Variant anatomy of the aortic arch
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Donna D'Souza had no recorded disclosures.
View Donna D'Souza's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Ashesh Ishwarlal Ranchod had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Ashesh Ishwarlal Ranchod's current disclosures- Congenital aortic anomalies
- Aortic arch variations
- Variations of the aortic arch
- Variant of the aortic arch
- Aortic arch variant
- Aortic arch variants
- Aortic arch variation
- Variants of the aortic arch
- Variants of aortic arch
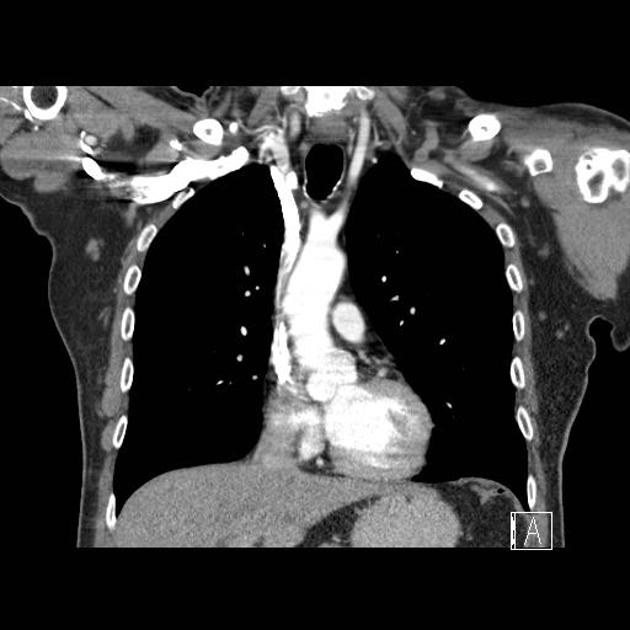
Variant anatomy of the aortic arch occurs when there is failure of normal aortic development. It results in a number of heterogenous anomalies of the aorta and its branch vessels.
Gross anatomy
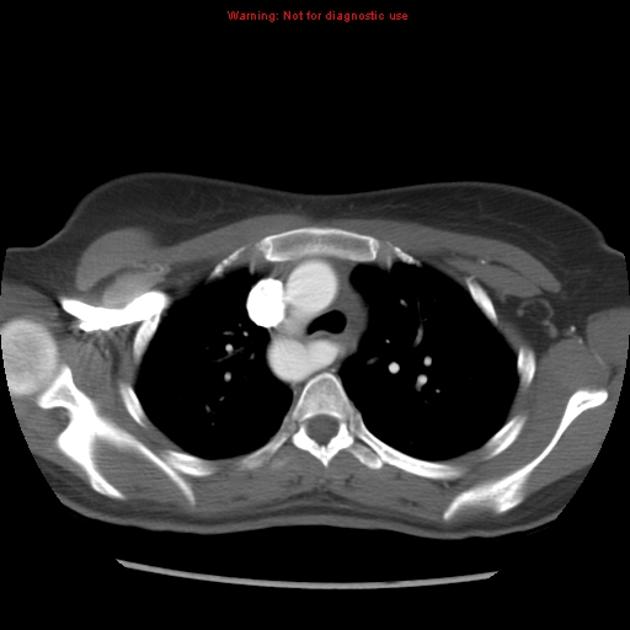
Normally, the aorta ascends in the superior mediastinum to the level of the sternal notch before arching posteriorly and descending in the left hemithorax. The arch gives off three branch vessels, the brachiocephalic (also called the innominate), left common carotid and left subclavian arteries.
Aortic development is a complex process that takes place during the third week of gestation. During development, the two dorsal aortae fuse to form the descending aorta, the ventral aortic limbs fuse to form the aortic sac, the left 4th arch vessel becomes the aortic arch and the right 4th arch vessel becomes atretic distally.
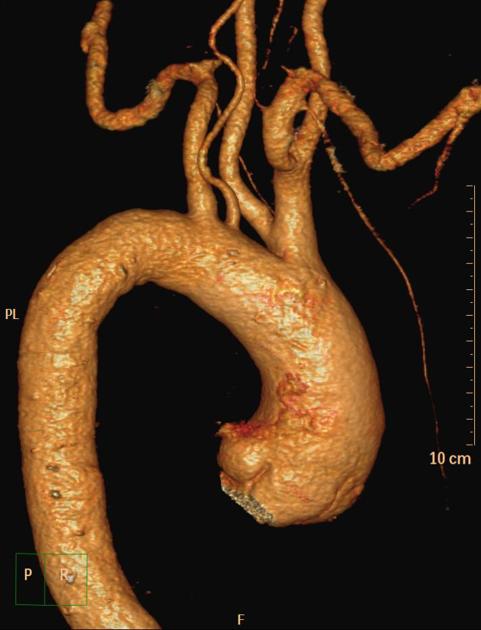
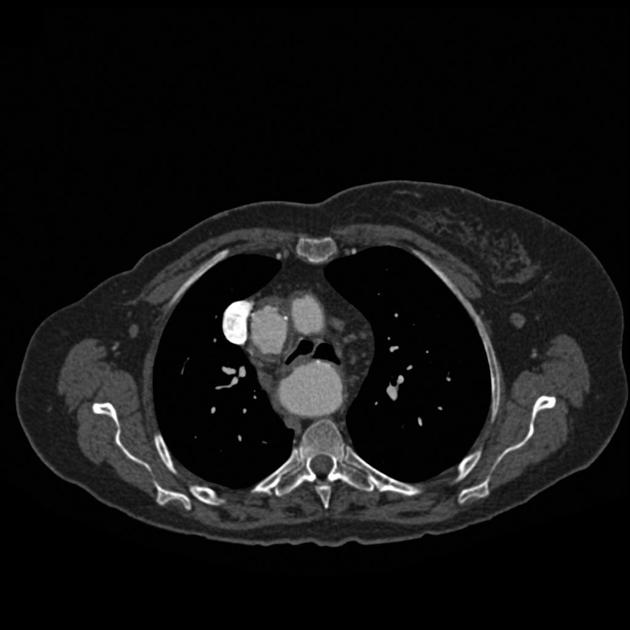
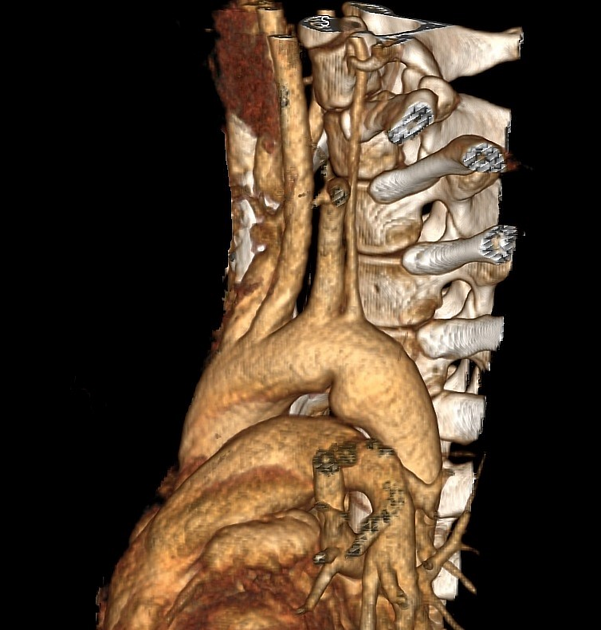
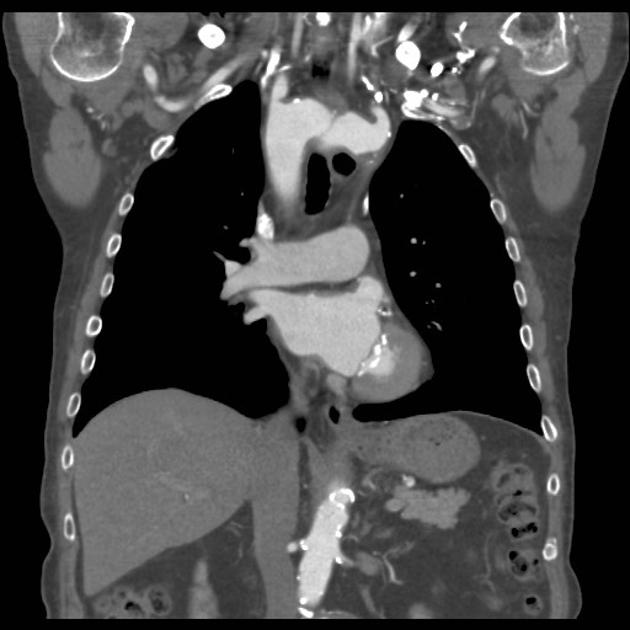
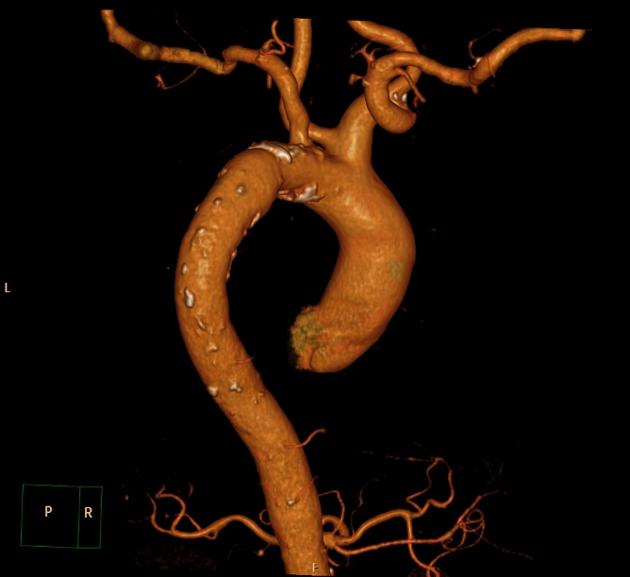
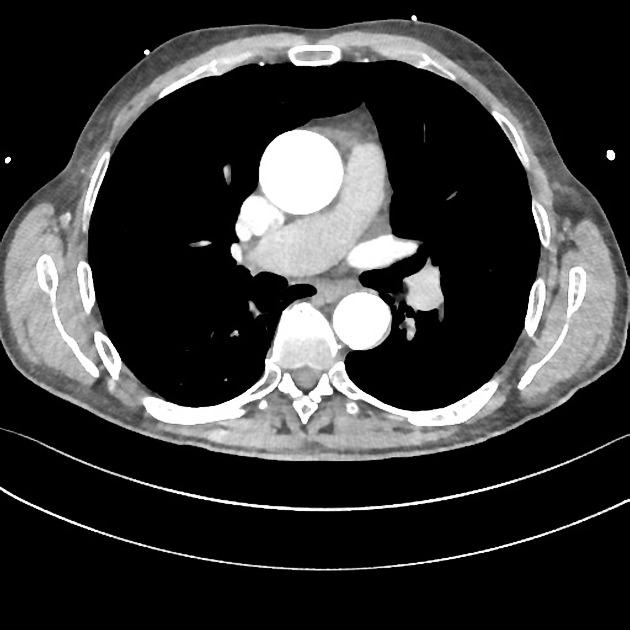
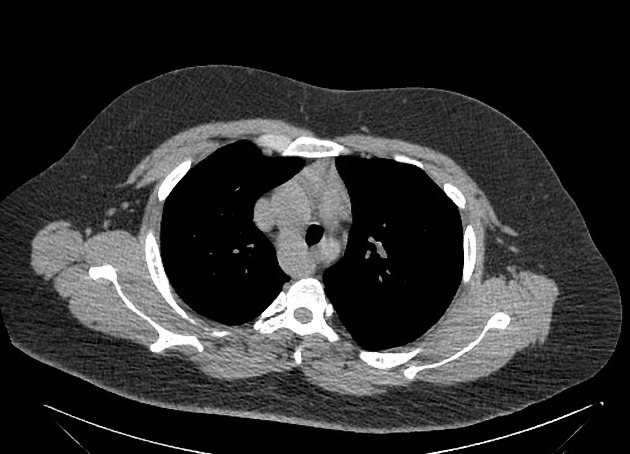
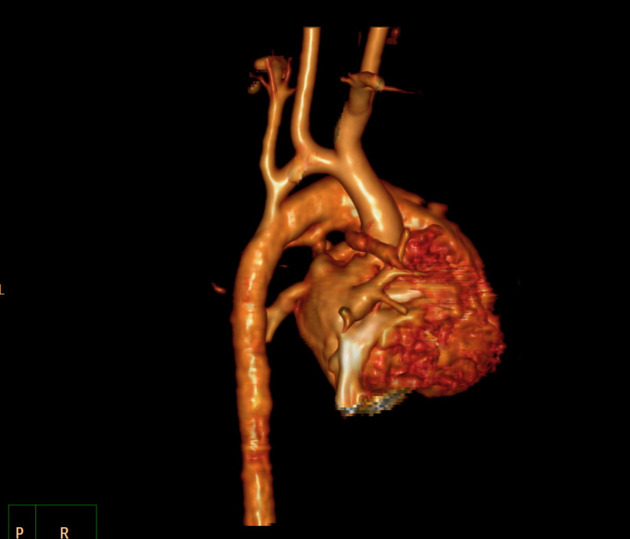
Variant anatomy
Common arch anomalies
When there is departure from normal development, variant anatomy occurs. Commonly, failure of normal regression of the 4th arch vessels results in a double aortic arch or right-sided aortic arch.
Other arch anomalies
- hypoplastic ascending aorta
- coarctation of the aorta
- interrupted aortic arch
- patent ductus arteriosus
- cervical aortic arch
- ductus diverticulum
- circumflex aorta
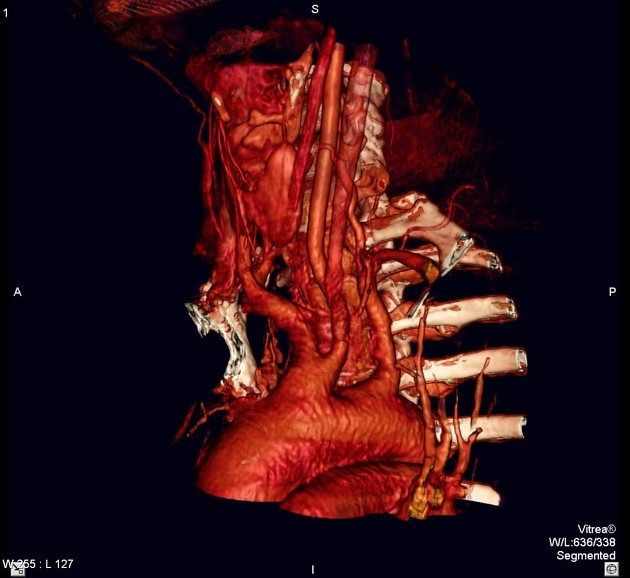
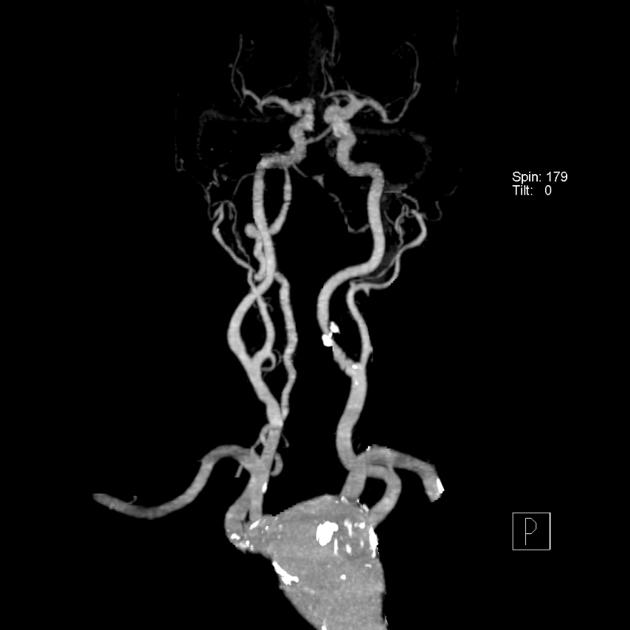
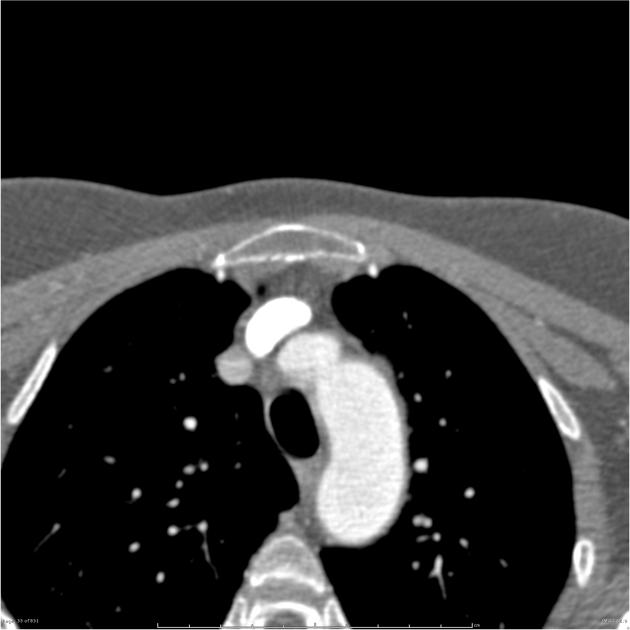
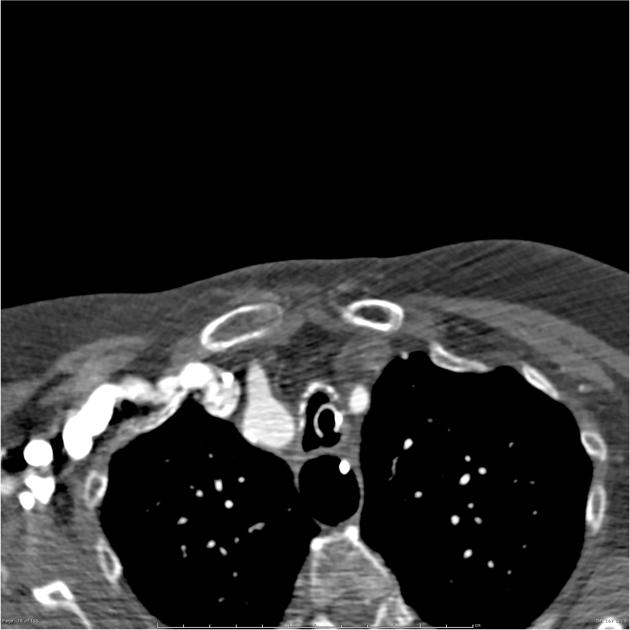
Branch vessel anomalies
Abnormal formation of the 1st, 2nd and 3rd arch vessels results in abnormal branch vessels:
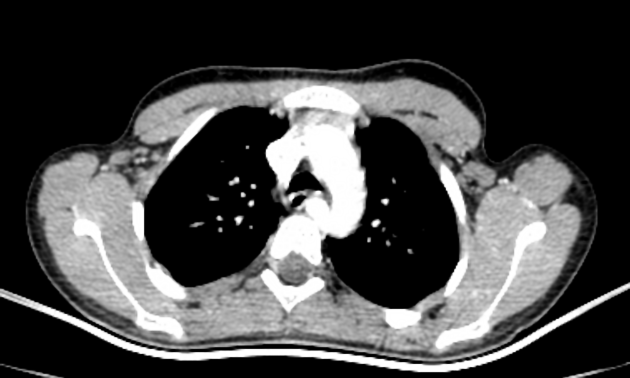
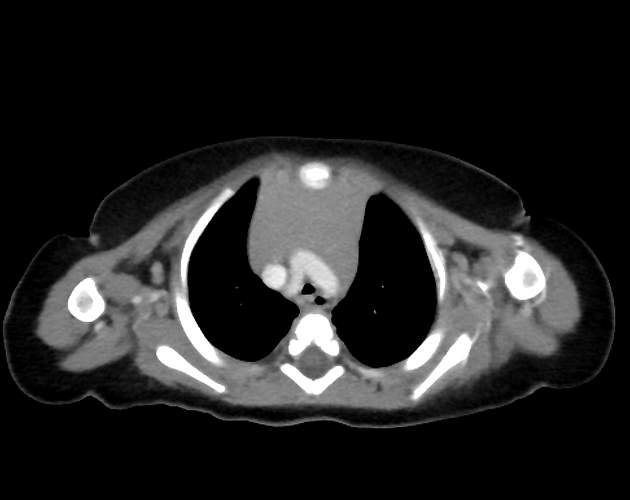
- bovine arch (commonest, occurring in 10-20% of the population) 4,5
- thyroidea ima artery (between 4-10 % of cases)
- variant origin of vertebral arteries (2.5-6% of cases) 4,5
- aberrant right subclavian artery (in 0.6% of cases) 5
- aberrant left subclavian artery (right-sided arch)
- variant aortic branch vessels
- bronchial arteries (case)
- common origin of both common carotid arteries
References
- 1. Kau T, Sinzig M, Gasser J et-al. Aortic development and anomalies. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2007;24 (2): 141-52. doi:10.1055/s-2007-980040 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 2. Dasari TW, Paliotta M. Images in clinical medicine. Cervical aortic arch. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014;371 (26): e38. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm1400771 - Pubmed citation
- 3. Bader V, Walayat M, Smith B et-al. Circumflex retroesophageal aorta mimicking aortic interruption: a rare cause of aortic obstruction in a neonate. World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg. 2014;5 (4): 599-602. doi:10.1177/2150135114539520 - Pubmed citation
- 4. Jakanani GC, Adair W. Frequency of variations in aortic arch anatomy depicted on multidetector CT. Clin Radiol. 2010;65 (6): 481-7. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2010.02.003 - Pubmed citation
- 5. Karacan A, Türkvatan A, Karacan K. Anatomical variations of aortic arch branching: evaluation with computed tomographic angiography. Cardiol Young. 2014;24 (03): 485-93. doi:10.1017/S1047951113000656 - Pubmed citation
- 6. Vučurević G, Marinković S, Puškaš L et-al. Anatomy and radiology of the variations of aortic arch branches in 1,266 patients. Folia Morphol. (Warsz). 2013;72 (2): 113-22. Pubmed citation
Incoming Links
- Aberrant right subclavian artery with dysphagia lusoria
- Bovine arch
- Right sided aortic arch
- Tetralogy of Fallot with aberrant right subclavian artery
- Innominate artery compression syndrome
- Aberrant left subclavian artery with diverticulum of Kommerell
- Scimitar syndrome
- Incomplete double aortic arch
- Aberrant right subclavian artery
- Aortic tubular hypoplasia/preductal coarctation with large patent ductus arteriosus
- Right-sided aortic arch
- Pseudocoarctation of aorta and aberrant origin of left vertebral artery
- Right side aortic arch
- Interrupted aortic arch- type B1
- Pseudocoarctation of the aorta
- Pseudocoarctation of the aorta
- Multiple congenital anomalies of aortic arch
- Aberrant right subclavian artery
- Aberrant right subclavian artery
- Right-sided aortic arch
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton[+][+]
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax[+][+]
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera[+][+]
- lower respiratory tract
-
heart
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart
- cardiac wall
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus
- thymus
- breast
- arterial supply of the thorax
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta[+][+]
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus[+][+]
- descending aorta[+][+]
-
ascending aorta[+][+]
- pulmonary trunk[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax[+][+]
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax[+][+]
Related articles: Pathology: Vascular: Aortic
- acute aortic syndrome
- aortic aneurysms
- inflammatory
- congenital
- aortic coarctation
- aortic pseudocoarctation
- cervical aortic arch
- interrupted aortic arch
- transposition of the great arteries
- variant anatomy of the aortic arch
- traumatic aortic injury
- miscellaneous







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.