Juxtaphrenic peak sign
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Andrew Dixon had no recorded disclosures.
View Andrew Dixon's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Calum Worsley had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Calum Worsley's current disclosures- Juxtaphrenic peak
- Juxta-phrenic peak sign
- Juxtaphrenic peak (JP)
- Diaphragmatic tenting
- Tenting of the diaphragm
- Kattan sign
- Kattan's sign
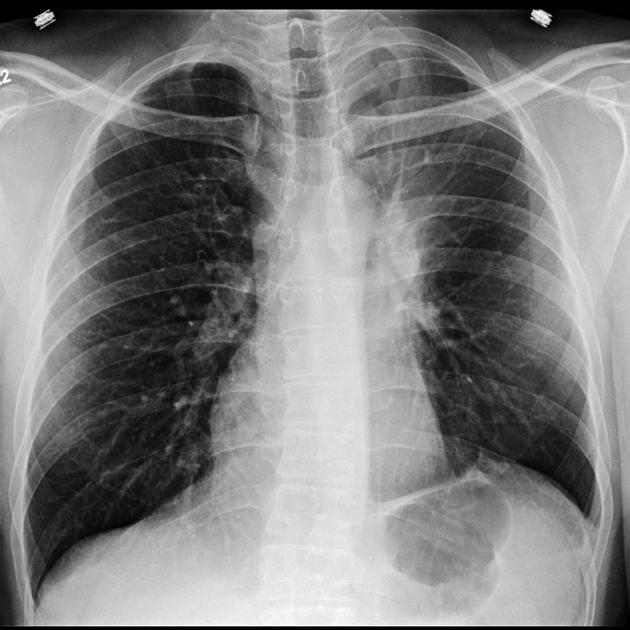
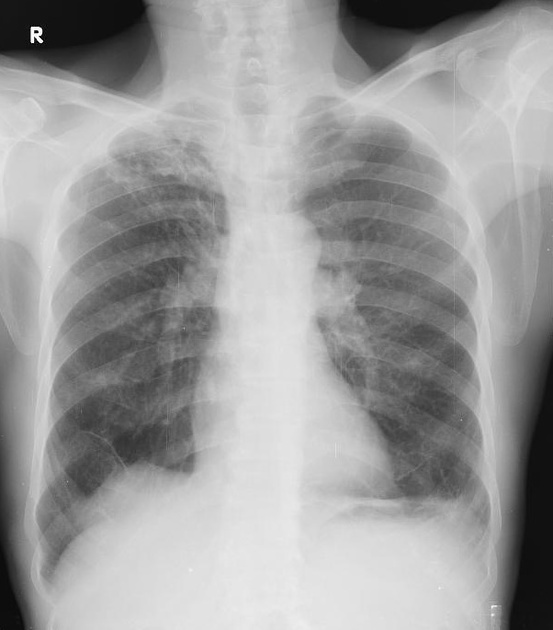
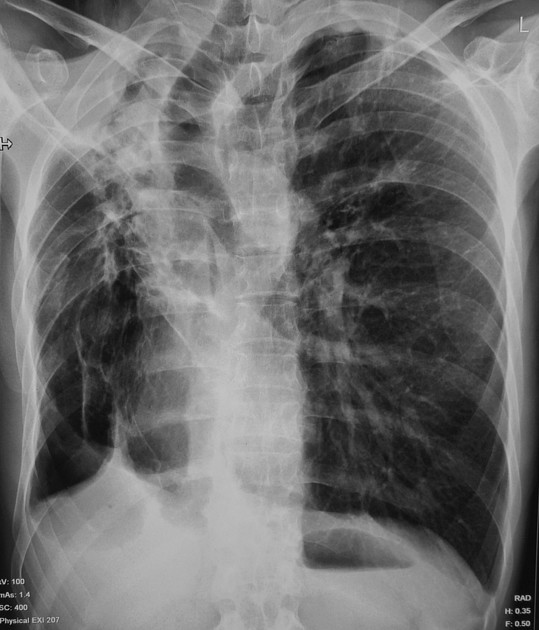
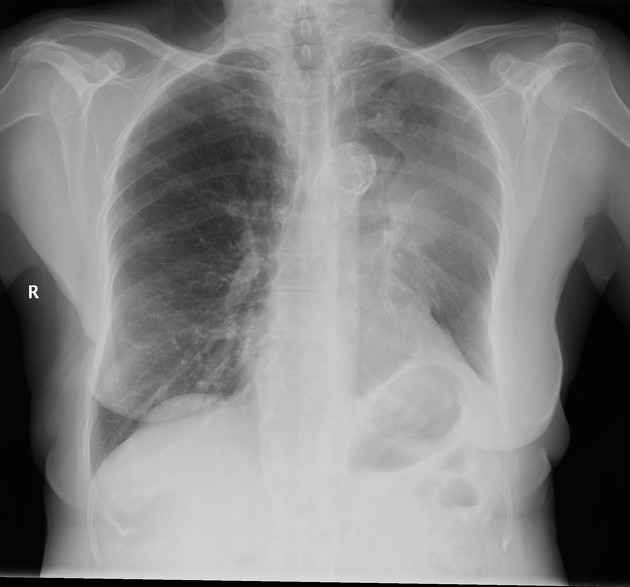
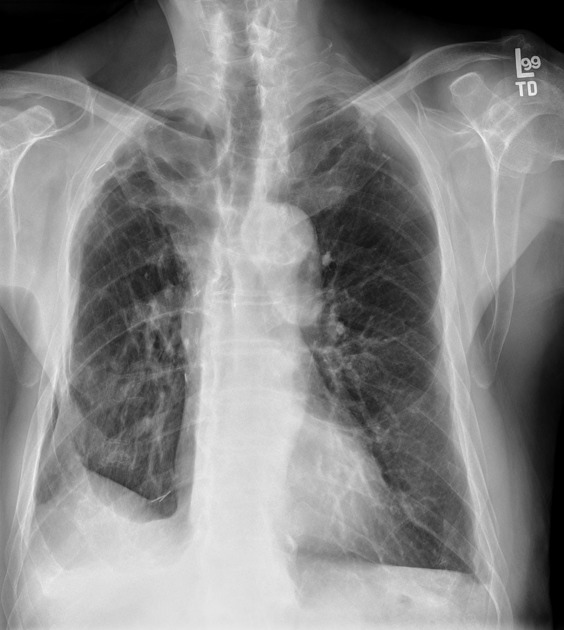
The juxtaphrenic peak sign, also known as diaphragmatic tenting or Kattan sign, refers to the peaked or tented appearance of a hemidiaphragm which can occur in the setting of lobar collapse or post lobectomy (lung). It is caused by retraction of the lower end of diaphragm at an inferior accessory fissure (most common 1), major fissure or inferior pulmonary ligament. It is commonly seen in collapse of the left or right upper lobes but may also be seen in middle lobe collapse.
History and etymology
It was first described by Kenneth R Kattan (1926-2015), an American radiologist from Cincinnati, Ohio, and his colleagues in 1980 6.
References
- 1. Davis S, Yankelevitz D, Wand A, Chiarella D. Juxtaphrenic Peak in Upper and Middle Lobe Volume Loss: Assessment with CT. Radiology. 1996;198(1):143-9. doi:10.1148/radiology.198.1.8539368 - Pubmed
- 2. Konen E, Rozenman J, Simansky D et al. Prevalence of the Juxtaphrenic Peak After Upper Lobectomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177(4):869-73. doi:10.2214/ajr.177.4.1770869 - Pubmed
- 3. Jannette Collins, Eric J. Stern. Chest Radiology. (2008) ISBN: 9780781763141 - Google Books
- 4. Hanke R. [The Pulmonary Ligament (Pulmo-Diaphragmatic Ligament) (Author's Transl)]. Rofo. 1978;129(1):1-12. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1230952 - Pubmed
- 5. Yeh H, Halton K, Gray C. Anatomic Variations and Abnormalities in the Diaphragm Seen with US. Radiographics. 1990;10(6):1019-30. doi:10.1148/radiographics.10.6.2259759 - Pubmed
- 6. Kattan K, Eyler W, Felson B. The Juxtaphrenic Peak in Upper Lobe Collapse. Semin Roentgenol. 1980;15(2):187-93. doi:10.1016/0037-198x(80)90007-3 - Pubmed
- 7. W. Richard Webb, Charles B. Higgins. Thoracic Imaging. (2011) ISBN: 9781605479767 - Google Books
- 8. Cameron D. The Juxtaphrenic Peak (Katten's Sign) is Produced by Rotation of an Inferior Accessory Fissure. Australas Radiol. 1993;37(4):332-5. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1673.1993.tb00091.x - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Chest
- imaging techniques
-
chest radiograph
- radiography[+][+]
-
approach
- ABCDE
- ABCDEFGHI
- congenital heart disease
- medical devices in the thorax
- common lines and tubes[+][+]
- nasogastric tubes
- endotracheal tubes
- central venous catheters
- esophageal temperature probe
- tracheostomy tube
- pleural catheters
- cardiac conduction devices
- prosthetic heart valve
- review areas
-
airspace opacification[+][+]
- differential diagnoses of airspace opacification
- lobar consolidation
-
atelectasis
- mechanism-based
- morphology-based
- lobar lung collapse
- chest x-ray in the exam setting[+][+]
- cardiomediastinal contour[+][+]
- chest radiograph zones[+][+]
- tracheal air column[+][+]
- fissures[+][+]
- normal chest x-ray appearance of the diaphragm[+][+]
- nipple shadow[+][+]
-
lines and stripes[+][+]
- anterior junction line
- posterior junction line
- right paratracheal stripe
- left paratracheal stripe
- posterior tracheal stripe/tracheo-esophageal stripe
- posterior wall of bronchus intermedius
- right paraspinal line
- left paraspinal line
- aortic-pulmonary stripe
- aortopulmonary window
- azygo-esophageal recess
- spaces[+][+]
- signs
- air bronchogram
- big rib sign
- Chang sign
- Chen sign
- coin lesion
- continuous diaphragm sign
- dense hilum sign
- double contour sign
- egg-on-a-string sign
- extrapleural sign
- finger in glove sign
- flat waist sign
- Fleischner sign
- ginkgo leaf sign
- Golden S sign
- Hampton hump
- haystack sign
- hilum convergence sign
- hilum overlay sign
- Hoffman-Rigler sign
- holly leaf sign
- incomplete border sign
- juxtaphrenic peak sign
- Kirklin sign
- medial stripe sign
- melting ice cube sign
- more black sign
- Naclerio V sign
- Palla sign
- pericardial fat tag sign
- Shmoo sign
- silhouette sign[+][+]
- snowman sign
- spinnaker sign
- steeple sign
- straight left heart border sign
- third mogul sign
- tram-track sign
- walking man sign
- water bottle sign
- wave sign
- Westermark sign
- HRCT[+][+]
-
chest radiograph
- airways[+][+]
- bronchitis
- small airways disease
-
bronchiectasis
- broncho-arterial ratio
- related conditions
- differentials by distribution
- narrowing
-
tracheal stenosis
- diffuse tracheal narrowing (differential)
-
bronchial stenosis
- diffuse airway narrowing (differential)
-
tracheal stenosis
- diverticula
- pulmonary edema[+][+]
-
interstitial lung disease (ILD)[+][+]
- Anti-Jo-1 antibody-positive interstitial lung disease
- drug-induced interstitial lung disease
-
hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- subacute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- etiology
- bird fancier's lung: pigeon fancier's lung
- farmer's lung
- cheese workers' lung
- bagassosis
- mushroom worker’s lung
- malt worker’s lung
- maple bark disease
- hot tub lung
- wine maker’s lung
- woodsman’s disease
- thatched roof lung
- tobacco grower’s lung
- potato riddler’s lung
- summer-type pneumonitis
- dry rot lung
- machine operator’s lung
- humidifier lung
- shower curtain disease
- furrier’s lung
- miller’s lung
- lycoperdonosis
- saxophone lung
-
idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (mnemonic)
- acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP)
- cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP)
- desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP)
- non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
- idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis
- lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
- respiratory bronchiolitis–associated interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD)
- usual interstitial pneumonia / idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (UIP/IPF)
-
pneumoconioses
- fibrotic
- non-fibrotic
-
lung cancer[+][+]
-
non-small-cell lung cancer
-
adenocarcinoma
- pre-invasive tumors
- minimally invasive tumors
- invasive tumors
- variants of invasive carcinoma
- described imaging features
- adenosquamous carcinoma
- large cell carcinoma
- primary sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung
- squamous cell carcinoma
- salivary gland-type tumors
-
adenocarcinoma
- pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors
- preinvasive lesions
-
lung cancer invasion patterns
- tumor spread through air spaces (STAS)
- presence of non-lepidic patterns such as acinar, papillary, solid, or micropapillary
- myofibroblastic stroma associated with invasive tumor cells
- pleural invasion
- vascular invasion
- tumors by location
- benign neoplasms
- pulmonary metastases
- lung cancer screening
- lung cancer staging
-
non-small-cell lung cancer





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.