Sternalis muscle
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created The Radswiki had no recorded disclosures.
View The Radswiki's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Mohammad Taghi Niknejad had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Mohammad Taghi Niknejad's current disclosures- Sternalis
- Sternalis muscles
- Parasternalis muscle
- Rectus sternalis muscle
- Musculus sternalis
- Parasternalis muscles
- Rectus sternalis muscles
The sternalis muscle (TA: musculus sternalis 8), also known as rectus sternalis or parasternalis 7, is an uncommon chest wall accessory muscle and is of uncertain etiology and function. Its importance lies in that it should not be mistaken for a pathological lesion.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Cadaveric studies have shown that the muscle is present in ~5% (range 1-8%) of both males and females and is twice as often unilateral as bilateral.
Gross anatomy
The sternalis muscle runs from the jugular notch of the manubrium superiorly, to approximately the caudal (inferior) aspect of the sternum. It is found adjacent to the medial edge of pectoralis major.
Radiographic features
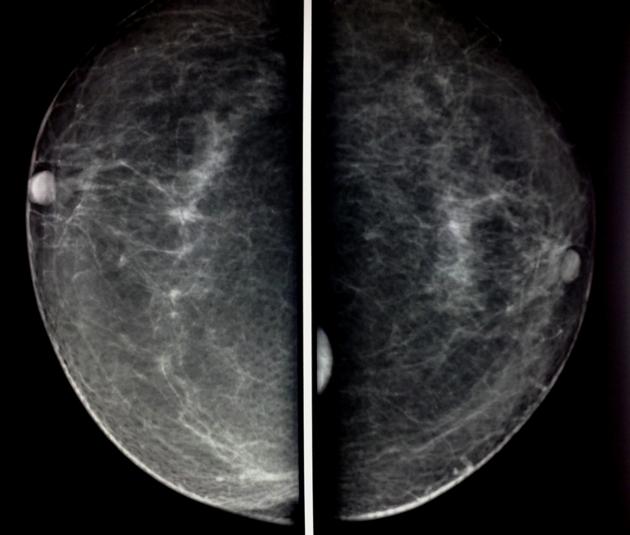
Mammography
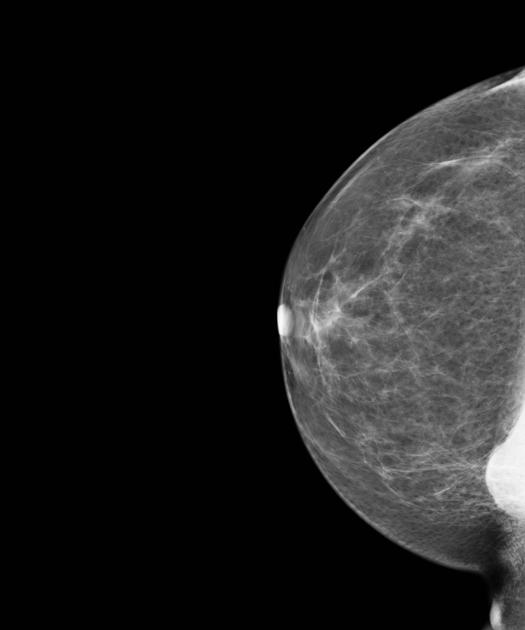
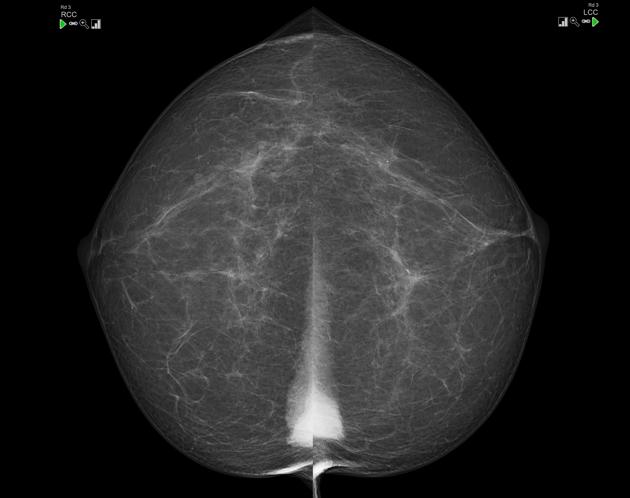
The mammographic appearance of the sternalis muscle is variable. Typically it is visible in the medial aspect of the breast on the craniocaudal mammogram and appears as a small soft tissue density/mass abutting the chest wall. Its margins and shape are variable (can range from flame shaped to an irregularly rounded density) 3. The muscle is usually not seen on the standard MLO or ML views. It typically measures 1-2 cm in maximum dimension.
As long as the radiologist is aware of the entity, there is usually little confusion. Ultrasound or CT or even MRI may be obtained for confirmation when the diagnosis is uncertain.
The sternalis muscle should be considered in the differential diagnosis if a posteromedial mass is noted on the CC view 2.
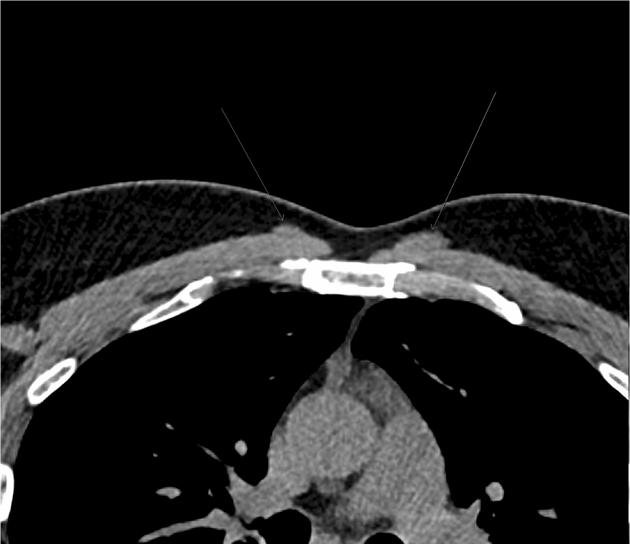
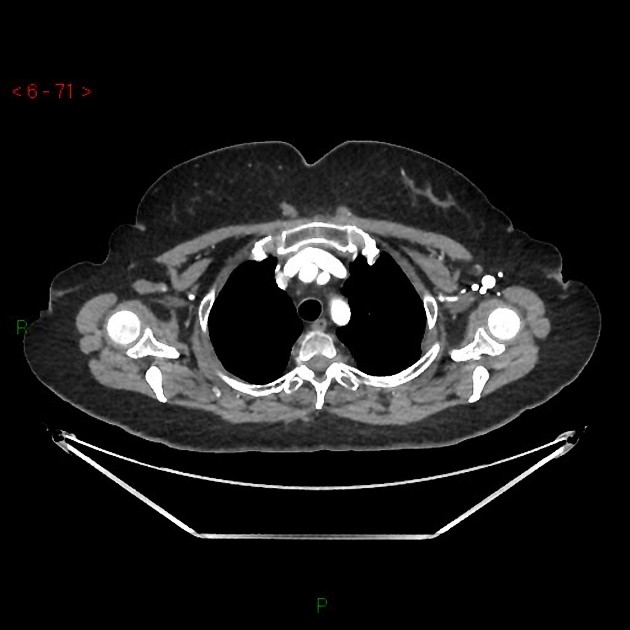
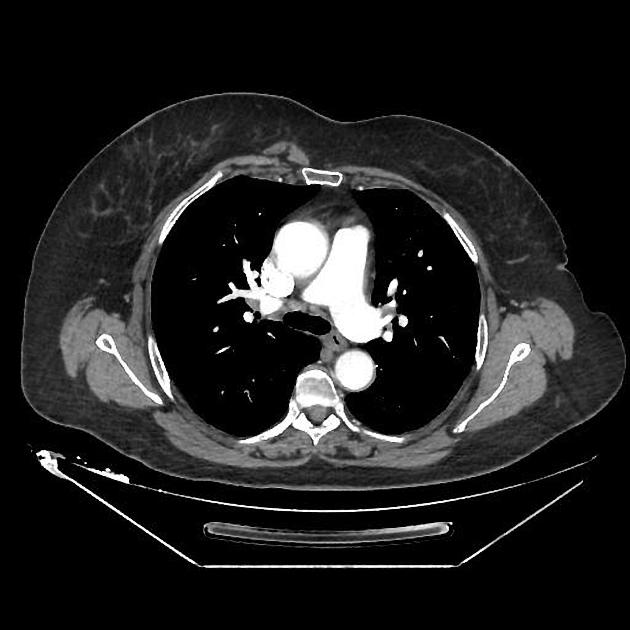
CT
- appears as a flat parasternal muscle, longitudinal in orientation 6
Additional work up
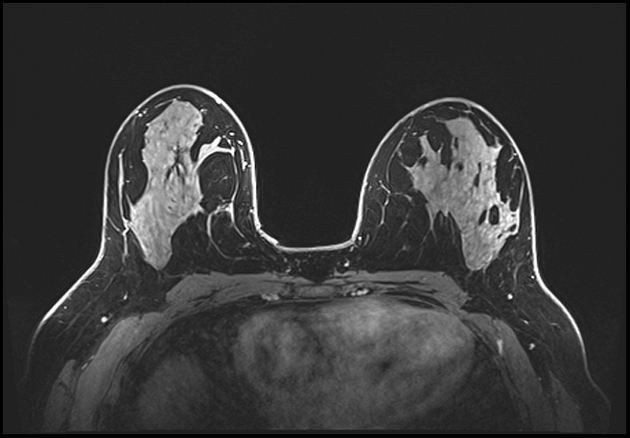
In occasional situations, a "cleavage/valley view" may help to confirm bilaterality.
References
- 1. Bradley F, Hoover H, Hulka C et al. The Sternalis Muscle: An Unusual Normal Finding Seen on Mammography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;166(1):33-6. doi:10.2214/ajr.166.1.8571900 - Pubmed
- 2. Thomas Lee Pope. Aunt Minnie's Atlas and Imaging-Specific Diagnosis. (2003) ISBN: 9780781741606 - Google Books
- 3. Emily F. Conant, Cecilia M. Brennecke. Breast Imaging. (2006) ISBN: 9780323017466 - Google Books
- 4. Ellen Shaw De Paredes. Atlas of Mammography. (2007) ISBN: 9780781764339 - Google Books
- 5. Jeng H & Su S. The Sternalis Muscle: An Uncommon Anatomical Variant Among Taiwanese. J Anat. 1998;193 ( Pt 2)(2):287-8. doi:10.1046/j.1469-7580.1998.19320287.x - Pubmed
- 6. Young Lee B, Young Byun J, Hee Kim H et al. The Sternalis Muscles: Incidence and Imaging Findings on MDCT. J Thorac Imaging. 2006;21(3):179-83. doi:10.1097/01.rti.0000208287.04490.db - Pubmed
- 7. Raikos A, Paraskevas G, Tzika M et al. Sternalis Muscle: An Underestimated Anterior Chest Wall Anatomical Variant. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;6(1):73. doi:10.1186/1749-8090-6-73 - Pubmed
- 8. FIPAT. Terminologia Anatomica. 2nd Ed. FIPAT.library.dal.ca. Federative International Programme for Anatomical Terminology, 2019. https://fipat.library.dal.ca/TA2/
Incoming Links
- Sternalis muscle
- Sternalis muscle
- Normal breast MRI (dense breasts)
- Sternalis muscle
- Sternalis muscle and right intramuscular lipoma of subscapularis muscle
- Sternalis muscle and right intramuscular lipoma of subscapularis muscle
- Sternalis muscle and right intramuscular lipoma of subscapularis muscle
- Sternalis muscle
- Bilateral sternalis muscle at mammography
- Sternalis muscle
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton[+][+]
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax
- diaphragm[+][+]
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles[+][+]
- variant anatomy
- sternalis muscle
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera[+][+]
- lower respiratory tract
-
heart
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart
- cardiac wall
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus
- thymus
- breast
- arterial supply of the thorax[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax[+][+]
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax[+][+]




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.