The left anterior descending (LAD) artery, also known as the anterior interventricular branch, is one of the two branches of the left coronary artery (the other branch being the circumflex (Cx) artery).
On this page:
Terminology
The left anterior descending artery is often given the sobriquet, the widow-maker, particularly by the lay media, due to the propensity for proximal disease of the left anterior descending artery to cause the death of male partners. However, women are also killed by disease at this location 6.
Gross anatomy
It descends along the interventricular groove.
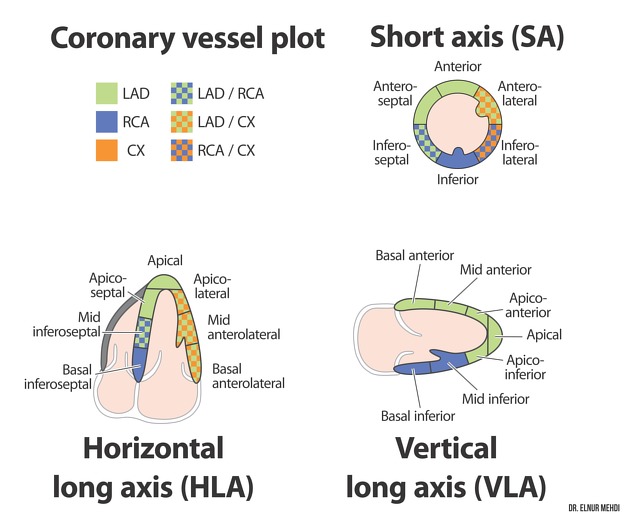
It can be divided into proximal, mid and distal segments and this helps to differentiate the names of its various small branches 1:
origin: left coronary artery
-
branches 4
septal perforators: course to the right towards the septum on axial CTCA
diagonal branches: course to the left on the anterolateral wall of the left ventricle on axial CTCA
-
segments
proximal: from the origin to the first diagonal branch (D1) (although some authors use the first septal perforator (S1) as the landmark)
mid: from the origin of D1 to half the distance from the D1 origin to the apex
distal: distal to half the distance from the D1 origin to the apex
The LAD should arise from the left coronary cusp which lies between 3 and 6 o'clock on an axial view.
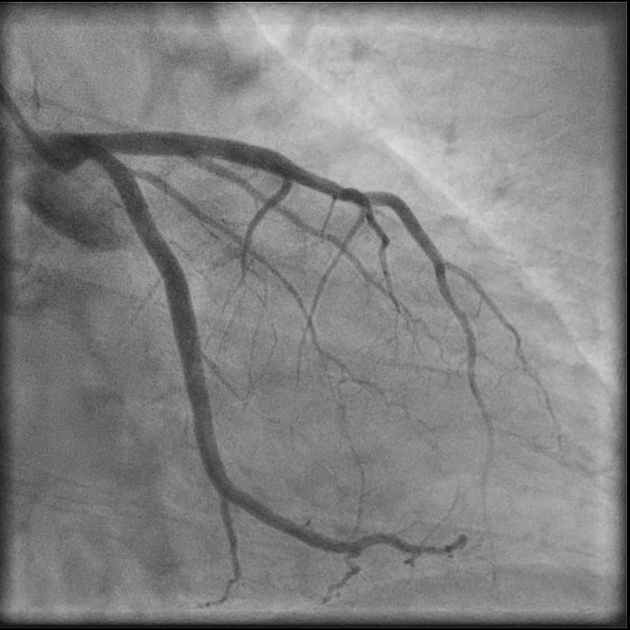
The length of the LAD can be highly variable. On angiography, it may be reported as types I-III:
type I: short vessel (can terminate before apex)
type II: intermediate vessel
type III: long wrap-around vessel (around the apex)
Relations
The LAD lies in the epicardial fat within the anterior interventricular septum 1:
inferior: myocardium
superior: pericardium
the great cardiac vein ascends in the anterior IV groove with the LAD
Supply
The LAD supplies the anterolateral myocardium and apex with one of its branches supplying the anterior two-thirds of the interventricular septum.
Variant anatomy
-
dual left anterior descending coronary artery2: two left anterior descending coronary arteries (one usually shorter in length) that are both situated in the anterior interventricular groove
it is important to know of this variation when planning surgical vascularization 3
the mid 1/3rd of the LAD is known on occasion to course through the myocardium, known as myocardial bridging; does not have any clinical significance
Related pathology
-
occlusion of LAD leading to myocardial infarction or sudden cardiac death
the LAD is the most commonly occluded of the coronary arteries
it provides the major blood supply to the interventricular septum and bundle branches of the conducting system
blockage of this artery can lead to impairment or death (infarction) of the conducting system
-
represents subacute occlusion of the LAD
-
indicates acute occlusion of the proximal LAD








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.