Cardiac valves
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Hacking C, Bell D, Weerakkody Y, et al. Cardiac valves. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 21 Feb 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-39222
Permalink:
rID:
39222
Article created:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures
Revisions:
22 times, by
7 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Sections:
Tags:
Synonyms:
- Cardiac valve
- Heart valve
- Cardiac valves
- Atrioventricular valves (AVs)
- Atrioventricular valve (AV)
- Semilunar valves
- Semilunar valve
- Heart valves
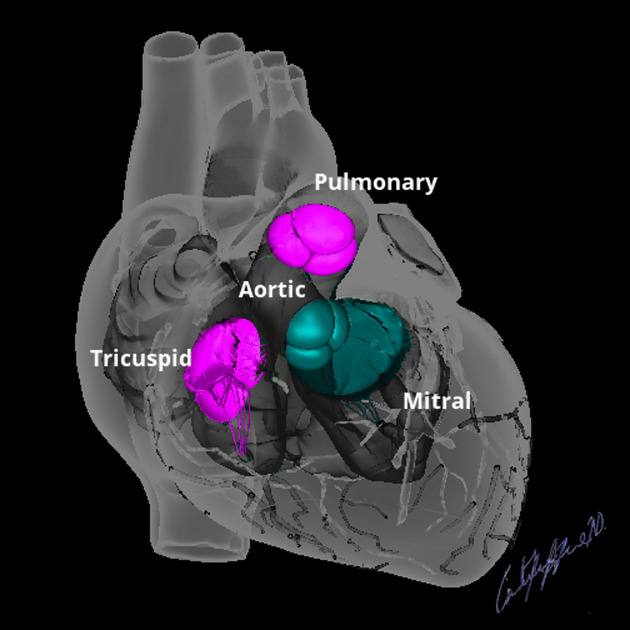
The four cardiac valves direct the flow of blood through the heart during the cardiac cycle.
Gross anatomy
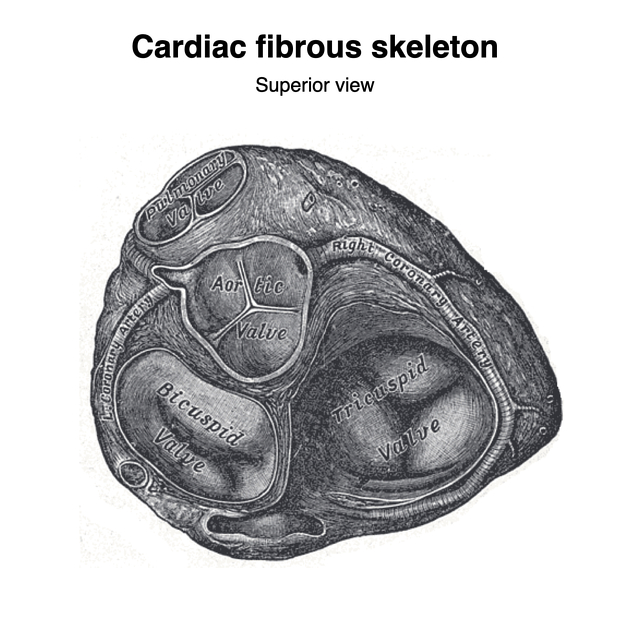
The heart valves are located in the cardiac fibrous skeleton:
- two are atrioventricular (AV) valves: the right-sided tricuspid valve (TV) and left-sided mitral (bicuspid) valve (MV)
- open during diastole to direct blood flow from the atria to the ventricles
- close during systole to prevent regurgitation back into the atria from the ventricles
- are attached to papillary muscles via chordae tendineae
- two are semilunar valves: the right-sided pulmonary valve (PV) and left-sided aortic valve (AV)
- open during systole to direct blood flow from the contracting ventricles through the right ventricle and left ventricle outflow tracts to the pulmonary trunk and ascending aorta, respectively
- close during diastole to prevent regurgitation back into the ventricles from the pulmonary trunk and ascending aorta
- these valves do not have chordae tendineae or papillary muscles
It is best to list the four valves in the order which blood travels through the heart:
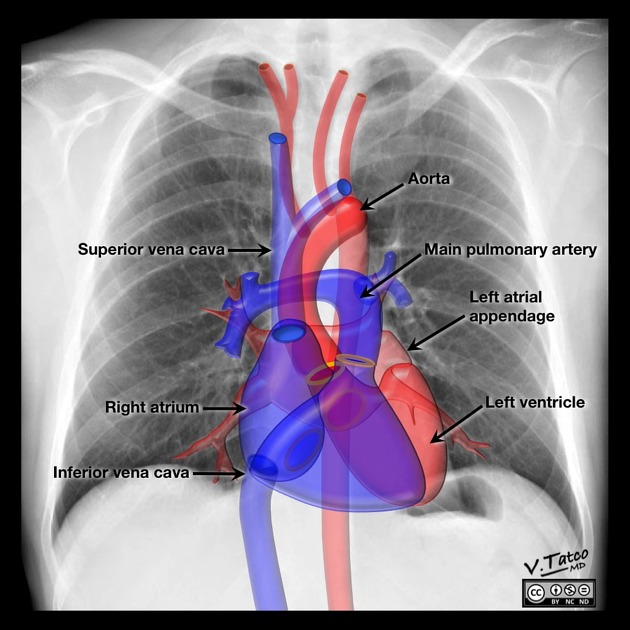
- venous blood returning from the body drains into the right atrium via the SVC, IVC and coronary sinus
- the right atrium pumps blood through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle
- the right ventricle pumps blood through the pulmonary semilunar valve into the pulmonary trunk to be oxygenated in the lungs
- blood returning from the lungs via the pulmonary veins drain into the left atrium via the four pulmonary veins
- the left atrium pumps blood through the bicuspid (mitral) valve into the left ventricle
- the left ventricle pumps blood through the aortic semilunar valve into the ascending aorta to supply the body
See also
References
- 1. Chen JJ, Manning MA, Frazier AA et-al. CT angiography of the cardiac valves: normal, diseased, and postoperative appearances. Radiographics. 2009;29 (5): 1393-412. Radiographics (full text) - doi:10.1148/rg.295095002 - Pubmed citation
- 2. Last's anatomy, regional and applied. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN:044304662X. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Butler P, Mitchell A, Healy JC. Applied Radiological Anatomy. Cambridge University Press. (2012) ISBN:0521766664. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Clinically oriented anatomy. LWW. ISBN:1451119453. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
Articles:
- Pulmonary valve
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (A)
- Atrioventricular septal defect
- Cardiac volumes and measurements
- Cardiac fibrous skeleton
- Mitral valve
- Development of the heart
- Valvular heart disease
- Infective endocarditis
- Point-of-care ultrasound (curriculum)
- Atrioventricular septum
- Regurgitant volume and regurgitant fraction
- Double inlet left ventricle
- Non-bacterial thrombotic endocarditis
- Lambl excrescence
- Echocardiography
- IgG4-related coronary disease
- Cardiac calcification
- Transthyretin amyloidosis
- Aortic valve
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton[+][+]
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax[+][+]
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera
- lower respiratory tract[+][+]
-
heart
- cardiac chambers[+][+]
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart[+][+]
- cardiac wall[+][+]
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus[+][+]
- thymus[+][+]
- breast[+][+]
- arterial supply of the thorax[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax[+][+]
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax[+][+]






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.