Haemorrhagic pancreatitis
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Jeremy Jones had no recorded disclosures.
View Jeremy Jones's current disclosures- Haemorrhagic complicating pancreatitis
- Pancreatitis complicated by haemorrhage
- Hemorrhagic pancreatitis
- Pancreatitis complicated by hemorrhage
Haemorrhagic pancreatitis is characterised by bleeding within or around the pancreas, and is usually considered a late sequela of acute pancreatitis.
Pathology
Haemorrhage can occur in patients with severe necrotising pancreatitis or as a result of pancreatic pseudoaneurysm rupture when it constitutes a life-threatening emergency.
Aetiology
According to one study, the usual causes of haemorrhage were 2:
- bleeding pancreatic pseudoaneurysm or peripancreatic pseudoaneurysm: ~60%
- diffuse bleeding with pancreatic necrosis: ~20%
- haemorrhagic pancreatic pseudocysts: ~20%
Radiographic features
CT
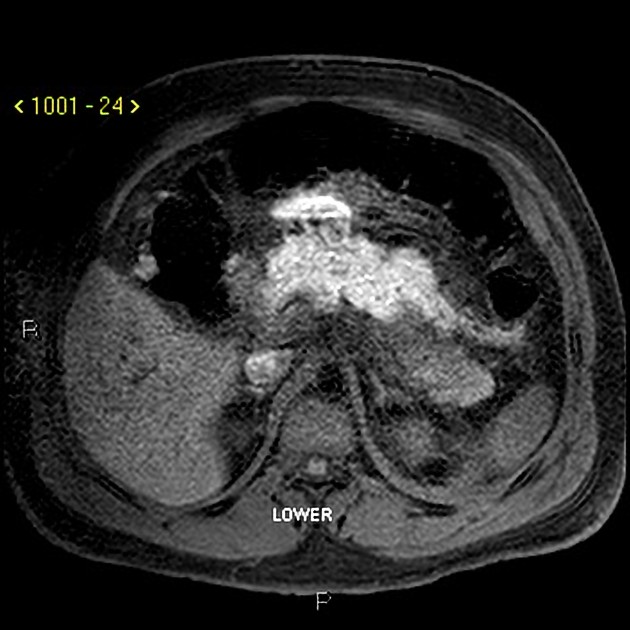
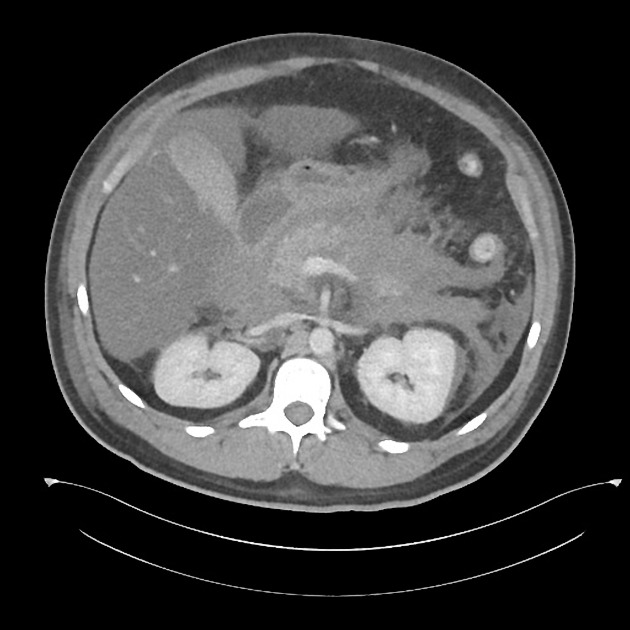
Acute haemorrhage typically has high attenuation on unenhanced CT scans. The attenuation value then decreases as the haematoma ages through time 5.
MRI
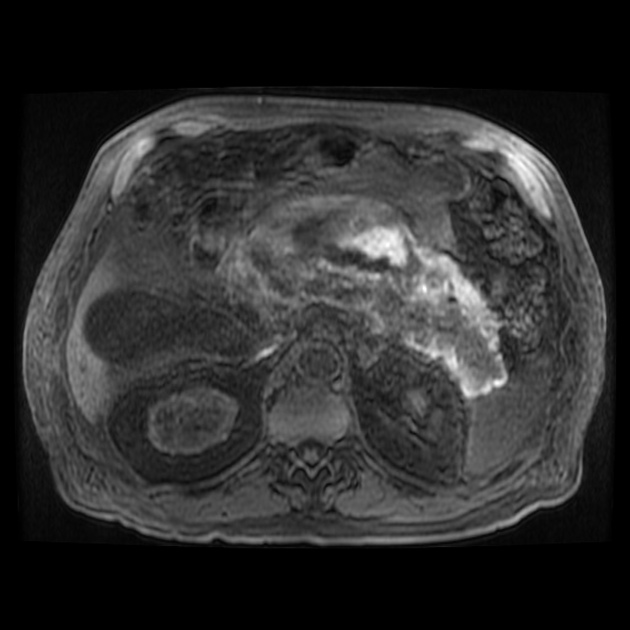
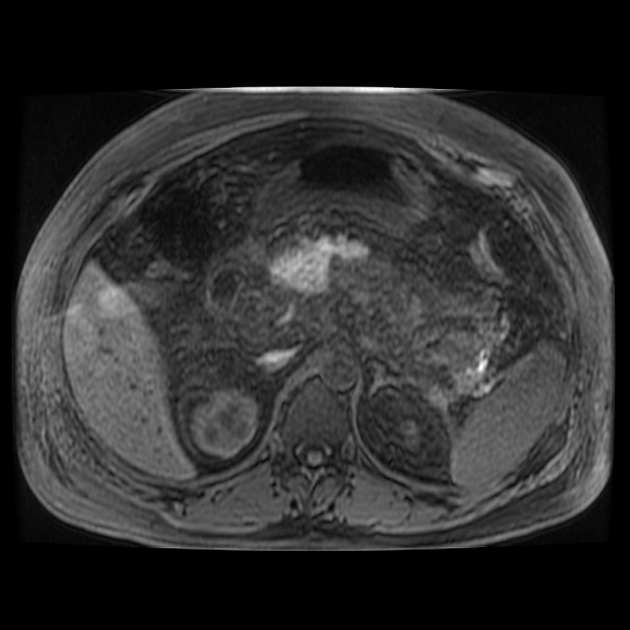
Haemorrhagic fluid collections are more evident on MRI than CT due to the following reasons 1:
- T1: high-signal intensity methaemoglobin
- T2: low-signal intensity haemosiderin rim
Signal abnormalities due to haemorrhage remain visible longer on MRI than on CT.
References
- 1. Miller FH, Keppke AL, Dalal K et-al. MRI of pancreatitis and its complications: part 1, acute pancreatitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183 (6): 1637-44. AJR Am J Roentgenol (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 2. Balthazar EJ, Fisher LA. Hemorrhagic complications of pancreatitis: radiologic evaluation with emphasis on CT imaging. Pancreatology. 2001;1 (4): 306-13. - Pubmed citation
- 3. Ammori BJ, Madan M, Alexander DJ. Haemorrhagic complications of pancreatitis: presentation, diagnosis and management. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1998;80 (5): 316-25. - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 4. Balthazar EJ. Acute pancreatitis: assessment of severity with clinical and CT evaluation. Radiology. 2002;223 (3): 603-13. doi:10.1148/radiol.2233010680 - Pubmed citation
- 5. Sahni VA, Mortelé KJ. The bloody pancreas: MDCT and MRI features of hypervascular and hemorrhagic pancreatic conditions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;192 (4): 923-35. doi:10.2214/AJR.08.1602 - Pubmed citation
- 6. Vujic I. Vascular complications of pancreatitis. Radiol. Clin. North Am. 1989;27 (1): 81-91. - Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
Related articles: Pathology: Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary
- liver[+][+]
- depositional disorders
- infection and inflammation
- liver abscess
- hepatic hydatid infection
- cirrhosis
- hepatitis
- cholecystitis
- cholangitis
- malignancy
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumours
- benign epithelial tumours
- hepatocellular hyperplasia
- hepatocellular adenoma
- hepatic/biliary cysts
- benign nonepithelial tumours
- primary malignant epithelial tumours
- hepatocellular carcinoma
- hepatocellular carcinoma variants
-
cholangiocarcinoma
- intra-hepatic
- mass-forming type
- periductal infiltrating type - Klatskin tumours
- intraductal growing type
- extra-hepatic/large duct type
- intra-hepatic
- biliary cystadenocarcinoma
- combined hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma
- hepatoblastoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma
- primary malignant nonepithelial tumours
- haematopoietic and lymphoid tumours
- primary hepatic lymphoma
- hepatic myeloid sarcoma (hepatic chloroma)
- secondary tumours
- miscellaneous
- adrenal rest tumours
- hepatic carcinosarcoma
- hepatic fibroma
- hepatic haemangioma
- hepatic Kaposi sarcoma
- hepatic lipoma
- hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma
- hepatic myxoma
- hepatic rhabdoid tumour
- hepatic solitary fibrous tumour
- hepatic teratoma
- hepatic yolk sac tumour
- inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour (inflammatory pseudotumour)
- nodular regenerative hyperplasia
- pancreatic rest tumours
- primary hepatic carcinoid
- benign epithelial tumours
- liver and intrahepatic bile duct tumours
- metabolic
- trauma
-
vascular and perfusion disorders
- portal vein related
- hepatic artery related
- hepatic veins related
- inferior vena cava related
- other
- third inflow
- liver thrombotic angiitis
- infra diaphragmatic total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR)
- hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)
- pancreas
-
pancreatic neoplasms[+][+]
- cystic neoplasm (cystic pancreatic mass differential diagnosis)
- solid neoplasm
- non-epithelial pancreatic neoplasms
- others
- simple pancreatic cyst
-
pancreatitis (mnemonic for the causes)
-
acute pancreatitis
- gallstone pancreatitis
- interstitial oedematous pancreatitis
- necrotising pancreatitis
- haemorrhagic pancreatitis
- revised Atlanta classification of acute pancreatitis[+][+]
- grading[+][+]
- chronic pancreatitis[+][+]
- Ascaris-induced pancreatitis
- tropical pancreatitis
- autoimmune pancreatitis[+][+]
- emphysematous pancreatitis
- hypertriglyceridaemia-induced pancreatitis
- hereditary pancreatitis
- pancreatitis associated with cystic fibrosis
- pancreaticopleural fistula
- segmental pancreatitis[+][+]
-
acute pancreatitis
- pancreatic atrophy
- pancreatic lipomatosis
- pancreatic trauma[+][+]
- pancreatic transplant
-
pancreatic neoplasms[+][+]
- gallbladder and biliary[+][+]
- congenital malformations and anatomical variants
- gallstones
- gallbladder inflammation
- bile ducts inflammation
- gallbladder wall abnormalities
- other gallbladder abnormalities
- bile duct dilatation (differential)
- bile duct wall thickening (differential)
- bile ducts neoplasms




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.