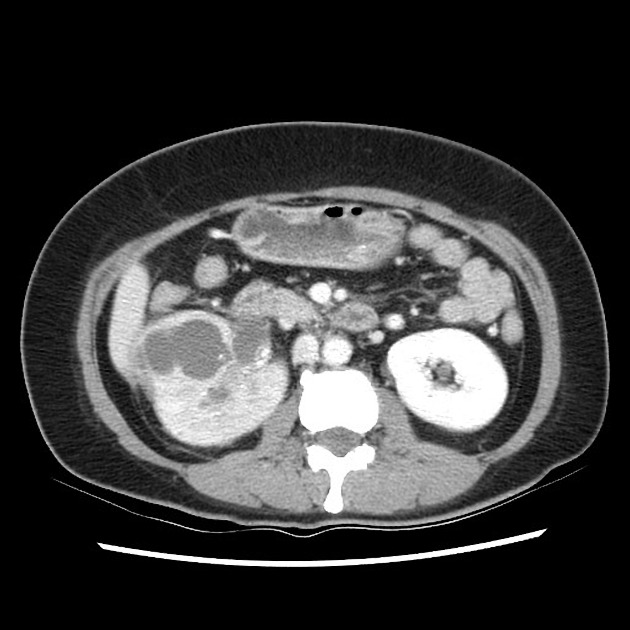
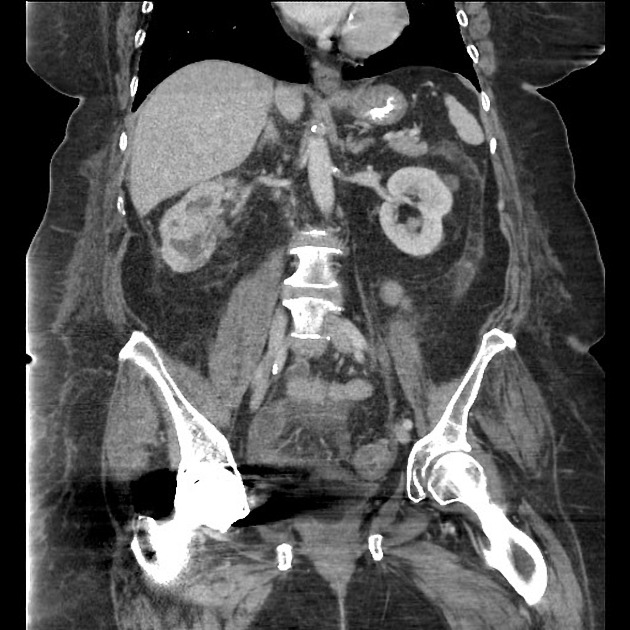
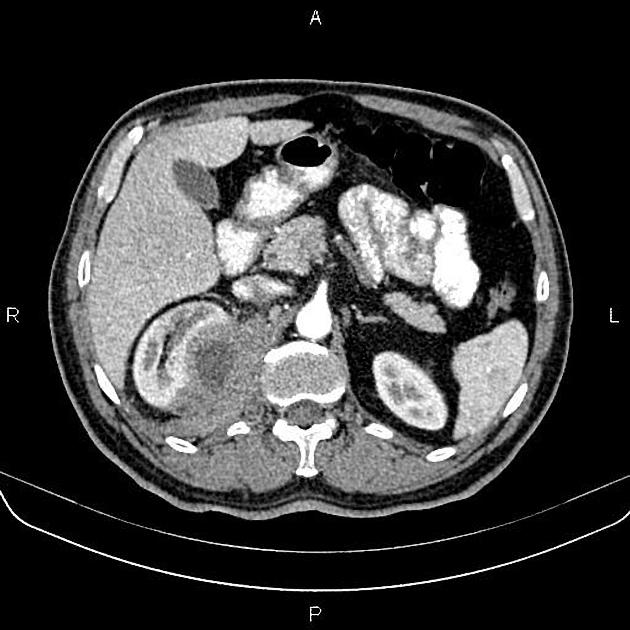
CT
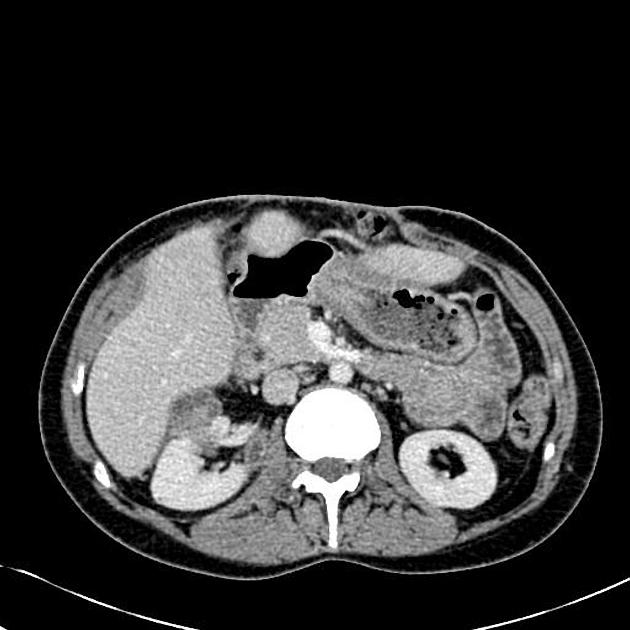
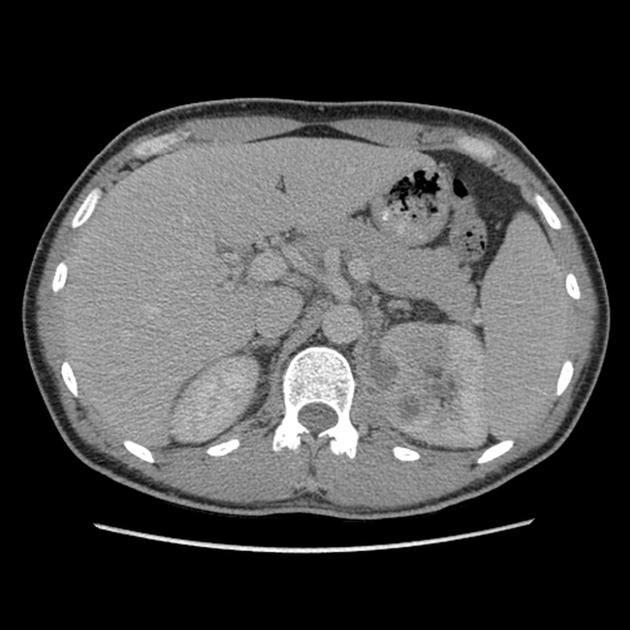
CT is the most accurate modality for diagnosis and follow-up of renal abscesses 1. An abscess appears as a well-defined low attenuation mass with a thick, irregular wall or pseudo capsule, which can be better visualized on contrast enhanced scans. Gas within a low attenuation/cystic mass strongly suggests abscess formation. Renal parenchyma around the abscess cavity may appear hypoenhancing in nephrogram phase and may appear hyperattenuating in delayed images. Associated fascial and septal thickening is seen with obliteration of perinephric fat.
In some cases, the formation of a discrete abscess is preceded by acute focal lobar nephronia which is a focal inflammation of the kidney without liquefaction. It appears as a solid mass.
It should be noted that the Bosniak classification is not indicated in renal lesions with inflammatory, infectious, or vascular etiology and should not be used 5.
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment consists of intravenous antibiotics and drainage, which may be performed under either ultrasound or CT guidance.
Complications
The main complication is abscess rupture, which can be described according to the space involved:
calyceal system - pyonephrosis
anterior or posterior pararenal space beyond the perirenal fascia - paranephric abscess
peritoneal cavity - subdiaphragmatic or pelvic abscess
These complications may lead to renal atrophy secondary to compression or obstruction.
Differential diagnosis
General imaging differential considerations include:





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.