Adenocarcinoma in situ of the lung
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Calum Worsley had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Calum Worsley's current disclosures- Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of lung
- AIS lung
- AIS
- AIS of lungs
- Adenocarcinoma in situ (lung)
- Adenocarcinoma in situ of lung
- Adenocarcinoma in situ (AIS) of the lung
- AID of lung
- AIS - lung
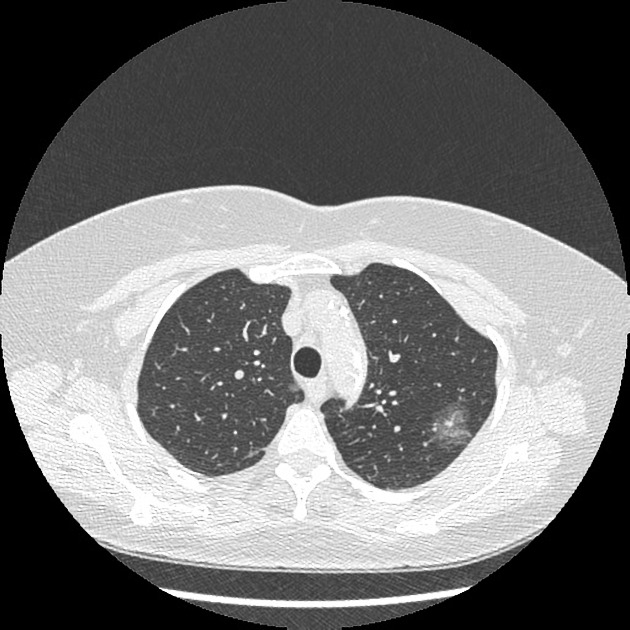
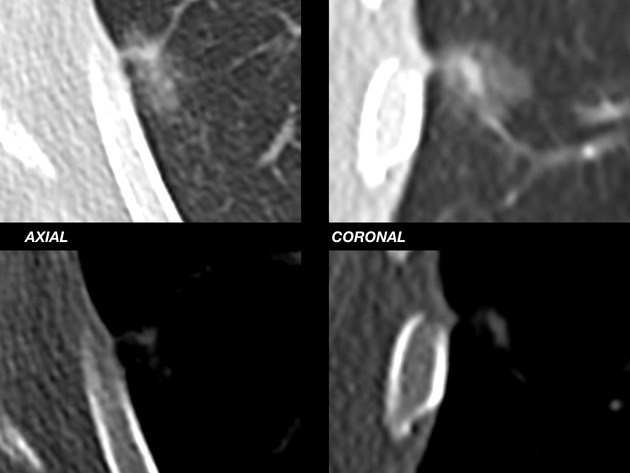
Adenocarcinomas in situ (AIS) of the lung refer to a relatively new entity which falls under the spectrum of pre-invasive lesions of the lungs. This entity partly replaces the noninvasive end of the previous term bronchoalveolar carcinoma. Adenocarcinoma in situ is defined as a localized adenocarcinoma of <3 cm that exhibits a lepidic growth pattern, with neoplastic cells along the alveolar structures but without stromal, vascular, or pleural invasion 1.
On this page:
Pathology
AISs are localized adenocarcinomas of ≤3 cm, with no growth pattern other than lepidic, with neoplastic cells along the alveolar structures but without stromal, vascular, lymphatic, or pleural invasion, and no features of necrosis 6.
There are three histopathological subtypes, the most common is non-mucinous, with mucinous or mixed subtypes being rarely found.
Radiographic features
CT
While adenocarcinoma in situ is usually seen as a pure ground-glass nodule or a part-solid lung nodule, there can be overlap among the imaging features of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia, adenocarcinoma in situ, and invasive adenocarcinoma of the lung 1.
Nuclear medicine
FDG PET-CT
Adenocarcinomas in situ are commonly associated with PET false-negative results. FDG PET-CT is recommended when assessing subsolid ground-glass lung lesions that have a solid component measuring more than 8 mm 5.
Treatment and prognosis
Adenocarcinoma in situ carries an excellent prognosis, with reported survival rates of 100% following complete tumor resection 6.
For follow-up guidelines consider - Fleischner Society pulmonary nodule recommendations
References
- 1. Lee SM, Goo JM, Park CM et-al. A new classification of adenocarcinoma: what the radiologists need to know. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2012;18 (6): 519-26. doi:10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.5778-12.1 - Pubmed citation
- 2. Kerr KM. Pulmonary adenocarcinomas: classification and reporting. Histopathology. 2009;54 (1): 12-27. Histopathology (full text) - doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2008.03176.x - Pubmed citation
- 3. Yatabe Y, Borczuk AC, Powell CA. Do all lung adenocarcinomas follow a stepwise progression?. Lung Cancer. 2011;74 (1): 7-11. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.05.021 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
- 4. Lee HJ, Lee CH, Jeong YJ et-al. IASLC/ATS/ERS International Multidisciplinary Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma: novel concepts and radiologic implications. J Thorac Imaging. 2012;27 (6): 340-53. doi:10.1097/RTI.0b013e3182688d62 - Pubmed citation
- 5. Kandathil A, Kay FU, Butt YM, Wachsmann JW, Subramaniam RM. Role of FDG PET/CT in the Eighth Edition of TNM Staging of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. (2018) Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 38 (7): 2134-2149. doi:10.1148/rg.2018180060 - Pubmed
- 6. Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, Nicholson AG, Geisinger KR, Yatabe Y, Beer DG, Powell CA, Riely GJ, Van Schil PE, Garg K, Austin JH, Asamura H, Rusch VW, Hirsch FR, Scagliotti G, Mitsudomi T, Huber RM, Ishikawa Y, Jett J, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Sculier JP, Takahashi T, Tsuboi M, Vansteenkiste J, Wistuba I, Yang PC, Aberle D, Brambilla C, Flieder D, Franklin W, Gazdar A, Gould M, Hasleton P, Henderson D, Johnson B, Johnson D, Kerr K, Kuriyama K, Lee JS, Miller VA, Petersen I, Roggli V, Rosell R, Saijo N, Thunnissen E, Tsao M, Yankelewitz D. International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. (2011) Journal of thoracic oncology : official publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer. 6 (2): 244-85. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318206a221 - Pubmed
- 7. Lambe G, Durand M, Buckley A, Nicholson S, McDermott R. Adenocarcinoma of the lung: from BAC to the future. (2020) Insights into imaging. 11 (1): 69. doi:10.1186/s13244-020-00875-6 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Non-small cell lung cancer
- Lymphangitic carcinomatosis (mnemonic)
- Ground-glass density nodule
- Preinvasive adenocarcinoma lesion of the lung
- Halo sign (chest)
- Lung carcinoma doubling time (mnemonic)
- Benign vs malignant pulmonary nodule
- Pseudocavitation (lung)
- Minimally invasive adenocarcinoma of the lung
- Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia of the lung
- Adenocarcinoma of the lung
- Preinvasive lesions of the lung
- Pure ground glass nodules
- Adenocarcinoma in situ, minimally invasive adenocarcinoma and invasive adenocarcinoma of lung
- Pulmonary nodules with air bronchograms (mnemonic)
Related articles: Chest
- imaging techniques[+][+]
-
chest radiograph
- radiography
-
approach
- ABCDE
- ABCDEFGHI
- congenital heart disease
- medical devices in the thorax
- common lines and tubes
- nasogastric tubes
- endotracheal tubes
- central venous catheters
- esophageal temperature probe
- tracheostomy tube
- pleural catheters
- cardiac conduction devices
- prosthetic heart valve
- review areas
-
airspace opacification
- differential diagnoses of airspace opacification
- lobar consolidation
-
atelectasis
- mechanism-based
- morphology-based
- lobar lung collapse
- chest x-ray in the exam setting
- cardiomediastinal contour
- chest radiograph zones
- tracheal air column
- fissures
- normal chest x-ray appearance of the diaphragm
- nipple shadow
-
lines and stripes
- anterior junction line
- posterior junction line
- right paratracheal stripe
- left paratracheal stripe
- posterior tracheal stripe/tracheo-esophageal stripe
- posterior wall of bronchus intermedius
- right paraspinal line
- left paraspinal line
- aortic-pulmonary stripe
- aortopulmonary window
- azygo-esophageal recess
- spaces
- signs
- air bronchogram
- big rib sign
- Chang sign
- Chen sign
- coin lesion
- continuous diaphragm sign
- dense hilum sign
- double contour sign
- egg-on-a-string sign
- extrapleural sign
- finger in glove sign
- flat waist sign
- Fleischner sign
- ginkgo leaf sign
- Golden S sign
- Hampton hump
- haystack sign
- hilum convergence sign
- hilum overlay sign
- Hoffman-Rigler sign
- holly leaf sign
- incomplete border sign
- juxtaphrenic peak sign
- Kirklin sign
- medial stripe sign
- melting ice cube sign
- more black sign
- Naclerio V sign
- Palla sign
- pericardial fat tag sign
- Shmoo sign
- silhouette sign
- snowman sign
- spinnaker sign
- steeple sign
- straight left heart border sign
- third mogul sign
- tram-track sign
- walking man sign
- water bottle sign
- wave sign
- Westermark sign
- HRCT
-
chest radiograph
- airways[+][+]
- bronchitis
- small airways disease
-
bronchiectasis
- broncho-arterial ratio
- related conditions
- differentials by distribution
- narrowing
-
tracheal stenosis
- diffuse tracheal narrowing (differential)
-
bronchial stenosis
- diffuse airway narrowing (differential)
-
tracheal stenosis
- diverticula
- pulmonary edema[+][+]
-
interstitial lung disease (ILD)[+][+]
- Anti-Jo-1 antibody-positive interstitial lung disease
- drug-induced interstitial lung disease
-
hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- subacute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- etiology
- bird fancier's lung: pigeon fancier's lung
- farmer's lung
- cheese workers' lung
- bagassosis
- mushroom worker’s lung
- malt worker’s lung
- maple bark disease
- hot tub lung
- wine maker’s lung
- woodsman’s disease
- thatched roof lung
- tobacco grower’s lung
- potato riddler’s lung
- summer-type pneumonitis
- dry rot lung
- machine operator’s lung
- humidifier lung
- shower curtain disease
- furrier’s lung
- miller’s lung
- lycoperdonosis
- saxophone lung
-
idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (mnemonic)
- acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP)
- cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP)
- desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP)
- non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
- idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis
- lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
- respiratory bronchiolitis–associated interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD)
- usual interstitial pneumonia / idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (UIP/IPF)
-
pneumoconioses
- fibrotic
- non-fibrotic
-
lung cancer
-
non-small-cell lung cancer[+][+]
- adenocarcinoma
- adenosquamous carcinoma
- large cell carcinoma
- primary sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung[+][+]
- squamous cell carcinoma
- salivary gland-type tumors[+][+]
- pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors[+][+]
- preinvasive lesions[+][+]
-
lung cancer invasion patterns[+][+]
- tumor spread through air spaces (STAS)
- presence of non-lepidic patterns such as acinar, papillary, solid, or micropapillary
- myofibroblastic stroma associated with invasive tumor cells
- pleural invasion
- vascular invasion
- tumors by location[+][+]
- benign neoplasms[+][+]
- pulmonary metastases[+][+]
- lung cancer screening[+][+]
- lung cancer staging[+][+]
-
non-small-cell lung cancer[+][+]




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.