Epididymis
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Praveen Jha had no recorded disclosures.
View Praveen Jha's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Craig Hacking had the following disclosures:
- Philips Australia, Paid speaker at Philips Spectral CT events (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosures- Epididymides
- Globus major
- Globus minor
The epididymis (plural: epididymides) is situated adjacent to the testis within the scrotal sac. Its primary function is the collection, maturation and transport of sperm via the ductus deferens.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
The epididymis is an elongated structure, posterolateral to the testis. It can be subdivided into three anatomic regions: head (also known as globus major), body and tail (also known as globus minor).
The total length of the epididymis is usually 6-7 cm but it is tightly coiled and would measure 6 m if uncoiled 3.
The head is the largest and most prominent part and is found at the superior pole of the testis. The head of the epididymis measures approximately 5-12 mm in length and may have a small projection called the appendix of the epididymis 3. The tail of the epididymis is found at the inferior pole of the testis 3.
Seminiferous tubules carry sperm via tubuli recti into a dilated space within the mediastinum testes known as the rete testis. The rete testis drains into the epididymis through 10-15 efferent ductules 1. Efferent ducts in the head of the epididymis unite to form a single duct in the body and tail region (globus minor), which continues as the ductus deferens.
Arterial supply
The deferential artery (a branch of superior vesical artery or sometimes inferior vesical artery), a branch of the testicular artery (a branch off the aorta), and branches of the cremasteric artery (branch off the inferior epigastric artery) form anastomoses to supply the epididymis 5.
Some sources state that the epididymis is supplied only by branches of the testicular artery 5.
Variant anatomy
Radiographic features
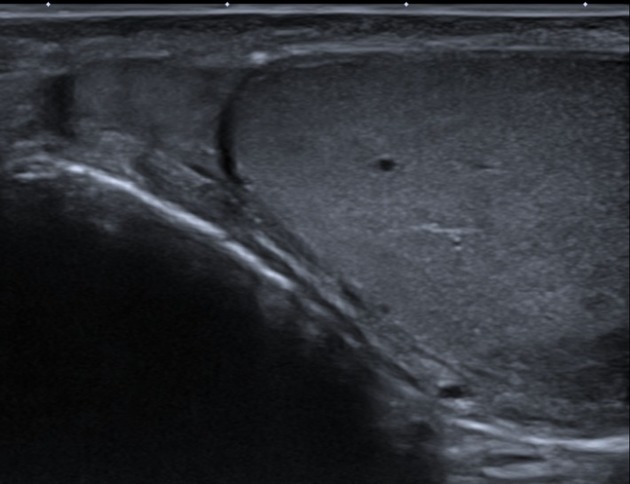
Ultrasound
See article: Testicular and scrotal ultrasound
The normal epididymis is iso-to-hyperechoic to the testes, with equal or less vascularity on color and spectral Doppler. The head of the epididymis is visualized superior and lateral to the testes, while the body and the tail are smaller with variable locations 2.
MRI
T1: epididymis has homogenously intermediate signal
T2: epididymis has hyperintense signal, with slightly lower signal than testes
History and etymology
"Epididymis" derives from the Greek έπιδιδυμίς (έπί "upon" + δίδυμος "testis"). Δίδυμοι (meaning "twins") was an older term for both testes and ovaries. Galen originally used the term to refer to what we now call the tunica, and used the term "parastates" ("standing beside") for what we call the epididymis. Herophilos may have been the first to use it in the current sense.
Related pathology
References
- 1. Dogra V, Gottlieb R, Oka M, Rubens D. Sonography of the Scrotum. Radiology. 2003;227(1):18-36. doi:10.1148/radiol.2271001744 - Pubmed
- 2. Kim W, Rosen MA, Langer JE et-al. US MR imaging correlation in pathologic conditions of the scrotum. Radiographics. 27 (5): 1239-53. doi:10.1148/rg.275065172 - Pubmed citationpubmed/12616012">Pubmed citation
- 3. Paul Butler, Adam Mitchell, Jeremiah C. Healy et al. Applied Radiological Anatomy. (2012) ISBN: 9780521766661 - Google Books
- 4. Origin of Medical Terms. (1961) ISBN: 0028523903 - Google Books
- 5. Chummy S. Sinnatamby. Last's Anatomy. (2011) ISBN: 9780702033957 - Google Books
Incoming Links
- Agenesis of the ductus deferens
- Scrotal tuberculosis
- Spermatocele
- Epididymitis
- Scrotolith
- Testicular appendix
- Orchitis
- Testicular torsion
- Dancing megasperm
- Sperm cell granuloma
- Torsion of the appendix testis
- Chronic epididymitis
- Testes
- Pampiniform plexus
- Papillary cystadenoma of the epididymis
- Tubular ectasia of the epididymis
- Synonyms
- Acute idiopathic scrotal edema
- Common medical misspellings
- Spermatic cord
- Polyorchidism
- Testicular torsion and infarction
- Seminoma
- Scrotal haematocele
- Nutcracker syndrome
- Epididymo-orchitis - acute
- Dancing megasperm
- Whirlpool sign (testicular torsion)
- Epididymitis leading to testicular infarction
- Testes and epididymis (Gray's illustration)
- Testes and spermatic cord (Gray's illustration)
- Bilateral funiculocele
- Testicular multifocal seminoma
- Epididymal abscesses
- Normal testis and epididymis (ultrasound)
- Testicular nonseminomatous mixed germ cell tumor
- Testis cross section
- Torsion of the appendix epididymis
- Metastatic yolk sac tumour, tumour thrombus in left atrium
- Epididymitis
Related articles: Anatomy: Abdominopelvic
- skeleton of the abdomen and pelvis
- muscles of the abdomen and pelvis
- spaces of the abdomen and pelvis
- anterior abdominal wall
- posterior abdominal wall
- abdominal cavity
- pelvic cavity
- perineum
- abdominal and pelvic viscera
- gastrointestinal tract
- spleen
- hepatobiliary system
-
endocrine system
-
adrenal gland
- adrenal vessels
- chromaffin cells
- variants
- pancreas
- organs of Zuckerkandl
-
adrenal gland
-
urinary system
-
kidney
- renal pelvis
- renal sinus
- avascular plane of Brodel
-
variants
- number
- fusion
- location
- shape
- ureter
- urinary bladder
- urethra
- embryology
-
kidney
- male reproductive system
-
female reproductive system
- vulva
- vagina
- uterus
- adnexa
- Fallopian tubes
- ovaries
- broad ligament (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- embryology
- blood supply of the abdomen and pelvis
- arteries
-
abdominal aorta
- inferior phrenic artery
- celiac artery
- superior mesenteric artery
- middle suprarenal artery
- renal artery (variant anatomy)
- gonadal artery (ovarian artery | testicular artery)
- inferior mesenteric artery
- lumbar arteries
- median sacral artery
-
common iliac artery
- external iliac artery
-
internal iliac artery (mnemonic)
- anterior division
- umbilical artery
- superior vesical artery
- obturator artery
- vaginal artery
- inferior vesical artery
- uterine artery
- middle rectal artery
-
internal pudendal artery
- inferior rectal artery
-
perineal artery
- posterior scrotal artery
- transverse perineal artery
- artery to the bulb
- deep artery of the penis/clitoris
- dorsal artery of the penis/clitoris
- inferior gluteal artery
- posterior division (mnemonic)
- variant anatomy
- anterior division
-
abdominal aorta
- portal venous system
- veins
- anastomoses
- arterioarterial anastomoses
- portal-systemic venous collateral pathways
- watershed areas
- arteries
- lymphatics
- innervation of the abdomen and pelvis
- thoracic splanchnic nerves
- lumbar plexus
-
sacral plexus
- lumbosacral trunk
- sciatic nerve
- superior gluteal nerve
- inferior gluteal nerve
- nerve to piriformis
- perforating cutaneous nerve
- posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
- parasympathetic pelvic splanchnic nerves
- pudendal nerve
- nerve to quadratus femoris and inferior gemellus muscles
- nerve to internal obturator and superior gemellus muscles
- autonomic ganglia and plexuses
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta previa
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumors
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumors of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumors
- mixed germ cell tumor
- yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumor
- sex cord / stromal tumors of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumor of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumors (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumors
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.