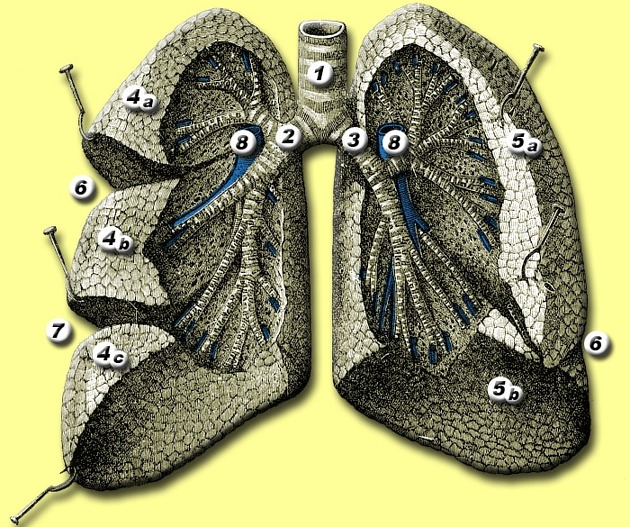
Oblique fissure
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Jack Ren had no recorded disclosures.
View Jack Ren's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Ashesh Ishwarlal Ranchod had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Ashesh Ishwarlal Ranchod's current disclosures- Major fissure
- Greater fissure
The oblique fissures (also called the major fissures or greater fissures) are bilateral structures in both lungs separating the lung lobes.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Right oblique fissure
The superior part of the right oblique fissure separates the right upper lobe from the right lower lobe and the inferior part separates the right middle lobe from the right lower lobe.
Its approximate position can be marked by a curved line on the thoracic wall that begins roughly at the spinous process of the T4 level of the thoracic spine, then crosses the fifth intercostal space laterally, and follows the contour of the right 6th rib anteriorly 1.
Left oblique fissure
The left oblique fissure separates the left upper lobe from the left lower lobe.
Its approximate position can be marked by a curved line on the thoracic wall that begins between the spinous processes of vertebrae T3 and T4, then crosses the fifth intercostal space laterally, and follows the contour of the 6th rib anteriorly 1.
Variant anatomy
The oblique fissures are highly variable and may be incomplete or absent, thus complicating the identification of various pathological processes. In the majority of cases the left oblique fissure is located at a higher level and courses more vertically than the right oblique fissure 2.
Both oblique fissures can present as incomplete fissures (48% on the right compared with 43% on the left). Absence of the oblique fissure is rare and occurs in <1% of the population 2.
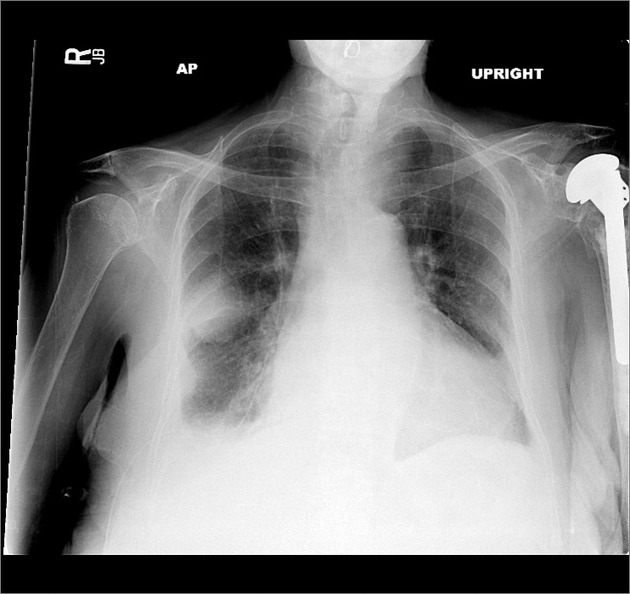
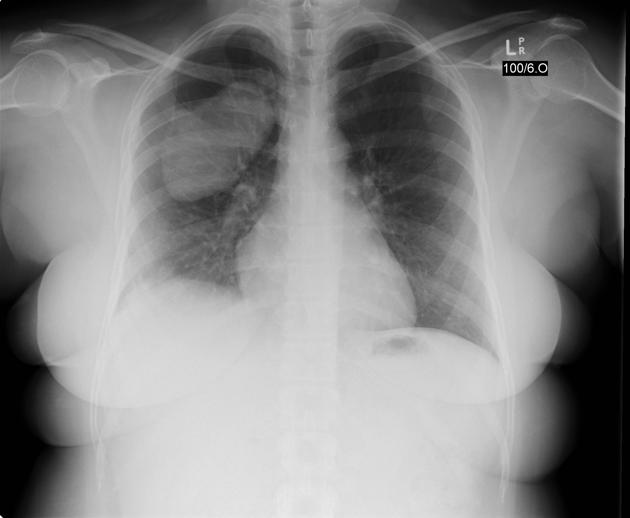
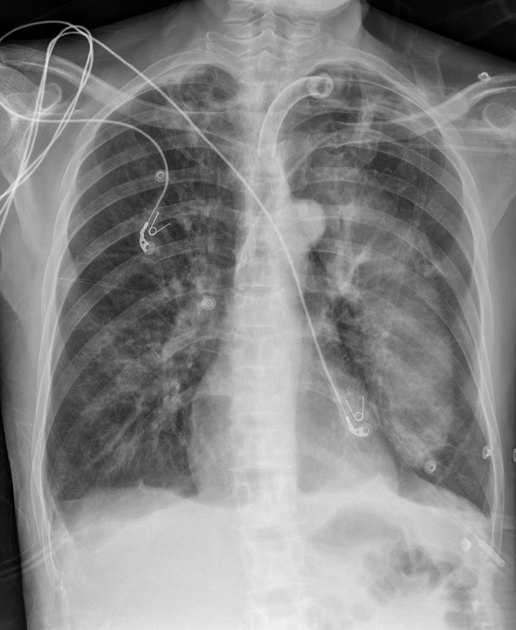
Radiographic features
The oblique fissures can be visualized on both conventional radiography and computed tomography (CT) scans. For transthoracic biopsies, especially those for lesions located in the upper lobes, knowledge of the exact anatomy of the oblique fissures is essential to avoid crossing the oblique fissures.
On a lateral radiograph, the right oblique fissure ends at the anterior costophrenic angle and the left oblique fissure ends about 5 cm posterior to the anterior costophrenic angle 3.
Occasionally the superior aspect of the left major fissure may mimic pneumomediastinum, so called pseudopneumomediastinum.
References
- 1. Gray's Anatomy for Students: With STUDENT CONSULT Online Access, 3e. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN:0702051314. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Gülsün M, Ariyürek OM, Cömert RB et-al. Variability of the pulmonary oblique fissures presented by high-resolution computed tomography. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006;28 (3): 293-9. doi:10.1007/s00276-006-0079-y - Pubmed citation
- 3. MCAR(Hon) MD DSMDFRCPFRCRDMRD, FRCR RRMDFRCP, FRCP JMMBBSMRCP. Textbook of Radiology and Imaging. Churchill Livingstone. (2003) ISBN:0443071098. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
- Right lower lobe consolidation
- Pleura
- Left lower lobe superior segment
- Right lower lobe
- Left upper lobe anterior segment
- Right lower lobe collapse
- Left lower lobe
- Lung fissures
- Left upper lobe consolidation
- Right upper lobe consolidation
- Right lung
- Pseudopneumomediastinum
- Horizontal fissure
- Lung
- Pneumonia (summary)
- Right middle lobe
- Chest radiograph assessment using ABCDEFGHI
- Left lung
- Right middle lobe consolidation
- Right upper lobe
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton[+][+]
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax[+][+]
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera
-
lower respiratory tract
- tracheobronchial tree[+][+]
-
lungs
-
bronchopulmonary segmental anatomy (Boyden Classification) (mnemonic)[+][+]
- left lung
- right lung
- variant anatomy
- lung parenchyma[+][+]
- hilum[+][+]
- pleura
-
bronchopulmonary segmental anatomy (Boyden Classification) (mnemonic)[+][+]
-
heart[+][+]
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart
- cardiac wall
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus[+][+]
- thymus[+][+]
- breast[+][+]
-
lower respiratory tract
- arterial supply of the thorax[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax[+][+]
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax[+][+]
Related articles: Chest
- imaging techniques
-
chest radiograph
- radiography[+][+]
-
approach
- ABCDE
- ABCDEFGHI
- congenital heart disease
- medical devices in the thorax
- common lines and tubes[+][+]
- nasogastric tubes
- endotracheal tubes
- central venous catheters
- esophageal temperature probe
- tracheostomy tube
- pleural catheters
- cardiac conduction devices
- prosthetic heart valve
- review areas
-
airspace opacification[+][+]
- differential diagnoses of airspace opacification
- lobar consolidation
-
atelectasis
- mechanism-based
- morphology-based
- lobar lung collapse
- chest x-ray in the exam setting[+][+]
- cardiomediastinal contour[+][+]
- chest radiograph zones[+][+]
- tracheal air column[+][+]
- fissures
- normal chest x-ray appearance of the diaphragm[+][+]
- nipple shadow[+][+]
-
lines and stripes[+][+]
- anterior junction line
- posterior junction line
- right paratracheal stripe
- left paratracheal stripe
- posterior tracheal stripe/tracheo-esophageal stripe
- posterior wall of bronchus intermedius
- right paraspinal line
- left paraspinal line
- aortic-pulmonary stripe
- aortopulmonary window
- azygo-esophageal recess
- spaces[+][+]
- signs[+][+]
- air bronchogram
- big rib sign
- Chang sign
- Chen sign
- coin lesion
- continuous diaphragm sign
- dense hilum sign
- double contour sign
- egg-on-a-string sign
- extrapleural sign
- finger in glove sign
- flat waist sign
- Fleischner sign
- ginkgo leaf sign
- Golden S sign
- Hampton hump
- haystack sign
- hilum convergence sign
- hilum overlay sign
- Hoffman-Rigler sign
- holly leaf sign
- incomplete border sign
- juxtaphrenic peak sign
- Kirklin sign
- medial stripe sign
- melting ice cube sign
- more black sign
- Naclerio V sign
- Palla sign
- pericardial fat tag sign
- Shmoo sign
- silhouette sign
- snowman sign
- spinnaker sign
- steeple sign
- straight left heart border sign
- third mogul sign
- tram-track sign
- walking man sign
- water bottle sign
- wave sign
- Westermark sign
- HRCT[+][+]
-
chest radiograph
- airways[+][+]
- bronchitis
- small airways disease
-
bronchiectasis
- broncho-arterial ratio
- related conditions
- differentials by distribution
- narrowing
-
tracheal stenosis
- diffuse tracheal narrowing (differential)
-
bronchial stenosis
- diffuse airway narrowing (differential)
-
tracheal stenosis
- diverticula
- pulmonary edema[+][+]
-
interstitial lung disease (ILD)[+][+]
- Anti-Jo-1 antibody-positive interstitial lung disease
- drug-induced interstitial lung disease
-
hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- subacute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- etiology
- bird fancier's lung: pigeon fancier's lung
- farmer's lung
- cheese workers' lung
- bagassosis
- mushroom worker’s lung
- malt worker’s lung
- maple bark disease
- hot tub lung
- wine maker’s lung
- woodsman’s disease
- thatched roof lung
- tobacco grower’s lung
- potato riddler’s lung
- summer-type pneumonitis
- dry rot lung
- machine operator’s lung
- humidifier lung
- shower curtain disease
- furrier’s lung
- miller’s lung
- lycoperdonosis
- saxophone lung
-
idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (mnemonic)
- acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP)
- cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP)
- desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP)
- non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
- idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis
- lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
- respiratory bronchiolitis–associated interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD)
- usual interstitial pneumonia / idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (UIP/IPF)
-
pneumoconioses
- fibrotic
- non-fibrotic
-
lung cancer[+][+]
-
non-small-cell lung cancer
-
adenocarcinoma
- pre-invasive tumors
- minimally invasive tumors
- invasive tumors
- variants of invasive carcinoma
- described imaging features
- adenosquamous carcinoma
- large cell carcinoma
- primary sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung
- squamous cell carcinoma
- salivary gland-type tumors
-
adenocarcinoma
- pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors
- preinvasive lesions
-
lung cancer invasion patterns
- tumor spread through air spaces (STAS)
- presence of non-lepidic patterns such as acinar, papillary, solid, or micropapillary
- myofibroblastic stroma associated with invasive tumor cells
- pleural invasion
- vascular invasion
- tumors by location
- benign neoplasms
- pulmonary metastases
- lung cancer screening
- lung cancer staging
-
non-small-cell lung cancer




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.