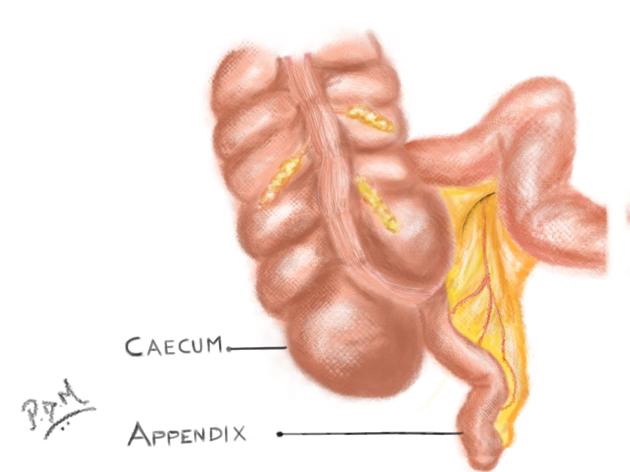
Duplex appendix
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Aditya Shetty had no recorded disclosures.
View Aditya Shetty's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Henry Knipe had the following disclosures:
- Micro-X Ltd, Shareholder (past)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures- Double appendix
- Duplication of appendix
- Duplicated appendix
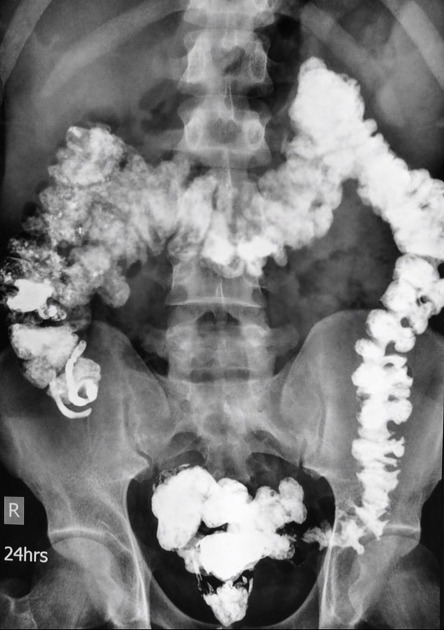
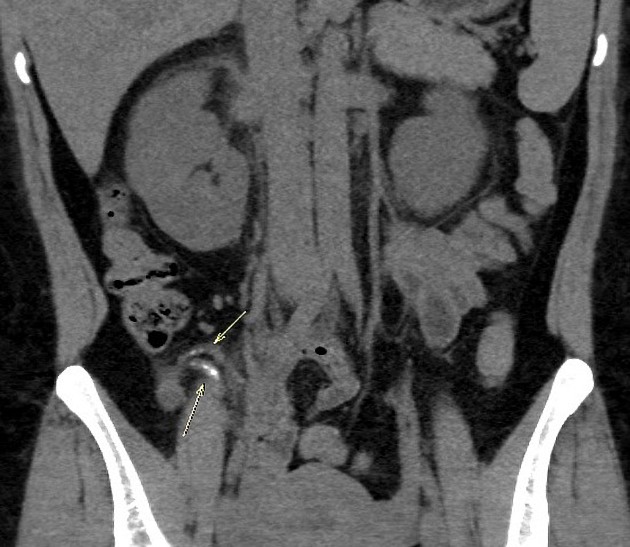
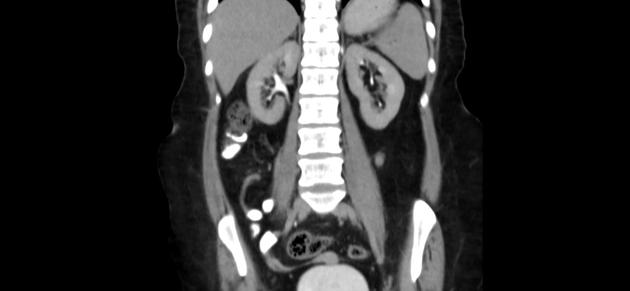
Duplex appendix is a rare anomaly of the appendix and is usually discovered incidentally during surgery for appendicitis.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Duplication of the vermiform appendix is extremely rare. It is found in only 1 in 25,000 patients (incidence ~0.004%) operated on for acute appendicitis. Although duplication anomalies are uncommon, they have clinical and medicolegal significance.
A case is also reported in which a child had two appendicectomies performed in a 5 month period.
Associations
When anomalies of the appendix are detected in childhood they are nearly always associated with severe intestinal, genitourinary or bony malformations, seen most often in conjunction with type B1 and C duplications.
Pathology
Classification
This classification was proposed by Wallbridge in 1963, and at the time of writing (July 2016) remains the most widely accepted classification.
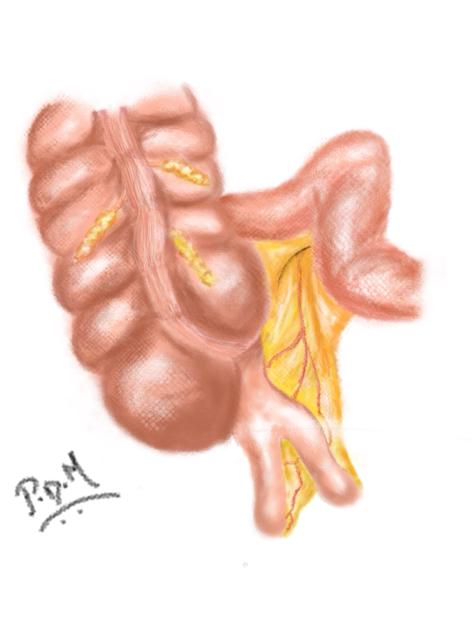
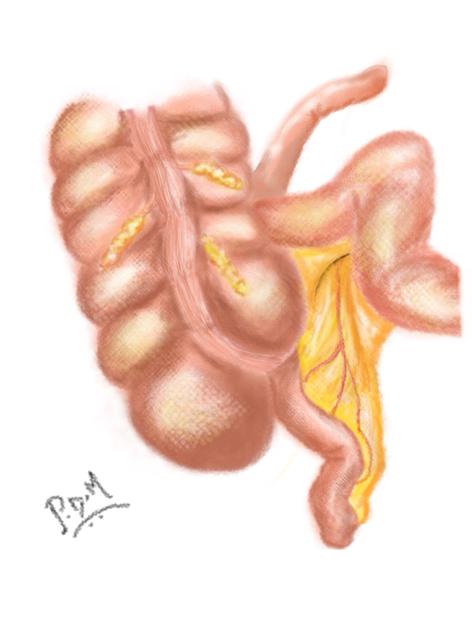
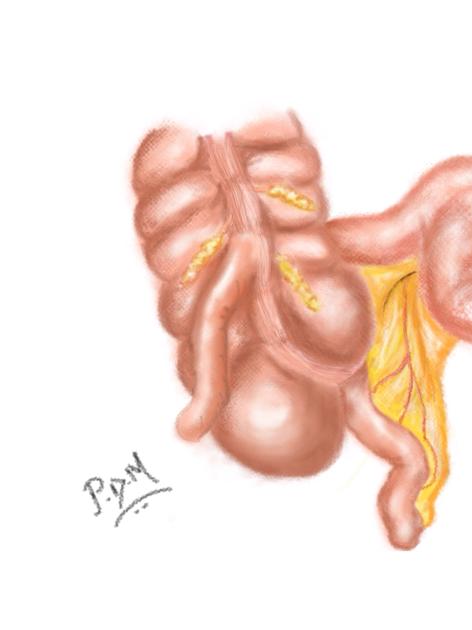
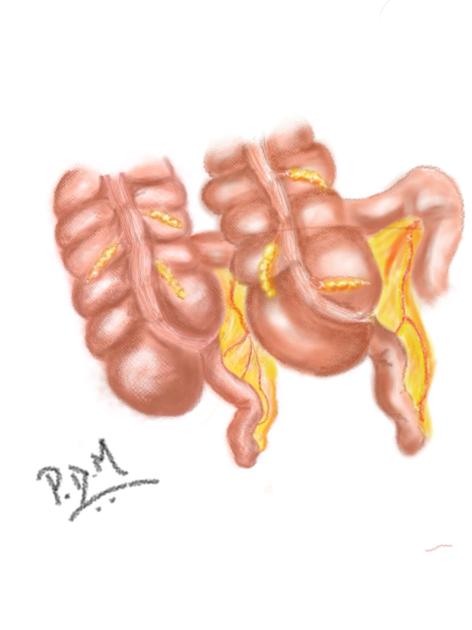
The Cave-Wallbridge classification divides appendix duplications into three types:
type A: single caecum with one normally localised appendix exhibiting partial duplication
-
type B: single caecum with two completely separate appendices and divided into two further subgroups
type B1 (‘bird-like type’): two appendices located symmetrically on either side of the ileocaecal valve, resembling the normal arrangement in birds
type B2 (‘taenia coli’ type): one appendix arises from the caecum at the usual site, and the second branches at varying distances along the lines of the taenia from the first
type C: double caecum, each bearing its own appendix
Some authors have since described further types of complex multiplicity of the appendix. For example, "horseshoe appendix", "duplicated appendix and caecum"6, and "triple appendix" but these are often only diagnosed at surgery and not with imaging.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Differential diagnosis
Possibilities to consider include:
References
- 1. Heetun M, Stavrinides V, Keeler B, Phillips D, Taylor A. A Tale of Two Appendices - an Unexpected Finding. S Afr J Surg. 2013;51(1):32-3. doi:10.7196/sajs.1217 - Pubmed
- 2. Christodoulidis G, Symeonidis D, Spyridakis M et al. Acute Appendicitis in a Duplicated Appendix. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2012;3(11):559-62. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2012.08.004 - Pubmed
- 3. Robertson D. Appendix Vermiformis Duplex. Can Med Assoc J. 1940;43(2):159-61. PMC538091 - Pubmed
- 4. Sobhian B, Mostegel M, Kunc C, Karner J. [Appendix Vermiformis Duplex--A Rare Surprise]. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2005;117(13-14):492-4. doi:10.1007/s00508-005-0390-3 - Pubmed
- 5. Peddu P & Sidhu P. Appearance of a Type B Duplex Appendix on Barium Enema. Br J Radiol. 2004;77(915):248-9. doi:10.1259/bjr/65763747 - Pubmed
- 6. Kim E & McClenathan J. Unusual Duplication of Appendix and Cecum: Extension of the Cave-Wallbridge Classification. J Pediatr Surg. 2001;36(9):E18. doi:10.1053/jpsu.2001.26400 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen[+][+]
- hepatobiliary system[+][+]
-
endocrine system[+][+]
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system[+][+]
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system[+][+]
-
female reproductive system[+][+]
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- coeliac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics[+][+]
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis[+][+]
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.