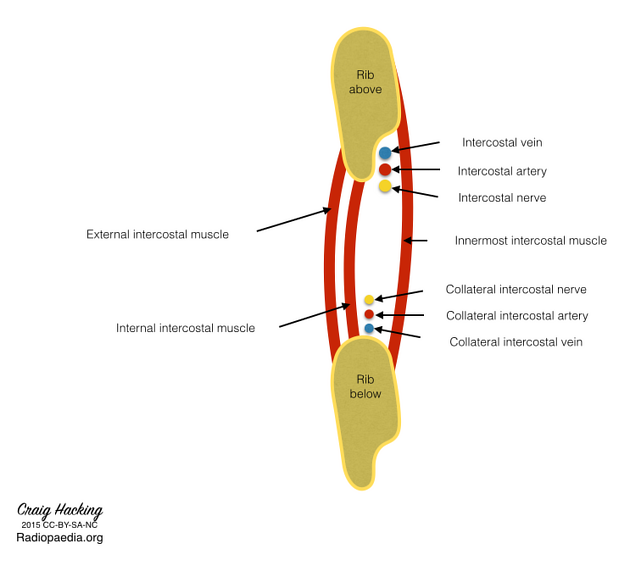
External intercostal muscle
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Balaji Vasu had no recorded disclosures.
View Balaji Vasu's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Daniel J Bell had no recorded disclosures.
View Daniel J Bell's current disclosures- Intercostales externi
- External intercostal muscles
- Outermost intercostal muscle
- Outermost intercostal muscles
The external (or outermost) intercostal muscles are important muscles of respiration. They number eleven on each side and are located in the intercostal space, expanding the transverse dimension of the thoracic cavity during inspiration.
On this page:
Images:
Gross anatomy
The external intercostal muscles are the outermost muscle of the three intercostal muscles and arise from the lower border of the rib above the respective intercostal space. The fibers run in a downwards, forwards and medial direction and insert into the outer lip of the superior border of the rib below. At their insertion they end in thin anterior intercostal membranes that continue towards the sternum. Anteriorly the lower muscles become continuous with the external oblique muscles in the anterolateral abdominal wall. As their name indicates, they are external to the internal intercostal muscles.
Blood supply
- arterial supply: anterior and posterior intercostal arteries
- venous drainage: internal thoracic vein and intercostal veins
Innervation
Muscular branches from the intercostal nerves of the respective intercostal space (T1-T11), which run with the intercostal vessels under the costal groove in between the internal and innermost intercostal muscles.
Action
External intercostal muscle contraction causes expansion of the thoracic cavity in the transverse dimension and causes an influx of air into the lungs during inspiration. They are stronger than the internal intercostal muscles.
References
- 1. Platzer W. Color Atlas of Human Anatomy locomotor system, Vol. 1. Thieme. ISBN:313533306X. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Handbook of Cardiac Anatomy, Physiology, and Devices. Humana Press. ISBN:1603273719. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Clinically oriented anatomy. LWW. ISBN:1451119453. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Last's anatomy, regional and applied. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN:044304662X. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton[+][+]
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax
- diaphragm[+][+]
- intercostal space
-
intercostal muscles
- external intercostal muscle
- internal intercostal muscle
- innermost intercostal muscles
- subcostal muscles
- transversus thoracis muscle
- variant anatomy[+][+]
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera[+][+]
- lower respiratory tract
-
heart
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart
- cardiac wall
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus
- thymus
- breast
- arterial supply of the thorax[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax[+][+]
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax[+][+]




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.