Atypical ribs
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Dinesh Palipana had no recorded disclosures.
View Dinesh Palipana's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Kajanan Nithiyananthan had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Kajanan Nithiyananthan's current disclosuresOwing to their features, the first, eleventh and twelfth ribs are considered atypical ribs. Some authors also include the second and tenth ribs as atypical. Atypical features are summarized below:
-
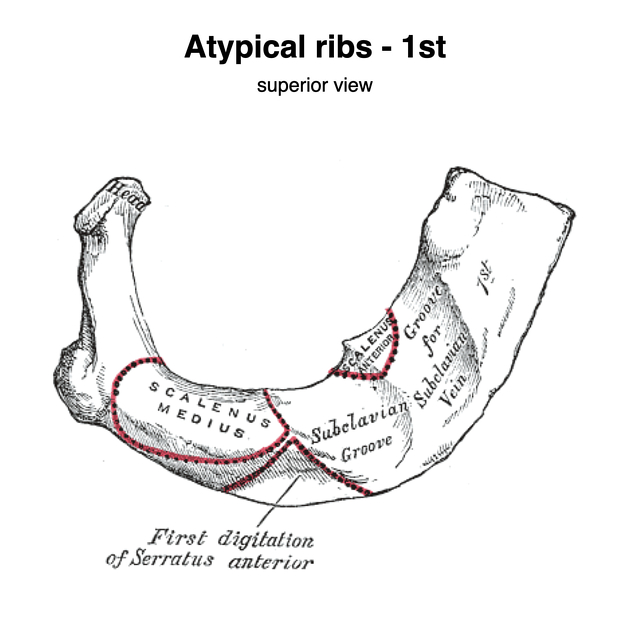
first rib
strongest, broadest and most curved
tubercle at the inner border marks the attachment of scalenus anterior muscle 2
subclavius is attached to sternal end of the rib
-
has grooves for the subclavian vein, artery, and brachial plexus
the subclavian vein (anterior) is separated from subclavian artery (posterior) by scalene tubercle 2
brachial plexus lies posterior to the subclavian artery 2
single facet articulation with T1 vertebrae 2
-
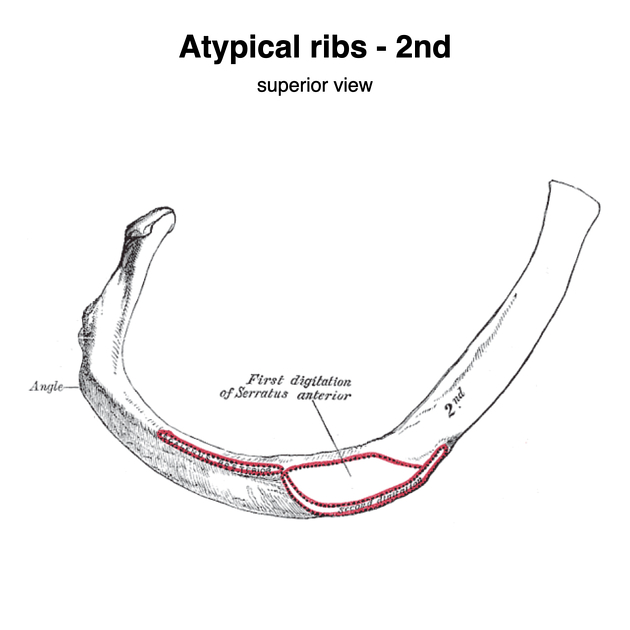
second rib
less curved and two times lengthier than the first rib 2
anterior surface marks one of the origins of the serratus anterior muscle
tubercle on its external border marks the attachment of second head of the scalenus anterior muscle 2
-
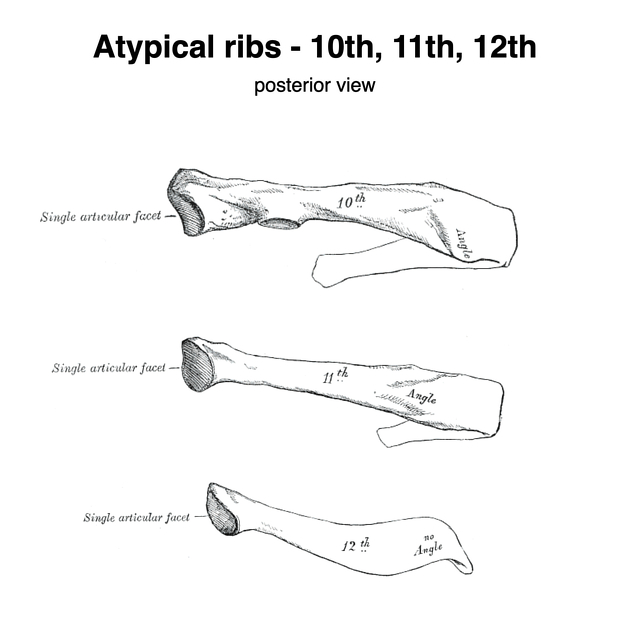
tenth rib
differs from other typical ribs by a single facet articulation with the T10 vertebrae 2
-
eleventh and twelfth ribs
shorter (no neck or tubercles) and do not attach to the sternum
single facet articulation with the same-level vertebrae
twelfth rib has no subcostal groove 2
References
- 1. Last's Anatomy. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN:0702033944. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. 10. Stephanie Ryan, Michelle McNicholas, Stephen J. Eustace. Anatomy for Diagnostic Imaging. (2011). Chapter 4: The thorax. Page 113, 114. ISBN: 9780702029714 - Google Books
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations[+][+]
- muscles of the thorax[+][+]
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera[+][+]
- lower respiratory tract
-
heart
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart
- cardiac wall
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus
- thymus
- breast
- arterial supply of the thorax[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax[+][+]
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax[+][+]




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.