Coronary arterial dominance
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures- Dominance of the coronary arteries
- Cardiac arterial dominance
- Coronary artery dominance
- Coronary dominance
- Cardiac dominance
- Dominance of coronary arteries
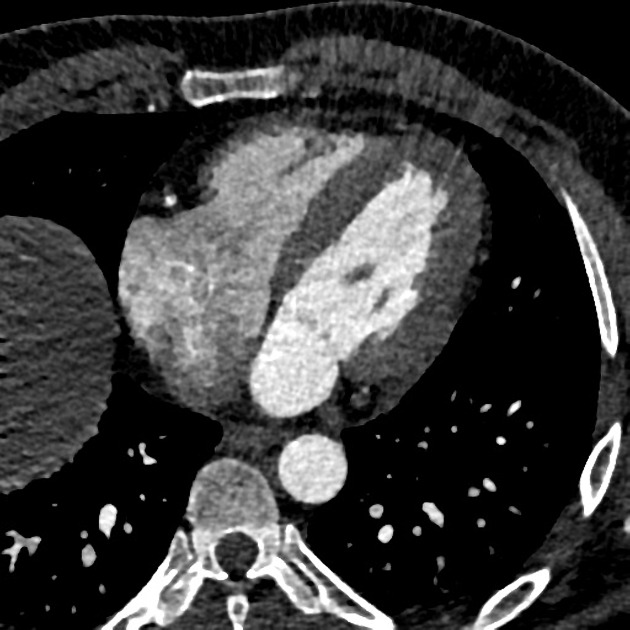
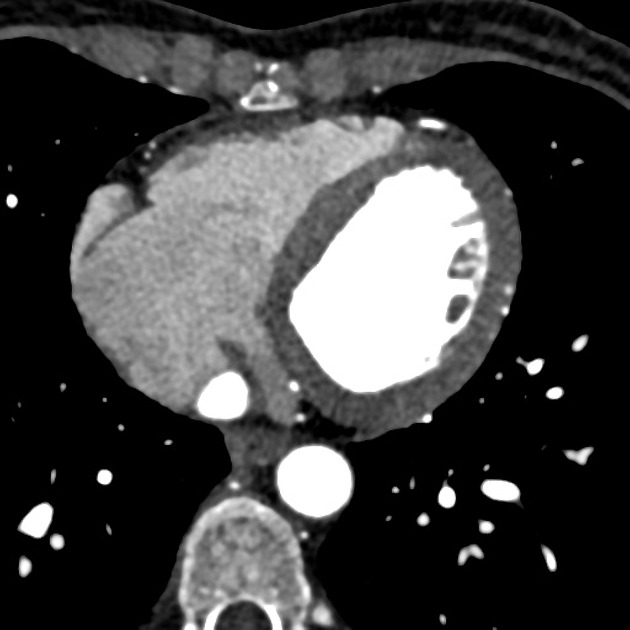
Coronary arterial dominance is defined by the vessel which gives rise to the posterior descending artery (PDA), which supplies the myocardium of the inferior third of the interventricular septum.
Most hearts (80-85%) are right dominant where the PDA is supplied by the right coronary artery (RCA). The remaining 15-20% of hearts are roughly equally divided between left dominant (~10%) and codominant (~20%). The strict definition of codominance can vary depending on which modality one uses to assess the coronary arteries (coronary angiography or CT coronary angiography (CTCA)) but is not overly important. In left dominant hearts the PDA is supplied by the left circumflex artery (LCx) wrapping around the left atrioventricular groove, or less commonly the left anterior descending artery (LAD) coursing around the apex of the heart. In a codominant heart a single or duplicated PDA is supplied by branches of both the RCA and the LAD or LCx.
Although the RCA is the dominant vessel in most hearts, it is important to consider that it is usually the LAD that supplies the majority of the left ventricular myocardium as well as the anterior and mid thirds of the interventricular septum.
Clinical relevance
Dominance has important implications in myocardial ischemia and infarction, imaging of the coronary arteries (CTCA and invasive coronary angiography) and the planning for coronary artery bypass grafting.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Keith L. Moore, Arthur F. Dalley, A. M. R. Agur. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. (2013) ISBN: 9781451119459 - Google Books
- 2. Chummy S. Sinnatamby. Last's Anatomy. (2011) ISBN: 9780702033940 - Google Books
- 3. Dewey M. Cardiac CT. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. ISBN:B00F76F5P2. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Pelter MM, Al-Zaiti SS, Carey MG. Coronary artery dominance. (2011) American journal of critical care : an official publication, American Association of Critical-Care Nurses. 20 (5): 401-2. doi:10.4037/ajcc2011734 - Pubmed
- 5. Gebhard C, Fuchs TA, Stehli J, Gransar H, Berman DS, Budoff MJ, Achenbach S, Al-Mallah M, Andreini D, Cademartiri F, Callister TQ, Chang HJ, Chinnaiyan KM, Chow BJ, Cury RC, Delago A, Gomez MJ, Hadamitzky M, Hausleiter J, Hindoyan N, Feuchtner G, Kim YJ, Leipsic J, Lin FY, Maffei E, Pontone G, Raff G, Shaw LJ, Villines TC, Dunning AM, Min JK, Kaufmann PA. Coronary dominance and prognosis in patients undergoing coronary computed tomographic angiography: results from the CONFIRM (COronary CT Angiography EvaluatioN For Clinical Outcomes: An InteRnational Multicenter) registry. (2015) European heart journal cardiovascular Imaging. 16 (8): 853-62. doi:10.1093/ehjci/jeu314 - Pubmed
- 6. O'Brien JP, Srichai MB, Hecht EM, Kim DC, Jacobs JE. Anatomy of the heart at multidetector CT: what the radiologist needs to know. (2007) Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 27 (6): 1569-82. doi:10.1148/rg.276065747 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Inferior interventricular artery
- Atrial septum
- Hypoplastic circumflex artery
- Right coronary artery
- Septal branches of the left anterior descending artery
- Atrioventricular nodal artery
- Coronary arteries
- Cardiac CT (an approach)
- Circumflex artery
- Heart
- Coronary hypoplasia
- Hypoplastic right coronary artery
- Myocardial area at risk
- Left main coronary artery
- Myocardial infarction
- Normal coronary CT angiogram, left dominant
- Normal coronary CT angiogram, right dominant
- Anomalous right coronary artery arising from the left coronary ostium seen on coronary catheter angiogram
- Coronary CTA (dual energy)
- Prepulmonic coursing left coronary artery
- "Malignant" anomalous interarterial course of the right coronary artery
- Coronary CTA (dual energy)
- Quadrifurcation of the left main stem
- Myocardial scarring
- Sinus venosus atrial septal defect with partial anomalous pulmonary venous return
- Aortic dissection with pulmonary artery intramural haematoma
- Coronary dominance (CT)
- Anomalous left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery (ALCAPA)
- Coronary arterial ectasia
- Aberrant left main coronary artery
- Right coronary arterial dominance with type III LAD
- Normal right dominant circulation
- Ramus intermedius in a left dominant circulation
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton[+][+]
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax[+][+]
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera[+][+]
- lower respiratory tract
-
heart
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart
- cardiac wall
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus
- thymus
- breast
- arterial supply of the thorax
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)[+][+]
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)[+][+]
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch[+][+]
- aortic isthmus[+][+]
- descending aorta[+][+]
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax[+][+]
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax[+][+]








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.