Twelfth rib
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Palipana D, Hacking C, Kang O, et al. Twelfth rib. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 08 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-44312
Permalink:
rID:
44312
Article created:
17 Apr 2016,
Dinesh Palipana
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Dinesh Palipana had no recorded disclosures.
View Dinesh Palipana's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures
Revisions:
5 times, by
4 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Sections:
Tags:
Synonyms:
- 12th rib
The twelfth rib is an atypical rib. It is the shortest rib, and one of two floating ribs.
On this page:
Article:
Images:
Images:
Gross anatomy
Osteology
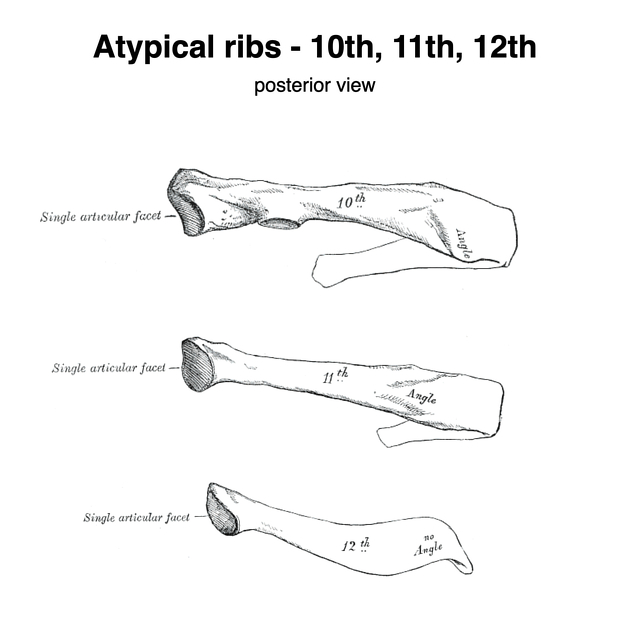
The 12th rib has a single facet on its head for articulation with the T12 vertebra. It has a short neck and no tubercle. It also lacks a costal groove and angle. internal surface of this word about slopes slightly upwards.
The pointed anterior end of the 12th rib is covered with costal cartilage. Its length is highly variable.
Attachments
- quadratus lumborum: anterior inferior surface on the medial half
- internal intercostal muscle: medially at or near the upper border of the anterior surface
- external intercostal muscle: the upper border of the external surface
- diaphragm: laterally at or near the upper border
- lumbocostal ligament: posteriorly, near the head, running to the first lumbar transverse process
- levator costae: external surface medially
- longissimus thoracis: external surface medially
- iliocostalis: external surface medially
- serratus posterior inferior: external surface laterally
- latissimus dorsi: external surface laterally
- external oblique: external surface laterally
Related pathology
- infection, e.g. septic arthritis, osteomyelitis
- malignancy, e.g. chondrosarcoma, enchondroma, metastases
- trauma, e.g. fracture
- fracture of the twelfth rib is rare
- may be associated with retroperitoneal hemorrhage, adrenal/splenic/renal trauma, and thoracolumbar vertebral injury
References
- 1. Gray's anatomy. Elsevier. ISBN:0808923714. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Moore KL, Dalley AF. Anatomy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. (1999) ISBN:0683061410. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Last's Anatomy. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN:0702033944. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Snell RS. Clinical Anatomy by Regions. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN:160913446X. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 5. Shweiki E, Klena J, Wood GC et-al. Assessing the true risk of abdominal solid organ injury in hospitalized rib fracture patients. J Trauma. 2001;50 (4): 684-8. Pubmed citation
- 6. Miller JA, Ghanekar D. Pneumothoraces secondary to blunt abdominal trauma: aids to plain film radiographic diagnosis and relationship to solid organ injury. Am Surg. 1996;62 (5): 416-20. Pubmed citation
- 7. Jabre A, Barest G, Sledge J et-al. Cord transection by guillotine effect of fractured ribs. J Trauma. 2001;50 (4): 733-4. Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations[+][+]
- muscles of the thorax[+][+]
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera[+][+]
- lower respiratory tract
-
heart
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart
- cardiac wall
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus
- thymus
- breast
- arterial supply of the thorax[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax[+][+]
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax[+][+]




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.