Hemiazygos vein
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yoshi Yu had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Yoshi Yu's current disclosures- Hemiazygous vein
- Hemi azygos vein
- Hemi azygous vein
- Hemiazygous veins
- Hemiazygos veins
The hemiazygos vein is the asymmetric counterpart to the azygos vein and forms part of the azygos venous system.
On this page:
Images:
Terminology
The spelling hemiazygous when referring to the vein is incorrect, regardless of whether British or American English is used 7. In the context of anatomy, hemiazygos vein is the sole correct spelling (see Terminologia Anatomica).
Gross anatomy
Origin
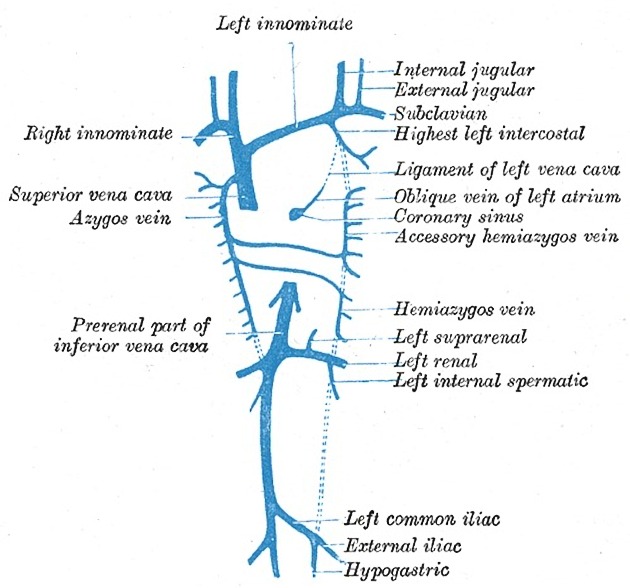
The hemiazygos vein is formed by the confluence of the left ascending lumbar and left subcostal veins.
Course
The hemiazygos vein enters the thorax either through the aortic hiatus or left diaphragmatic crus. It then courses superiorly to the left of the midline in the posterior mediastinum, adjacent to the thoracic vertebrae until the level of T8 or T9 vertebral bodies, where it crosses the midline anteriorly to the vertebral column to drain into the azygos vein.
Tributaries
left posterior 8th-11th intercostal veins
left superior phrenic vein
left renal vein (occasionally)
IVC (occasionally)
Variant anatomy
hemiazygos continuation of the IVC: often occurs with duplicated IVCs
interazygos vein: occurs when forming a common trunk with the accessory hemiazygos vein anterior to the aorta 6
superior continuation of the hemiazygos vein to join the brachiocephalic vein in the superior mediastinum
References
- 1. Demos T, Posniak H, Pierce K, Olson M, Muscato M. Venous Anomalies of the Thorax. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;182(5):1139-50. doi:10.2214/ajr.182.5.1821139 - Pubmed
- 2. Matthew A. Mauro, Kieran P. J. Murphy, Kenneth R. Thomson et al. Image-Guided Interventions. (2013) ISBN: 9781455705962 - Google Books
- 3. Jeffrey P. Kanne. Clinically Oriented Pulmonary Imaging. (2012) ISBN: 9781617795411 - Google Books
- 4. John J. Bergan, Nisha Bunke. The Vein Book. (2014) ISBN: 9780195399639 - Google Books
- 5. Michael Schünke, Erik Schulte, Udo Schumacher. Thieme Atlas of Anatomy. (2006) ISBN: 9783131420916 - Google Books
- 6. Blackmon J & Franco A. Normal Variants of the Accessory Hemiazygos Vein. Br J Radiol. 2011;84(1003):659-60. doi:10.1259/bjr/13695502 - Pubmed
- 7. Holemans J. Azygos, Not Azygous. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176(6):1602. doi:10.2214/ajr.176.6.1761602b - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Thoracic duct
- Intercostal spaces
- Descending aorta
- Lesser diaphragmatic apertures
- Accessory hemiazygos vein
- Diaphragm
- Posterior abdominal wall
- Esophagus
- Cardiac arrest
- Superior vena cava obstruction
- Azygos vein
- Azygos venous system
- Contrast agent pooling sign
- Absent azygos vein
- Left-sided superior vena cava
- Venous drainage of the thoracic wall
- Heart
- Ascending lumbar vein
- Retrocrural space
- Aortic hiatus
- Azygos continuation of inferior vena cava
- Truncal venous development (Gray's illustration)
- Hepatic hydatid cyst and Nutcracker phenomenon
- Azygos continuation of the inferior vena cava
- Pneumothorax with an azygos lobe
- Azygos and hemiazygos veins
- Azygos venous system anatomy (CT pulmonary angiography)
- Double IVC with azygos and hemiazygos continuation
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton[+][+]
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax[+][+]
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera[+][+]
- lower respiratory tract
-
heart
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart
- cardiac wall
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus
- thymus
- breast
- arterial supply of the thorax[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)[+][+]
-
coronary veins[+][+]
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax[+][+]





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.