Mitral valve
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Arlene Campos had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Arlene Campos's current disclosures- Bicuspid valve
- Mitral valve (MV)
- Mitral valves (MVs)
- Bicuspid valves
The mitral valve (MV) (or bicuspid valve) is one of the four cardiac valves. It is the atrioventricular valve that allows blood to flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle. It opens during diastole and closes during systole.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
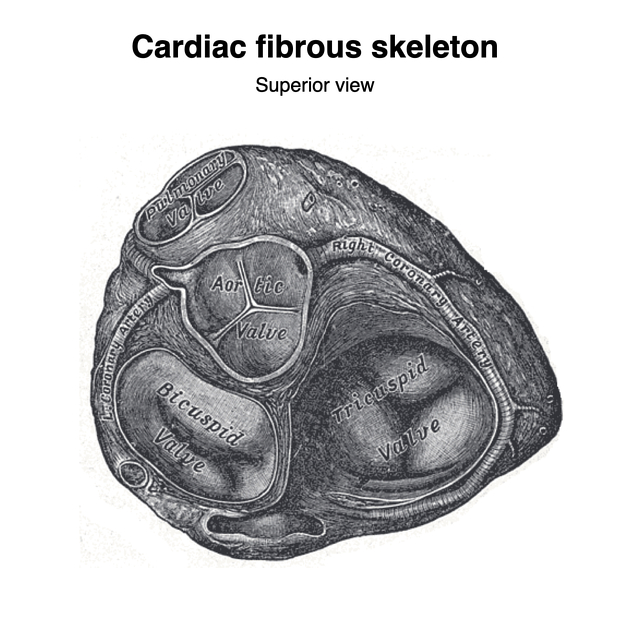
The valve has anterior and posterior leaflets, the bases of which attach around the AV orifice to a fibrous ring known as the mitral valve annulus (MVA), forming part of the fibrous skeleton of the heart. The chordae tendineae are thin, strong, inelastic, fibrous chords that extend from the free edge of the cusps to the apices of the papillary muscles within the left ventricle. Both cusps receive chordae tendineae from both papillary muscles. The anterior leaflet is thicker and more mobile than the posterior cusp ref, and in general, the cusps of the mitral valve are smaller and thicker than those of the tricuspid valve.
Related pathology
mitral valve papillary muscle rupture
History and etymology
The Latin word 'mitra' refers to a turban used to describe the ceremonial head-dress worn by Catholic bishops (hence the modern word mitre). The valve was initially described as resembling such a hat.
References
- 1. Paul Butler, Adam Mitchell, Jeremiah C. Healy et al. Applied Radiological Anatomy. (2012) ISBN: 9780521766661 - Google Books
- 2. Last, R. J., McMinn, R. M. H.. Last's Anatomy, Regional and Applied. (1994) ISBN: 044304662X - Google Books
- 3. Keith L. Moore, Arthur F. Dalley, A. M. R. Agur. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. (2013) ISBN: 9781451119459 - Google Books
Incoming Links
- Congenital heart disease in echocardiography (an approach)
- Flail leaflet
- Double outlet left ventricle
- Tricuspid valve stenosis
- Cardiac calcification
- Rheumatic heart disease
- Chordae tendineae
- Diastolic dysfunction (point of care ultrasound)
- Papillary muscle rupture
- Porcelain left atrium
- Atrioventricular septal defect
- Cardiac valves
- Mitral valve leaflet calcification
- Atrioventricular septum
- Cardiac myxoma
- Mitral annular disjunction
- Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
- Prosthetic heart valve
- Blunt cardiac injury
- Mitral valve stenosis
- Mitral valve disease findings on plain chest x-ray
- Mitral valve (M-mode echocardiogram)
- Apical 4 chamber view - normal (transthoracic echocardiography)
- Parasternal short axis view - normal (transthoracic echocardiography)
- Caseous mitral annular calcification
- Mitral valve replacement
- Mitral annular calcification
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton[+][+]
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax[+][+]
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera
- lower respiratory tract[+][+]
-
heart
- cardiac chambers[+][+]
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart[+][+]
- cardiac wall[+][+]
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus[+][+]
- thymus[+][+]
- breast[+][+]
- arterial supply of the thorax[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax[+][+]
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax[+][+]





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.