Diagonal branches of the left anterior descending artery
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Matt A. Morgan had no recorded disclosures.
View Matt A. Morgan's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures- Diagonal branch - LAD
- Diagonal branches - LAD
- Diagonal branches
- Diagonal arteries of the heart
- LAD diagonal branches
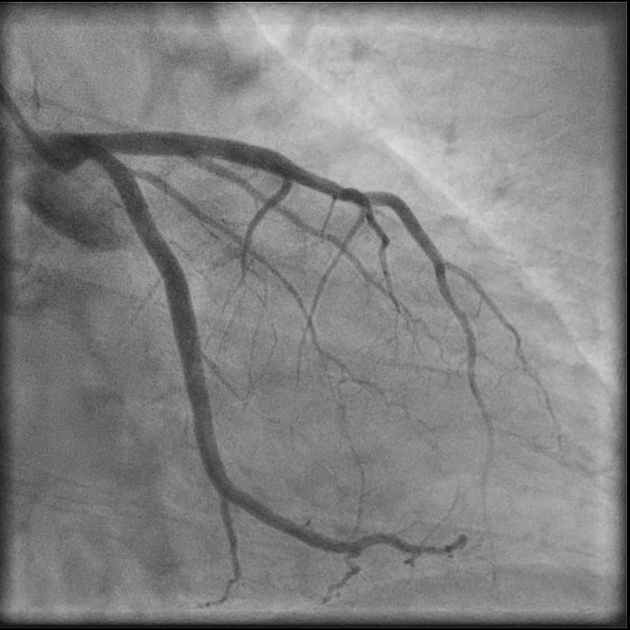
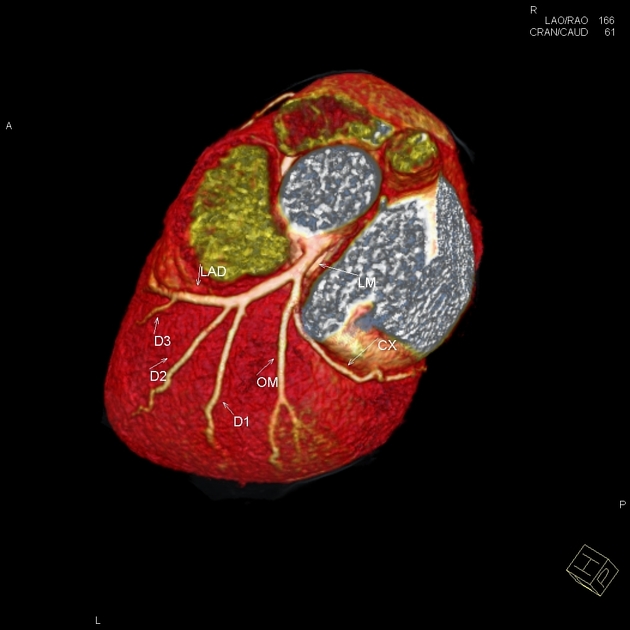
Diagonal branches of the left anterior descending coronary artery supply blood flow to the anterior and anterolateral walls of the left ventricle. There are usually denoted as D1, D2, D3, etc.
There are termed "diagonal" due to them branching from their parent vessel at acute angles. They extend over the left ventricle in a diagonal fashion toward the acute margin and the cardiac apex. They often run parallel to one another and are variable in number (often 2 to 9). If a ramus intermedius artery is present, the diagonal arteries are less prominent and arise more distally. The first diagonal (D1) branch tends to be the most prominent. When the first diagonal is large, the other diagonal vessels tend to be small and run a shorter course.
References
- 1. Halpern EJ. Clinical Cardiac CT. Thieme. ISBN:1604063750. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. O'Brien JP, Srichai MB, Hecht EM, Kim DC, Jacobs JE. Anatomy of the heart at multidetector CT: what the radiologist needs to know. (2007) Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 27 (6): 1569-82. doi:10.1148/rg.276065747 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton[+][+]
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax[+][+]
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera[+][+]
- lower respiratory tract
-
heart
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart
- cardiac wall
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus
- thymus
- breast
- arterial supply of the thorax
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)[+][+]
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)[+][+]
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch[+][+]
- aortic isthmus[+][+]
- descending aorta[+][+]
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax[+][+]
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax[+][+]




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.