Centrilobular lung nodules
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Raymond Chieng had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Raymond Chieng's current disclosures- Centrilobular nodular opacities
- Centrilobular nodule
- Centri-lobular nodules
- Centri-lobular nodule
- Centrilobular lung nodule
- Centrilobular pulmonary nodules
- Centrilobular pulmonary nodule
- Centrilobular nodules - lung
- Centrilobular nodularity - lung
- Centrilobular lung nodules
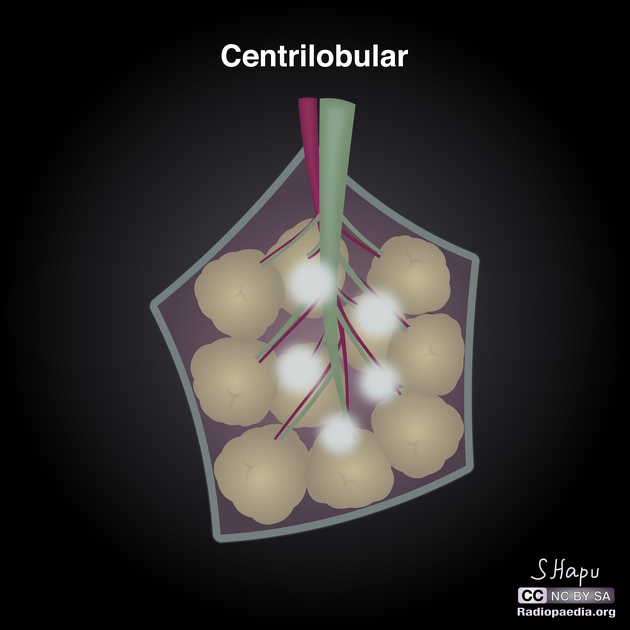
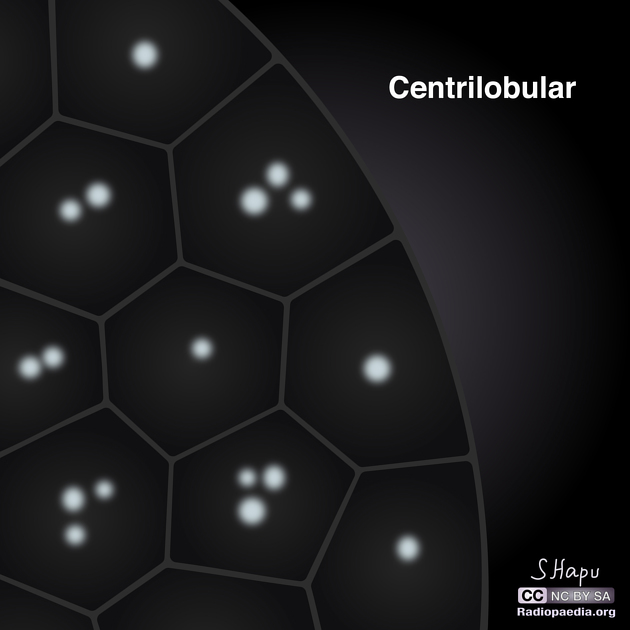
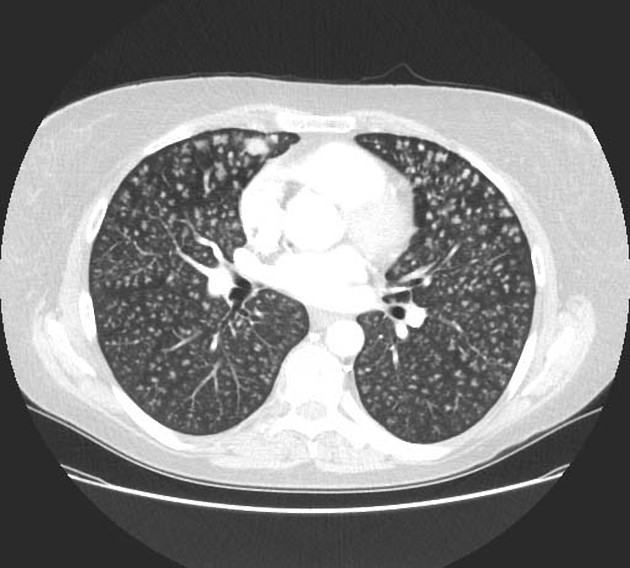
Centrilobular lung nodules are an HRCT chest imaging descriptor for 5-10 mm lung nodules anatomically located centrally within secondary pulmonary lobules. The term is applied based on the nodule's location, not its morphology; they may appear as well-defined solid or poorly-defined ground glass nodules. If extremely small, they are termed centrilobular micronodules.
On this page:
Images:
Pathology
Etiology
Centrilobular nodules can be observed in a wide variety of lung pathology. In particular, pathologies involving the bronchioles and the arterioles (i.e., bronchiolitis and vasculitis), as both are located centrally in the secondary pulmonary lobule. Specific conditions include:
-
infection with endobronchial spread
airway spread of tuberculosis
airway spread of non-tuberculous mycobacterial infection
respiratory bronchiolitis (RB) and respiratory bronchiolitis interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD) 5
-
pulmonary vasculitides (GGO may correspond to perivascular inflammation or hemorrhage)
pulmonary arterial hypertension (particularly PVOD)
lung adenocarcinoma with airway spread
metastatic pulmonary calcification (increased density, may be calcified)
When centrilobular nodules are interspersed with linear and branching densities, it is then termed a tree-in-bud pattern.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Radiographic features
CT
On HRCT chest, centrilobular nodules are typically found around the small airways and spare the subpleural surfaces. They are typically at least 5-10 mm away from the pleural surfaces ref.
See also
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Kazerooni E. High-Resolution CT of the Lungs. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177(3):501-19. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.3.1770501 - Pubmed
- 2. Franquet T, Müller N, Giménez A, Guembe P, de La Torre J, Bagué S. Spectrum of Pulmonary Aspergillosis: Histologic, Clinical, and Radiologic Findings. Radiographics. 2001;21(4):825-37. doi:10.1148/radiographics.21.4.g01jl03825 - Pubmed
- 3. Rossi S, Franquet T, Volpacchio M, Giménez A, Aguilar G. Tree-In-Bud Pattern at Thin-Section CT of the Lungs: Radiologic-Pathologic Overview. Radiographics. 2005;25(3):789-801. doi:10.1148/rg.253045115 - Pubmed
- 4. Engelke C, Schaefer-Prokop C, Schirg E, Freihorst J, Grubnic S, Prokop M. High-Resolution CT and CT Angiography of Peripheral Pulmonary Vascular Disorders. Radiographics. 2002;22(4):739-64. doi:10.1148/radiographics.22.4.g02jl01739 - Pubmed
- 5. Park J, Brown K, Tuder R, Hale V, King T, Lynch D. Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: Radiologic Features with Clinical and Pathologic Correlation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2002;26(1):13-20. doi:10.1097/00004728-200201000-00003 - Pubmed
- 6. Webb W, Higgins C. Thoracic Imaging. (2010) ISBN: 9781605479767 - Google Books
- 7. Boitsios G, Bankier A, Eisenberg R. Diffuse Pulmonary Nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;194(5):W354-66. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.4345 - Pubmed
- 8. Winningham P, Martínez-Jiménez S, Rosado-de-Christenson M, Betancourt S, Restrepo C, Eraso A. Bronchiolitis: A Practical Approach for the General Radiologist. Radiographics. 2017;37(3):777-94. doi:10.1148/rg.2017160131 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Pulmonary nodule
- Acute eosinophilic pneumonia
- Follicular bronchiolitis
- Pulmonary pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
- AIDS-related pulmonary lymphoma
- Chest curriculum
- Hot tub lung
- COVID-19
- Perilymphatic lung nodules
- Small airways disease
- Excipient lung disease
- Tropical pulmonary eosinophilia
- Subpleural sparing
- Klebsiella pneumonia
- Centrilobular region
- Non-fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- Kartagener syndrome
- Non-specific interstitial pneumonia
- Aspiration bronchiolitis
- Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage
- Tropical pulmonary eosinophilia
- Fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- Pulmonary tuberculosis
- Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia (DIPNECH)
- Excipient lung disease
- Miliary tuberculosis with spondylitis
- Sarcoidosis - perilymphatic nodular thicknening
- Excipient lung disease
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis - acute
- Silicosis with progressive massive fibrosis
- Thoracic tuberculosis - paediatric
- Acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- Infectious bronchiolitis
- Respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD)
- Miliary tuberculosis
- Pulmonary tuberculosis with COPD
- Bronchiolitis
- Tree-in-bud appearance
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Related articles: Chest
- imaging techniques
-
chest radiograph[+][+]
- radiography
-
approach
- ABCDE
- ABCDEFGHI
- congenital heart disease
- medical devices in the thorax
- common lines and tubes
- nasogastric tubes
- endotracheal tubes
- central venous catheters
- esophageal temperature probe
- tracheostomy tube
- pleural catheters
- cardiac conduction devices
- prosthetic heart valve
- review areas
-
airspace opacification
- differential diagnoses of airspace opacification
- lobar consolidation
-
atelectasis
- mechanism-based
- morphology-based
- lobar lung collapse
- chest x-ray in the exam setting
- cardiomediastinal contour
- chest radiograph zones
- tracheal air column
- fissures
- normal chest x-ray appearance of the diaphragm
- nipple shadow
-
lines and stripes
- anterior junction line
- posterior junction line
- right paratracheal stripe
- left paratracheal stripe
- posterior tracheal stripe/tracheo-esophageal stripe
- posterior wall of bronchus intermedius
- right paraspinal line
- left paraspinal line
- aortic-pulmonary stripe
- aortopulmonary window
- azygo-esophageal recess
- spaces
- signs
- air bronchogram
- big rib sign
- Chang sign
- Chen sign
- coin lesion
- continuous diaphragm sign
- dense hilum sign
- double contour sign
- egg-on-a-string sign
- extrapleural sign
- finger in glove sign
- flat waist sign
- Fleischner sign
- ginkgo leaf sign
- Golden S sign
- Hampton hump
- haystack sign
- hilum convergence sign
- hilum overlay sign
- Hoffman-Rigler sign
- holly leaf sign
- incomplete border sign
- juxtaphrenic peak sign
- Kirklin sign
- medial stripe sign
- melting ice cube sign
- more black sign
- Naclerio V sign
- Palla sign
- pericardial fat tag sign
- Shmoo sign
- silhouette sign
- snowman sign
- spinnaker sign
- steeple sign
- straight left heart border sign
- third mogul sign
- tram-track sign
- walking man sign
- water bottle sign
- wave sign
- Westermark sign
-
HRCT
- HRCT terminology
- secondary pulmonary lobule
-
lung nodules
- ground-glass nodules
- calcified lung nodules
- by location
- centrilobular lung nodules
- random pulmonary nodules
- perilymphatic nodules[+][+]
-
chest radiograph[+][+]
- airways[+][+]
- bronchitis
- small airways disease
-
bronchiectasis
- broncho-arterial ratio
- related conditions
- differentials by distribution
- narrowing
-
tracheal stenosis
- diffuse tracheal narrowing (differential)
-
bronchial stenosis
- diffuse airway narrowing (differential)
-
tracheal stenosis
- diverticula
- pulmonary edema[+][+]
-
interstitial lung disease (ILD)[+][+]
- Anti-Jo-1 antibody-positive interstitial lung disease
- drug-induced interstitial lung disease
-
hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- subacute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- etiology
- bird fancier's lung: pigeon fancier's lung
- farmer's lung
- cheese workers' lung
- bagassosis
- mushroom worker’s lung
- malt worker’s lung
- maple bark disease
- hot tub lung
- wine maker’s lung
- woodsman’s disease
- thatched roof lung
- tobacco grower’s lung
- potato riddler’s lung
- summer-type pneumonitis
- dry rot lung
- machine operator’s lung
- humidifier lung
- shower curtain disease
- furrier’s lung
- miller’s lung
- lycoperdonosis
- saxophone lung
-
idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (mnemonic)
- acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP)
- cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP)
- desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP)
- non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
- idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis
- lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
- respiratory bronchiolitis–associated interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD)
- usual interstitial pneumonia / idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (UIP/IPF)
-
pneumoconioses
- fibrotic
- non-fibrotic
-
lung cancer[+][+]
-
non-small-cell lung cancer
-
adenocarcinoma
- pre-invasive tumors
- minimally invasive tumors
- invasive tumors
- variants of invasive carcinoma
- described imaging features
- adenosquamous carcinoma
- large cell carcinoma
- primary sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung
- squamous cell carcinoma
- salivary gland-type tumors
-
adenocarcinoma
- pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors
- preinvasive lesions
-
lung cancer invasion patterns
- tumor spread through air spaces (STAS)
- presence of non-lepidic patterns such as acinar, papillary, solid, or micropapillary
- myofibroblastic stroma associated with invasive tumor cells
- pleural invasion
- vascular invasion
- tumors by location
- benign neoplasms
- pulmonary metastases
- lung cancer screening
- lung cancer staging
-
non-small-cell lung cancer





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.