Crista terminalis
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Prashant Mudgal had no recorded disclosures.
View Prashant Mudgal's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures- Terminal crest
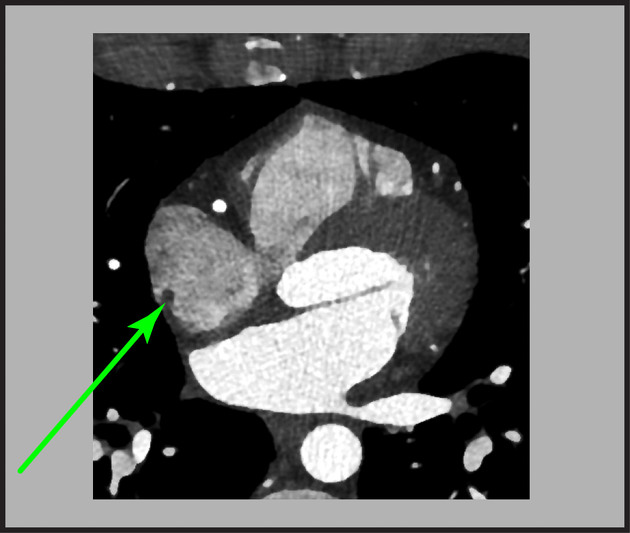
The crista terminalis is a smooth muscular ridge in the superior aspect of the right atrium, formed following resorption of the right valve of the sinus venosus. It represents the junction between the sinus venarum, the "smooth" portion of the right atrium derived from the embryologic sinus venosus, and the heavily trabeculated right atrial appendage.
Coursing between the caval orifices, it divides the pectinate muscle origin and the right atrial appendages in the right atrium. Its identification is significant in the determination of atrial situs.
Radiographic features
The crista terminalis is found closely associated with the posterolateral right atrial wall. It divides the right atrium into smooth posteromedial and trabeculated anterolateral portions.
Ultrasound
Echocardiography
A prominent crista terminalis may be incidentally discovered on transthoracic echocardiography, typically best visualized in the apical four chamber view. When a mass is visualized in the right atrium, features suggestive of a prominent crista terminalis include 4:
rounded margins, closely apposing the posterolateral wall of the right atrium 5
isoechoic to adjoining myocardium
dynamic increase in size during atrial contraction
If transesophageal echocardiography is performed the bicaval view in the midesophageal position allows simultaneous visualization of the venae cavae, atria, and interatrial septum 6.
Related pathology
While its presence is of no pathologic significance, unusual prominence of the crista terminalis has been associated with:
-
atrial fibrillation and/or flutter
implicated as the ectopic focus of arrythmogenesis
inappropriate sinus tachycardia (IST) 2
References
- 1. Caruso G & Becker A. How to Determine Atrial Situs? Considerations Initiated by 3 Cases of Absent Spleen with a Discordant Anatomy Between Bronchi and Atria. Br Heart J. 1979;41(5):559-67. doi:10.1136/hrt.41.5.559 - Pubmed
- 2. Kalman JM, Olgin JE, Karch MR, Hamdan M, Lee RJ, Lesh MD. "Cristal tachycardias": origin of right atrial tachycardias from the crista terminalis identified by intracardiac echocardiography. (1998) Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 31 (2): 451-9. Pubmed
- 3. Prabhakar Rajiah, James MacNamara, Abhishek Chaturvedi, Ravi Ashwath, Nicholas L. Fulton, Harold Goerne. Bands in the Heart: Multimodality Imaging Review. (2019) RadioGraphics. 39 (5): 1238-1263. doi:10.1148/rg.2019180176 - Pubmed
- 4. Kim M & Jung H. Anatomic Variants Mimicking Pathology on Echocardiography: Differential Diagnosis. J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2013;21(3):103. doi:10.4250/jcu.2013.21.3.103
- 5. Bolognesi M, Bolognesi D. A prominent crista terminalis associated with atrial septal aneurysm that mimics right atrial mass leading to atrial arrhythmias: a case report. (2012) Journal of medical case reports. 6: 403. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-6-403 - Pubmed
- 6. Ravi Rasalingam, Majesh Makan, Julio E. Perez. The Washington Manual of Echocardiography. (2012) ISBN: 9781451113402 - Google Books
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton[+][+]
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax[+][+]
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera
- lower respiratory tract[+][+]
-
heart
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves[+][+]
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart[+][+]
- cardiac wall[+][+]
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus[+][+]
- thymus[+][+]
- breast[+][+]
- arterial supply of the thorax[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax[+][+]
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax[+][+]




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.