Lung hilum
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Don Ngo had no recorded disclosures.
View Don Ngo's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures- Pulmonary hila
- Pulmonary hilum
- Lung root
- Lung roots
- Pulmonary roots
- Pulmonary root
- Lung hila
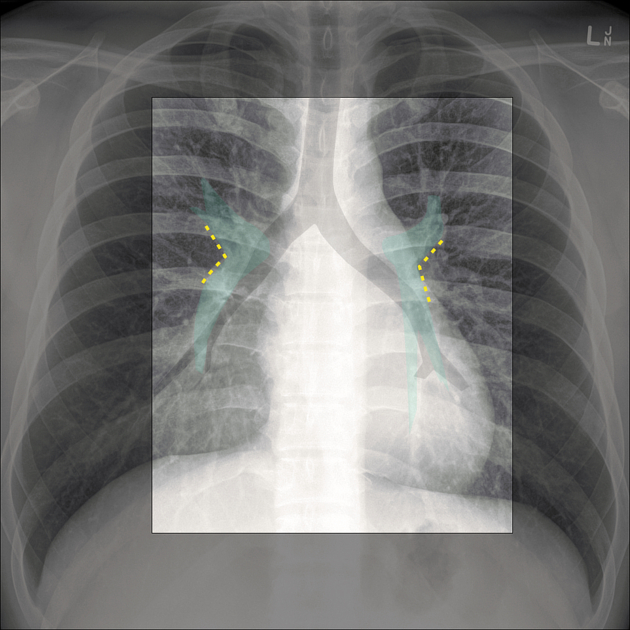
The lung hila or roots are found on the medial aspect of each lung and transmit structures between the lung and mediastinum. The left and right lung roots are similar but not identical. The roots of the lung lie between T5 to T7 vertebrae 5.
The hilar point is a point where the upper lobe vein crosses over the pulmonary artery. The hilar angle is the angle between the vessels at the hilar point, which usually measures 120° 5.
Gross anatomy
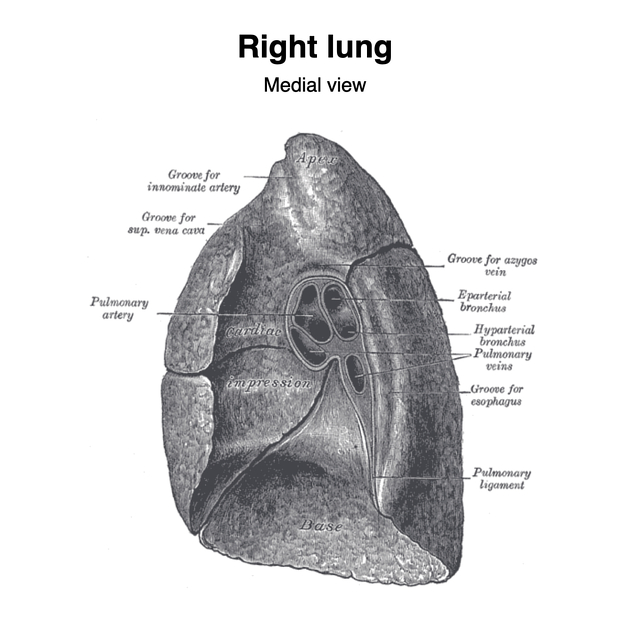
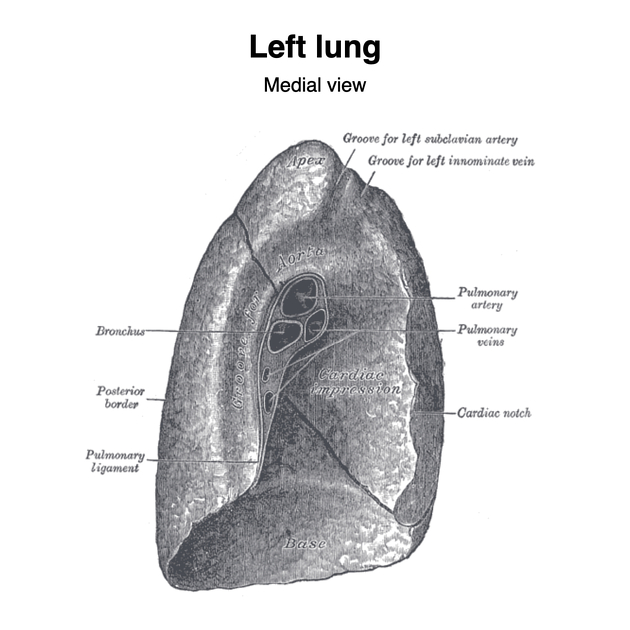
The structures of the lung hilum are enclosed in a sleeve of pleura continuous below with the pulmonary ligament 5. Each hilum contains the following:
a main bronchus that divides based on the lobar anatomy
superior and inferior pulmonary veins
lymph nodes and lymphatic channels
bronchial arteries and veins
autonomic nerves
Left hilum
The left hilum lies below the aortic arch and anterior to the descending aorta. The left main bronchus lies at the most posterior aspect of the hilum, with the left superior pulmonary vein located anteriorly and the left inferior pulmonary vein occupying the inferior portion of the hilum. The left pulmonary artery is anterosuperior to the left main bronchus. Pulmonary veins always lie anteroinferior to the pulmonary artery 5.
Right hilum
The right hilum lies below the arch of the azygous vein, posterior to the superior vena cava and right atrium. Right pulmonary veins are located at the anterior part of the hilum, followed by right pulmonary arteries, and lobar bronchi 5.
References
- 1. Susan Standring. Gray's Anatomy. (2008) ISBN: 9780443066849 - Google Books
- 2. Last, R. J., McMinn, R. M. H.. Last's Anatomy, Regional and Applied. (1994) ISBN: 044304662X - Google Books
- 3. Keith L. Moore, Arthur F. Dalley, A. M. R. Agur. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. (2013) ISBN: 9781451119459 - Google Books
- 4. Paul Butler, Adam Mitchell, Jeremiah C. Healy et al. Applied Radiological Anatomy. (2012) ISBN: 9780521766661 - Google Books
- 5. Stephanie Ryan, Michelle McNicholas, Stephen J. Eustace. Anatomy for Diagnostic Imaging. (2011) ISBN: 9780702029714 - Google Books
Incoming Links
- Bronchial vein
- Lung fissures
- Inferior pulmonary ligament
- Dense hilum sign
- Right middle lobe
- Upper zone
- Superior triangle sign (right lower lobe collapse)
- Lung cancer (staging - IASLC 8th edition)
- Hilum convergence sign
- Left main bronchus
- Right main bronchus
- Right pulmonary artery
- Bronchus intermedius
- Modified PIOPED II criteria for diagnosis of pulmonary embolus
- Horizontal fissure
- Assessment of pulmonary hila on chest x-ray (approach)
- Normal hilar position (mnemonic)
- Review areas on chest radiograph
- Golden S-sign (lung)
- Mid zone
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton[+][+]
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax[+][+]
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera
-
lower respiratory tract
- tracheobronchial tree[+][+]
-
lungs
-
bronchopulmonary segmental anatomy (Boyden Classification) (mnemonic)[+][+]
- left lung
- right lung
- variant anatomy
- lung parenchyma[+][+]
- hilum
- pleura[+][+]
-
bronchopulmonary segmental anatomy (Boyden Classification) (mnemonic)[+][+]
-
heart[+][+]
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart
- cardiac wall
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus[+][+]
- thymus[+][+]
- breast[+][+]
-
lower respiratory tract
- arterial supply of the thorax[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax[+][+]
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax[+][+]







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.