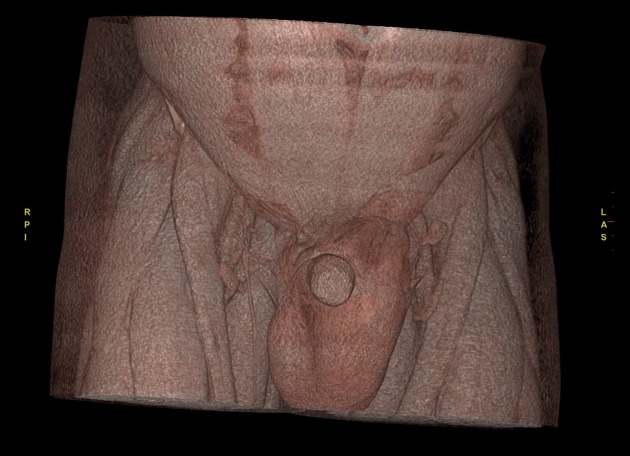
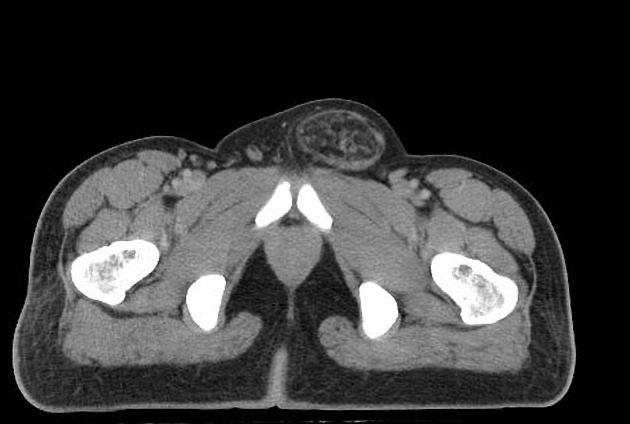
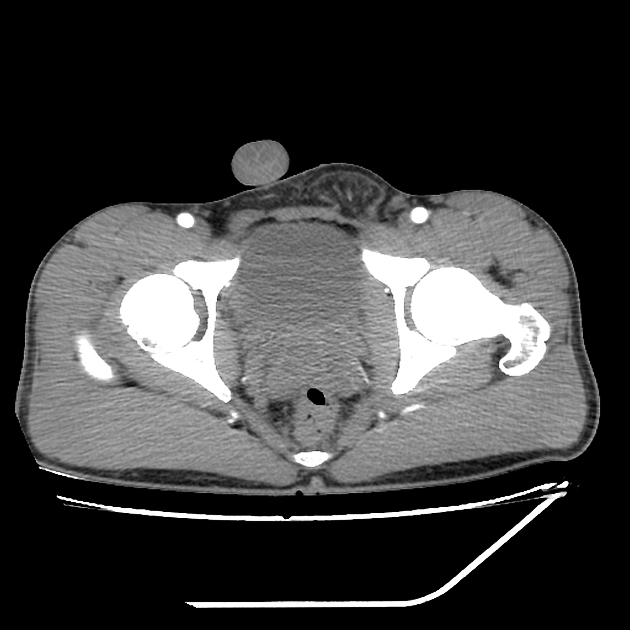
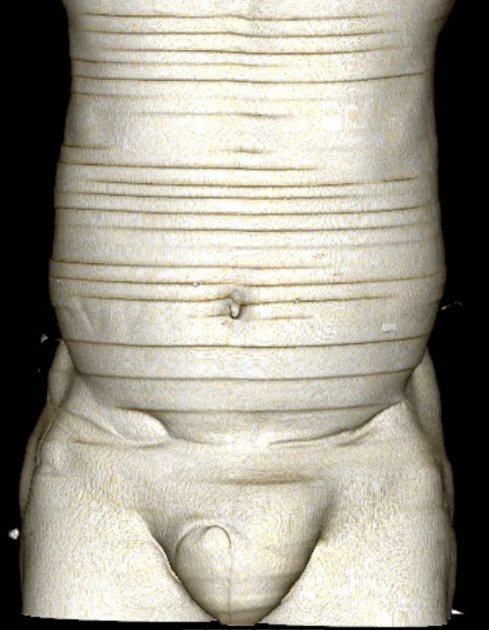
Indirect inguinal hernia
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Vikas Shah had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Vikas Shah's current disclosures- Indirect inguinal hernias
- Indirect inguinal herniation
- Indirect inguinal herniae
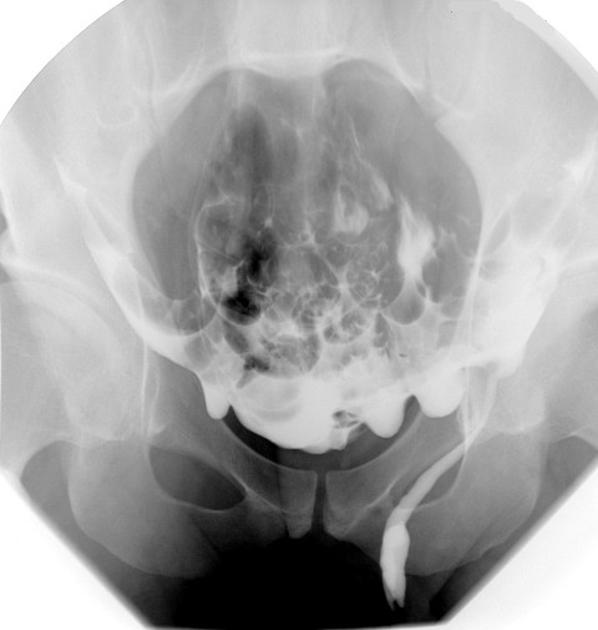
Indirect inguinal hernias (alternative plural: herniae), a type of groin herniation, are the most common type of abdominal hernia.
On this page:
Epidemiology
It is five times more common than a direct inguinal hernia, and is seven times more frequent in males, due to the persistence of the processus vaginalis during testicular descent.
In children, the vast majority of inguinal hernias are indirect.
Clinical presentation
Many are longstanding and asymptomatic, although the sheer size can become burdensome.
Pathology
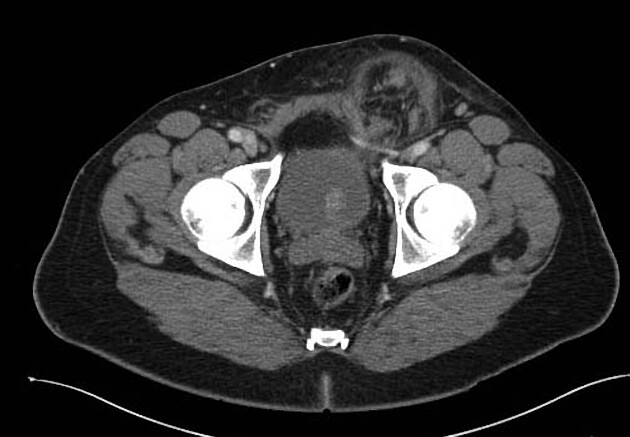
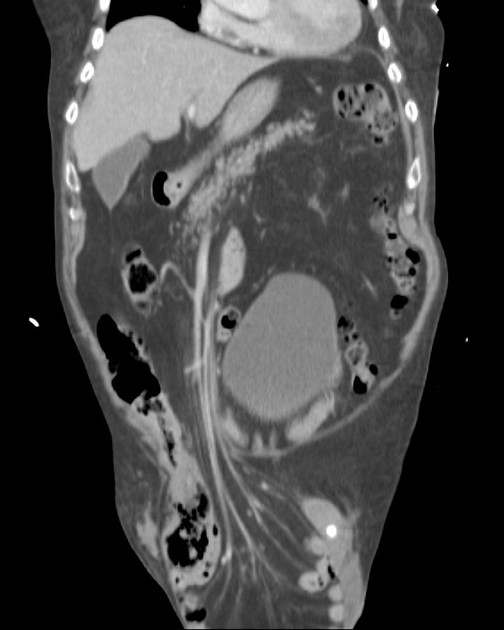
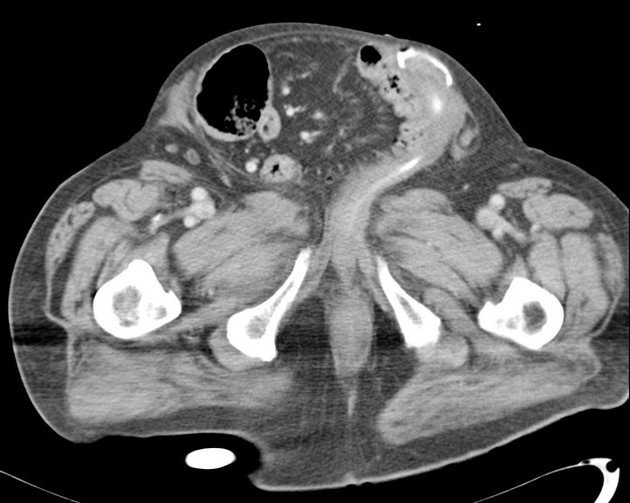
Indirect inguinal hernias arise lateral and superior to the course of the inferior epigastric vessels, lateral to Hesselbach's triangle, and then protrude through the deep (internal) inguinal ring into the inguinal canal. The hernial sac and content often pass inferomedially within the canal to emerge via the superficial inguinal ring.
Gender differences
males: they enter the canal anterior to the spermatic cord and may extend through the superficial inguinal ring into the scrotum
females: they tend to follow the round ligament into the labia majora
Contents
Contents may include mesenteric fat (most common), peritoneal fluid, small bowel loops, mobile colon segments (sigmoid, cecum, appendix), bladder and ureter 7.
Treatment and prognosis
Complications
incarceration: the most common complication associated with inguinal hernias, the incidence could be as high as 30% for infants younger than 2 months
strangulation with bowel ischemia and perforation
Differential diagnosis
On imaging, consider:
-
emerges medially to the inferior epigastric vessels and above the inguinal ligament
the inguinal canal is usually compressed/displaced ("lateral crescent sign")
-
exit below the inguinal ligament and caudal to the emergence of the inferior epigastric vessels
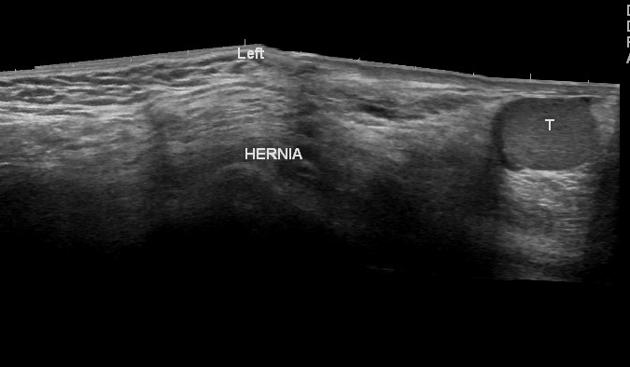
On testicular ultrasound, one could consider spermatic cord lipoma on the differential if an inguinal hernia contains only omental fat. Movement of the fat with the Valsalva maneuver is more likely an indirect hernia.
References
- 1. Shadbolt CL, Heinze SB, Dietrich RB. Imaging of groin masses: inguinal anatomy and pathologic conditions revisited. Radiographics. 2001;21 Spec No : S261-71. Radiographics (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 2. Burkhardt JH, Arshanskiy Y, Munson JL et-al. Diagnosis of inguinal region hernias with axial CT: the lateral crescent sign and other key findings. Radiographics. 2011;31 (2): E1-12. Radiographics (full text) - doi:10.1148/rg.312105129 - Pubmed citation
- 3. Suzuki S, Furui S, Okinaga K et-al. Differentiation of femoral versus inguinal hernia: CT findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189 (2): W78-83. doi:10.2214/AJR.07.2085 - Pubmed citation
- 4. Hahn-Pedersen J, Lund L, Højhus JH et-al. Evaluation of direct and indirect inguinal hernia by computed tomography. Br J Surg. 1994;81 (4): 569-72. Pubmed citation
- 5. Cherian PT, Parnell AP. The diagnosis and classification of inguinal and femoral hernia on multisection spiral CT. Clin Radiol. 2008;63 (2): 184-92. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2007.07.018 - Pubmed citation
- 6. Di Nicolò P, Aleo D, Riccioli E, Granata A. Case 230: Congenital Inguinal Herniation of the Left Ureter (Extraperitoneal Form). Radiology. 2016;279(3):972-7. doi:10.1148/radiol.16141805 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Pantaloon hernia
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (I)
- Groin herniation
- Inguinal hernia
- Round ligament varicosities
- Busoga hernia
- Canal of Nuck
- Hydrocele of the canal of Nuck
- Lateral fossa
- Direct inguinal hernia
- Abdominal hernia
- Extratesticular cystic lesions (differential)
- Hesselbach triangle
- Lateral umbilical folds
- Testicular development and descent
- Indirect inguinal hernia
- Small bowel obstruction due to inguinal hernia
- Inguinoscrotal hernia - massive
- Indirect inguinal hernia
- Direct inguinal hernia
- Female inguinal canal
- Rupert Bear (Rorschach radiology)
- Obstructed indirect inguinal hernia
- Ureteroinguinal hernia
- Massive ascites
- Indirect inguinal hernia containing sigmoid colon
- Amyand hernia
- Inguinal hernia containing urinary bladder
- Indirect inguinal hernia with distal large bowel obstruction
- Urinary bladder hernia
- Urinary bladder hernia
- Plugoma
- Myelofibrosis
- Inguinal hernia plug repair
- Bladder-containing indirect inguinal hernia
Related articles: Hernias
-
hernias
-
anterior abdominal wall herniation
- epigastric hernia
- incisional hernia
- port site hernia
- interparietal hernia
- parastomal hernia
- paraumbilical hernia
- Spigelian hernia
- umbilical hernia
- miscellaneous
- Maydl hernia
- Richter hernia: contains only one wall of a bowel loop
-
lumbar hernias
- superior lumbar hernia
- inferior lumbar hernia
-
groin herniation
-
inguinal hernia
- direct inguinal hernia
- indirect inguinal hernia: five times commoner than direct
- pantaloon hernia (combined direct and indirect inguinal herniae)
- femoral hernia
- obturator hernia
-
inguinal hernia
- diaphragmatic herniation
-
internal herniation: an uncommon cause of bowel obstruction
- paraduodenal hernia: left and right
- lesser sac (foramen of Winslow) hernia
- pericaecal hernia
-
sigmoid mesocolon hernias
- intersigmoid hernia
- transmesosigmoid hernia
- intramesosigmoid hernia
-
small bowel mesentery internal hernia
- transmesenteric hernia
- intramesenteric hernia
- transomental hernia
- supravesical hernia
- pelvic internal hernia
- falciform ligament hernia
- internal hernia due to gastric bypass surgery
- Littre hernia: hernia containing a Meckel diverticulum
- pelvic hernia
- lung hernia
-
anterior abdominal wall herniation
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta previa
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumors
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumors of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumors
- mixed germ cell tumor
- yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumor
- sex cord / stromal tumors of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumor of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumors (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumors
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys









 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.