Inferior cervical ganglion
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yoshi Yu had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Yoshi Yu's current disclosures- inferior cervical ganglia
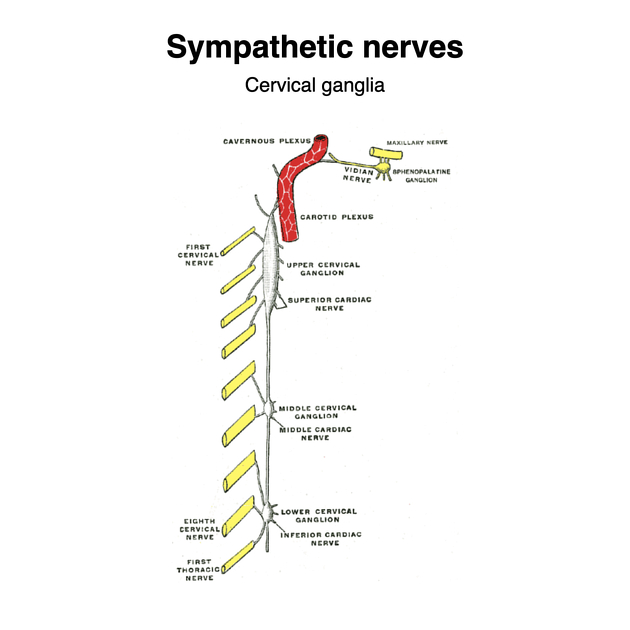
The inferior cervical ganglion (plural: ganglia) is the second largest ganglion of the cervical sympathetic trunk and provides autonomic innervation to the head and neck region.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The inferior cervical ganglion is formed by embryologically fused C7 and C8 sympathetic ganglia. It has superior connections to the middle cervical ganglion and in 80% of individuals, it is fused with the first thoracic ganglion, in which it is called the stellate ganglion.
Location
It is bilaterally located at the level of C7 anterior to the transverse processes.
Relations
anterior: preforaminal segment of the vertebral artery and vertebral veins
posterior: longus colli muscle and neck of the first rib
lateral: superior intercostal artery
inferior: costocervical trunk, suprapleural membrane, cupola of the pleura
Innervation
The inferior cervical ganglion provides sympathetic innervation to the head and neck.
It sends branches to the vertebral artery (form a vertebral plexus) which ascends on its surface through the transverse foramina. It gives off small branches to the posterolateral corners of the cervical intervertebral discs and the cervical spinal meninges at each cervical segment. The vertebral plexus enters the skull on the vertebral and basilar arteries.
Small branches extend to the inferior thyroid artery, along with small branches from the recurrent laryngeal nerve and external laryngeal nerves, which enter the thyroid gland.
A large branch containing preganglionic efferent fibres forms the inferior cardiac nerve which courses inferiorly behind the subclavian artery and anterior to the trachea to join the deep part of the cardiac plexus. This branch also receives fibres from the recurrent laryngeal nerve and often fibres from the middle cardiac nerve of the middle cervical ganglion.
The ganglion supplies:
vasomotor tone to the vertebrobasilar system
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Variant anatomy
The inferior cervical ganglion is often fused with the first thoracic ganglion, forming the stellate ganglion, which is present in 80% of individuals.
Clinical importance
Horner syndrome can be caused by pathology of the cervical sympathetic ganglia.
References
- 1. Robert H. Whitaker, Neil R. Borley. Instant Anatomy. ISBN: 9780632054039
- 2. Susan Standring. Gray's Anatomy. ISBN: 9780702052309
- 3. Last's anatomy, regional and applied. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN:044304662X. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Clinically oriented anatomy. LWW. ISBN:1451119453. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: General
- anatomic position
-
anatomic nomenclature
-
Terminologia Anatomica
- superseded nomenclature
-
Terminologia Anatomica
- anatomic variants
- labelled imaging anatomy cases
- regional anatomy
- systems anatomy
- endocrine system
- lymphatic system
- reticuloendothelial system
- nervous system
- systems based on location
- systems based on function
- somatic nervous system
-
autonomic nervous system
- sympathetic nervous system
- parasympathetic nervous system
-
autonomic ganglia and plexuses
- craniofacial
- cervical
- thoracic
- abdominopelvic
- coccygeal
- histology
- osteology
- skeleton
- bones
- macroscopic structure
- microscopic structure
- bone growth
- fetal bone formation
- developmental ossification
- tubulation
- bone types
- nutrient foramen
- joints
- muscles
- organs
- embryology
- skin
- blood vessels
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck[+][+]
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck[+][+]
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia[+][+]
-
deep spaces of the neck[+][+]
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck[+][+]
- orbit[+][+]
- ear[+][+]
- paranasal sinuses[+][+]
- upper respiratory tract[+][+]
- viscera of the neck[+][+]
- blood supply of the head and neck[+][+]
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves[+][+]
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck[+][+]
-
cervical sympathetic ganglia
- superior cervical ganglion
- middle cervical ganglion
- inferior cervical ganglion
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus[+][+]
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves[+][+]
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck[+][+]
- embryological development of the head and neck[+][+]
Related articles: Anatomy: Spine
-
osteology
- vertebrae
- spinal canal
- cervical spine
- thoracic spine
- lumbar spine
- sacrum
- coccyx
-
anatomical variants
- vertebral body
- neural arch
- transitional vertebrae
- ossicles
- ossification centres
- intervertebral disc
- articulations
- ligaments
- musculature of the vertebral column
- muscles of the neck
- muscles of the back
-
suboccipital muscle group
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- splenius capitis muscle
- splenius cervicis muscle
- erector spinae group
- transversospinalis group
- quadratus lumborum muscle
-
suboccipital muscle group
- spinal meninges and spaces
-
spinal cord
- gross anatomy
-
white matter tracts (white matter)
- corticospinal tract
- anterolateral columns
- lateral columns
-
dorsal columns
- fasiculus gracilis (column of Goll)
- fasiculus cuneatus (column of Burdach)
- grey matter
- nerve root
- central canal
- functional anatomy
- spinal cord blood supply
- sympathetic chain





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.