The coronary sinus is the largest cardiac venous structure. It returns the majority of the blood supply for the left ventricle to the right atrium.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
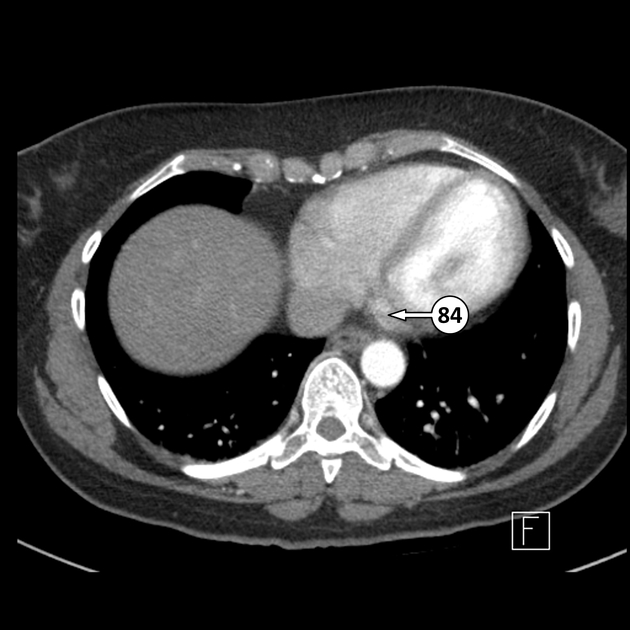
The coronary sinus courses along the posterior wall of the left atrium into the left atrioventricular groove. It normally drains into the right atrium. The ostium of the coronary sinus is partially covered by the Thebesian valve.
Veins draining into the coronary sinus are highly variable, but usually, include:
Development
The coronary sinus develops from one of the two sinus horns of the sinus venosum. The other horn becomes part of the right atrium. The right venous valve of the sinus venosum develops into the Thebesian valve and the Eustachian valve. For further detail see cardiac development.
Variant anatomy
the coronary sinus may act as a conduit between a persistent left superior vena cava and the right atrium
rarely, the coronary sinus may drain into the left atrium, causing a right-to-left shunt (unroofed coronary sinus)
Related pathology
The coronary sinus may be involved in a number of different procedures or pathologic processes:
the coronary sinus is a good position for lead placement in biventricular pacing
the coronary sinus may be an ablation target for some arrhythmia/dysrhythmias (e.g. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome)
-
the coronary sinus rarely may have an abnormal connection to the left atrium on its way to the right atrium (unroofed coronary sinus), a rare kind of atrial septal defect
associated with heterotaxy syndromes and persistent left-sided superior vena cava






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.