Pulmonary valve
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures- Pulmonary semilunar valve
- Pulmonic valve
- Pulmonary valve (PV)
- Pulmonary valves (PVs)
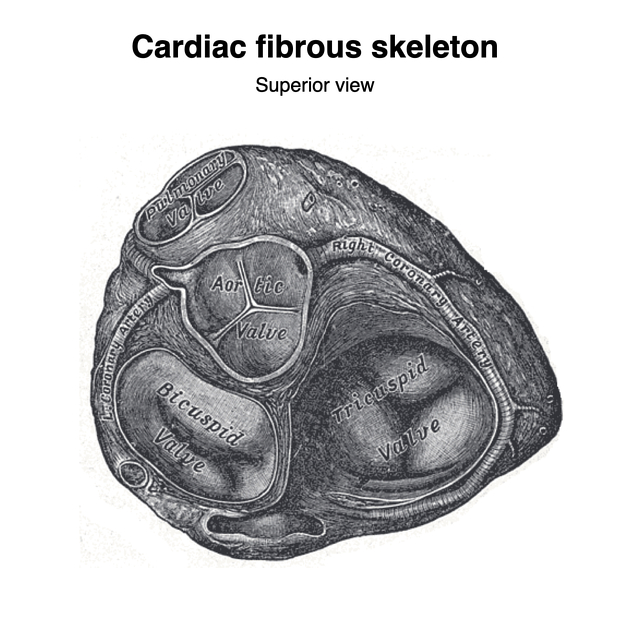
The pulmonary valve or pulmonic valve (PV) is one of the four cardiac valves. It is the semilunar valve that allows blood to exit the right ventricle (RV). It opens during systole and closes during diastole.
The valve has anterior, left and right cusps, the bases of which attach around the valve orifice to a fibrous ring or annulus, forming part of the fibrous skeleton of the heart. The cusps attach to each other and the annulus at the commissures. The free edge of each cusp (lunule) is thickened where it contacts the free edges of adjacent cusps and at the angulated apex of each free edge there is further nodular thickening, known as the nodule. The cusps bulge inferiorly into the outflow tract of the right ventricle.
Immediately superior to the cusps, the pulmonary trunk is mildly dilated forming the pulmonary sinuses, the spaces between the dilated wall of the pulmonary trunk and the cusps of the semilunar valve. During systole these sinuses prevent the cusps from flattening against the walls of the sinuses, which may restrict valve closure during diastole. The pulmonary valve lies horizontally and is superior and to the left of the aortic valve (AV).
The relationship of the aortic valve to the pulmonary valve can be recalled by the mnemonic: PALS: P = pulmonary valve, A = anterior, L = lateral, S = superior. The pulmonary valve is anterior, lateral and superior to the aortic valve.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Related pathology
References
- 1. Butler P, Mitchell A, Healy JC. Applied Radiological Anatomy. Cambridge University Press. (2012) ISBN:0521766664. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Clinically oriented anatomy. LWW. ISBN:1451119453. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Last's anatomy, regional and applied. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN:044304662X. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. William Herring. Learning Radiology. (2015) ISBN: 9780323328074
- 5. Farhood Saremi, Atul Gera, S. Yen Ho, Ziyad M. Hijazi, Damián Sánchez-Quintana. CT and MR Imaging of the Pulmonary Valve. (2014) RadioGraphics. 34 (1): 51-71. doi:10.1148/rg.341135026 - Pubmed
- 6. Pignatelli RH, Noel C, Reddy SCB. Imaging of the pulmonary valve in the adults. (2017) Current opinion in cardiology. 32 (5): 529-540. doi:10.1097/HCO.0000000000000436 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Right ventricular outflow tract
- Pulmonary valve regurgitation
- Cardiac valves
- Pulmonary trunk
- Right ventricle
- Passive hepatic congestion
- Rastelli procedure
- Total repair of tetralogy of Fallot
- Pulmonary valve calcification
- Heart chambers
- Carcinoid heart disease
- Hypoplastic right heart syndrome
- Transposition of the great arteries
- Cardiac curriculum
- Pulmonary valve stenosis
- Heart
- Anomalous origin of one pulmonary artery
- Cardiac dyssynchrony
- Congenital pulmonary stenosis
- Aortic valve
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton[+][+]
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax[+][+]
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera
- lower respiratory tract[+][+]
-
heart
- cardiac chambers[+][+]
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart[+][+]
- cardiac wall[+][+]
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus[+][+]
- thymus[+][+]
- breast[+][+]
- arterial supply of the thorax[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax[+][+]
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax[+][+]





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.