Medical devices in the thorax are regularly observed by radiologists when reviewing radiographs and CT scans.
On this page:
Extrathoracic devices
tubing, clamps, syringes, scissors, lying on or under the patient
rubber sheets, foam mattresses, clothing, hair braids, nipple piercings, etc., may also be visible
These devices are a common cause of artifacts and may trip the unweary, but in general, are recognized for what they are.
The following are more important to be recognized by the radiologist:
oxygen masks and ventilator support tubing
temperature and humidity sensor attachments
ECG electrodes/leads
external pacemaker-defibrillator (typically seen in a cardiac patient transported by helicopter or ambulance) 1
bioreactance leads (e.g. Cheetah Starling SV sensors)
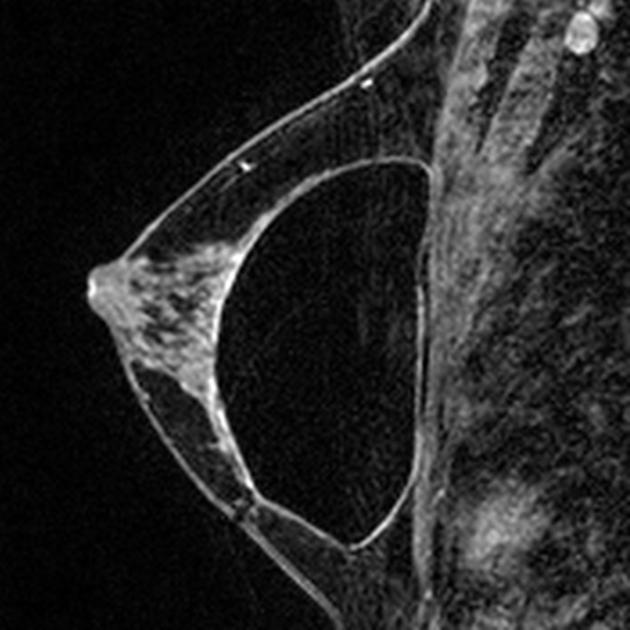
breast tissue expander (used for breast reconstruction)
Pleural devices
-
usually placed anterosuperiorly to drain pneumothorax, and posteroinferiorly to drain pleural effusion
a well-positioned tube should lie between the visceral and parietal pleura, and there should not be any kinking
to check the correct positioning, frequently AP and lateral views are required. A supplemental CT scan may also be performed.
should not enter the interlobar fissure, else it may be blocked 1; tip should not be within the lung parenchyma or subcutaneous tissue
all drain holes should be in the pleural cavity to ensure adequate drainage 5
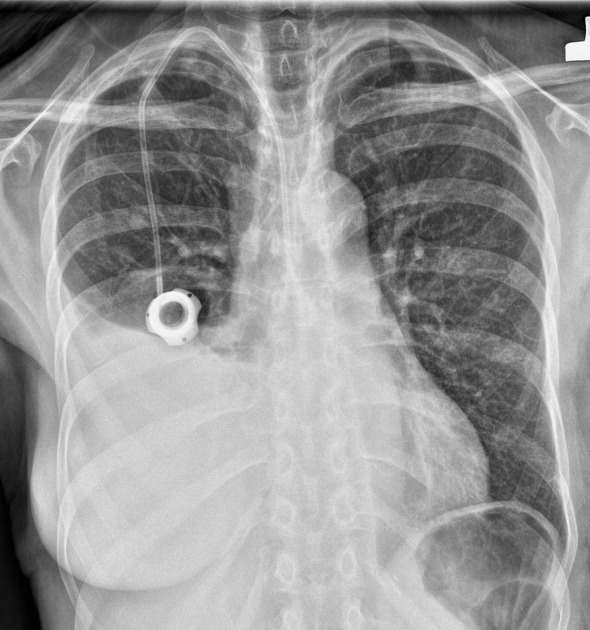
pigtail catheter: used in empyema drainage
Heimlich valve: it is a one-way valve used for pleural space drainages, which prevents the return of gases or fluids into the pleural space
plombage: "ping-pong ball" plombage and wax plombage (historically used for tuberculosis, but no longer)
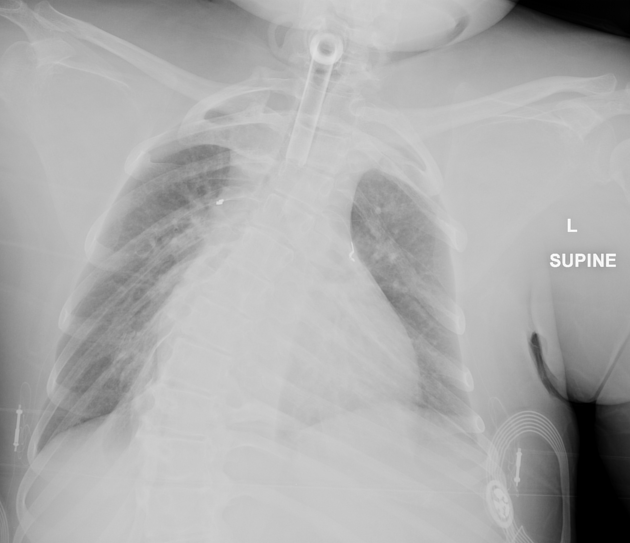
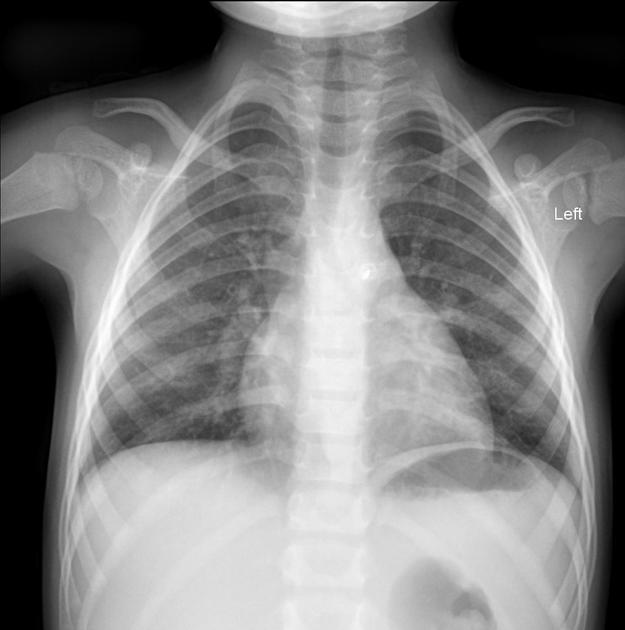
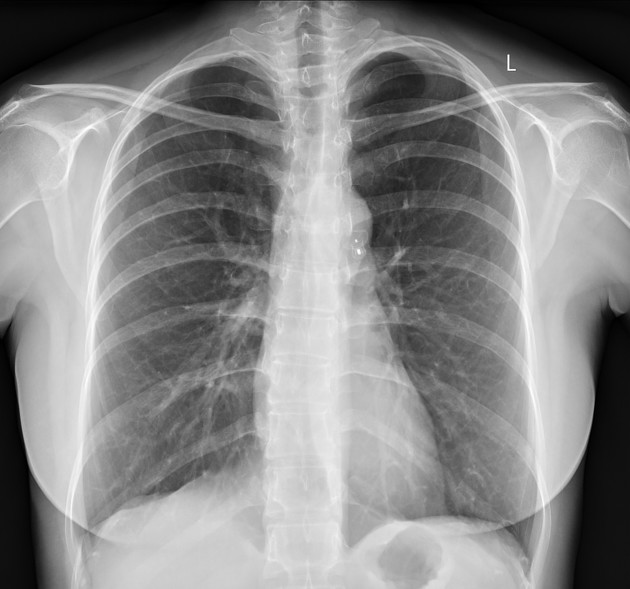
Tracheal, bronchial and esophageal devices
-
tip of the tube should be 5 cm +/- 2 cm above the carina 2 (carina is just caudad to the aortic arch, if not clearly visible)
may wrongly enter right main bronchus, esophagus or even the soft tissues of the neck
sometimes, a deliberate double-lumen ET tube is used to check differential ventilation of the two lungs 1
esophageal Doppler probe
esophageal manometer
esophageal pH probe (seen just above gastro-esophageal junction)
temperature probe (usually within the oropharynx or esophagus)
bronchial stents / tracheobronchial stents (in lung transplant patients or due to obstructing tumors)
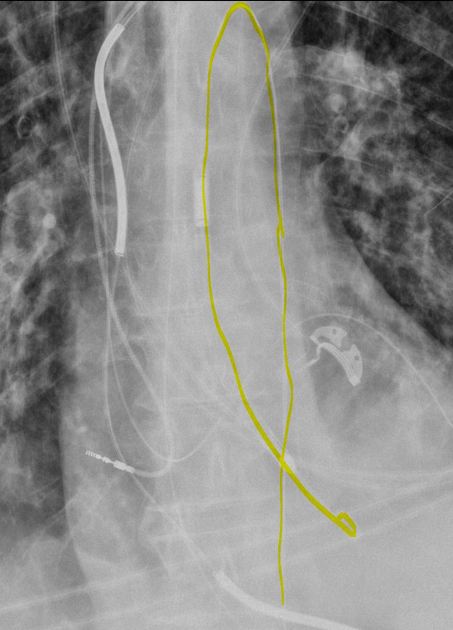
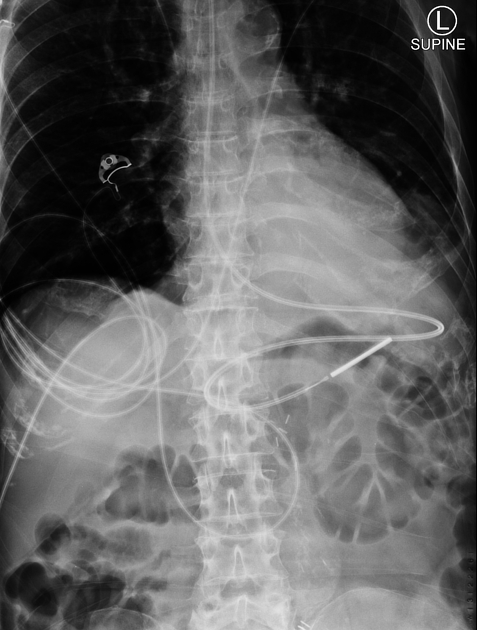
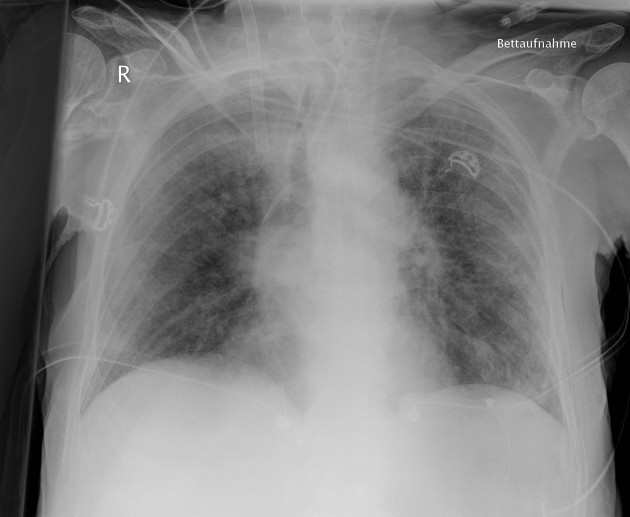
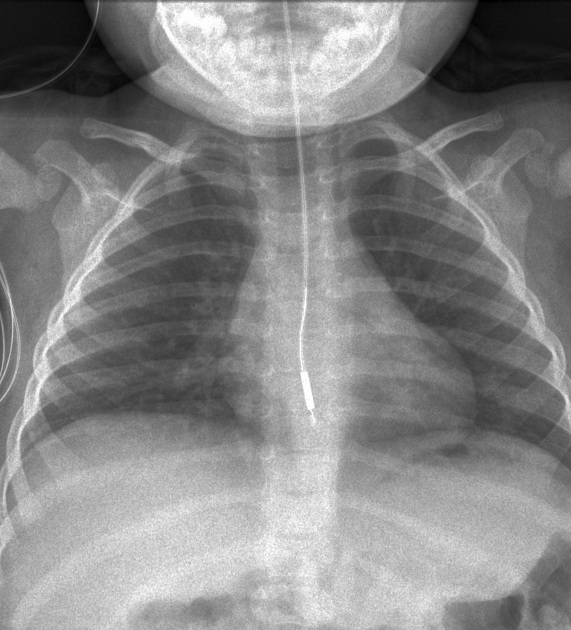
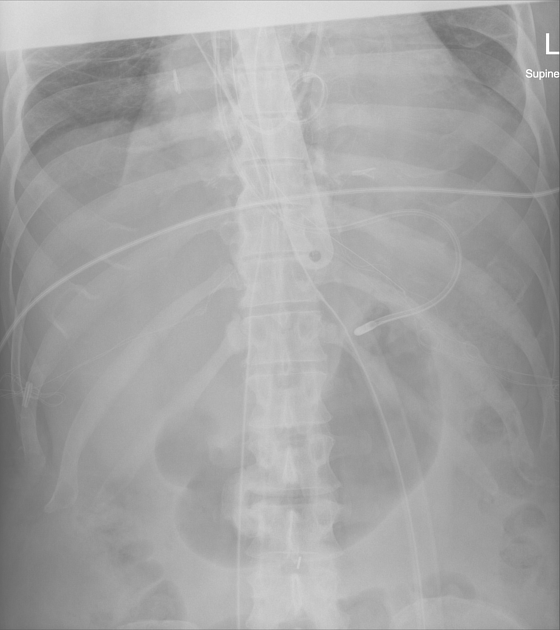
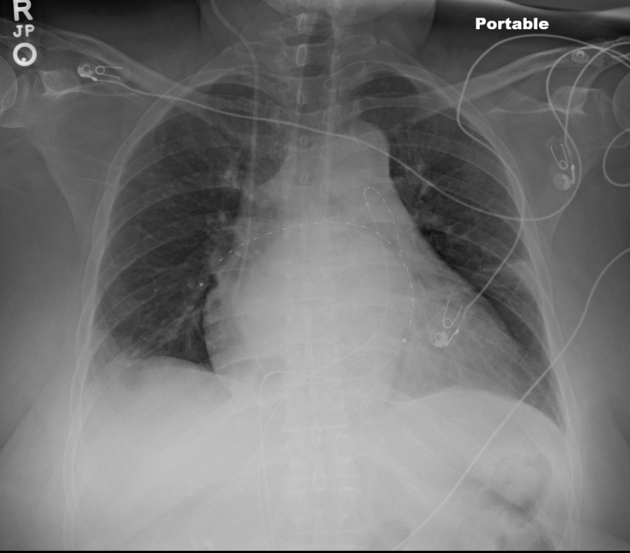
Vascular devices
peripherally inserted central catheters (PICC): central portion only
-
central venous catheters: central tip ideally positioned at the superior cavoatrial junction and should not enter the right atrium
temporary non-tunneled lines: internal jugular and subclavian lines
tunneled lines: e.g. Hickman line, Broviac line
permanent, implantable access line with subcutaneous ports: e.g. Port-A-Cath, Infus-a-Port
left atrial catheter
right atrial line often used postpaediatric cardiac surgery
thoracic aortic stent
superior vena caval filter
carotid artery clamps
-
cannulas of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) devices
in the right jugular vein (in case of peripheral cannulation), rarely in the left jugular vein
in case of central cannulation, both cannulas are placed directly via central vessels into the atria
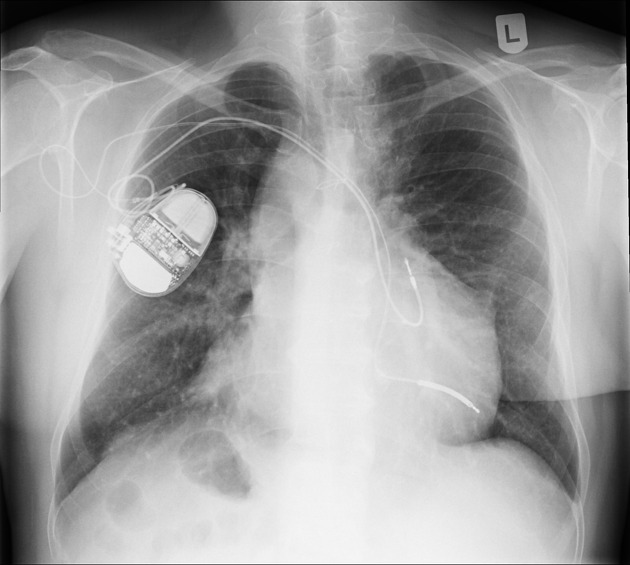
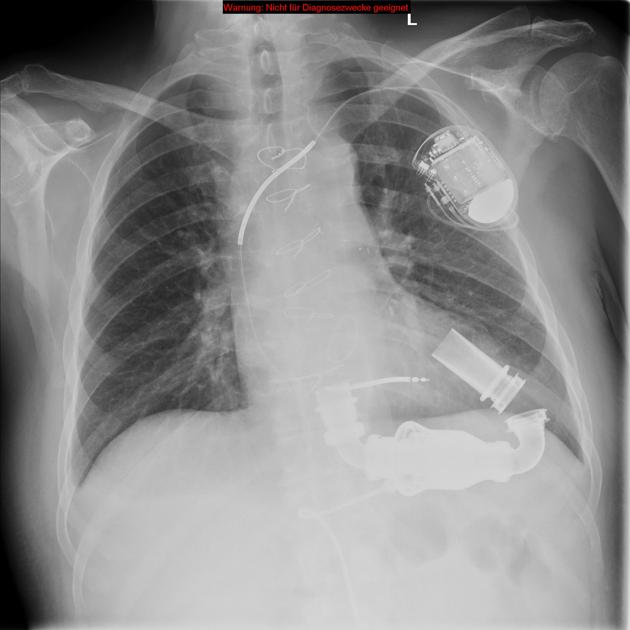
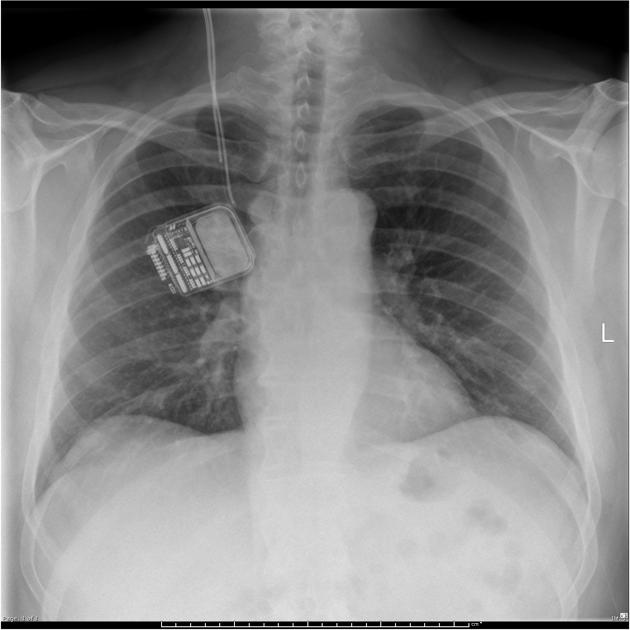
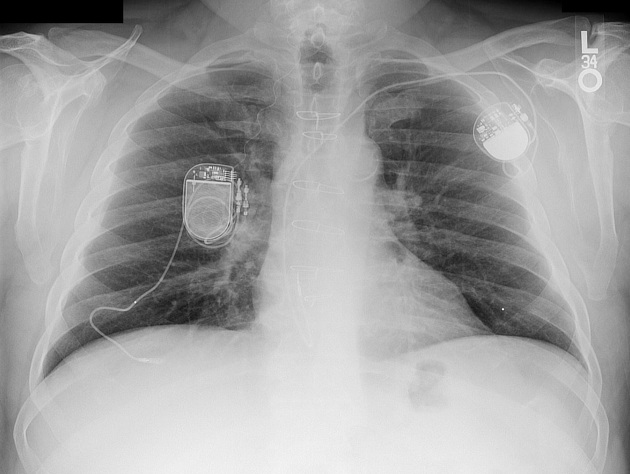
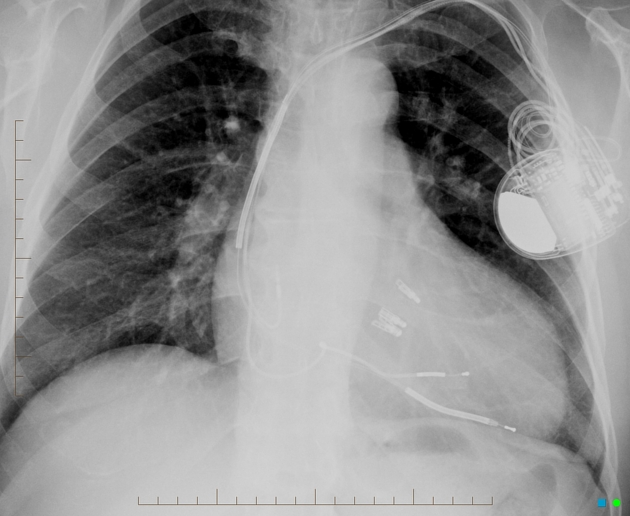
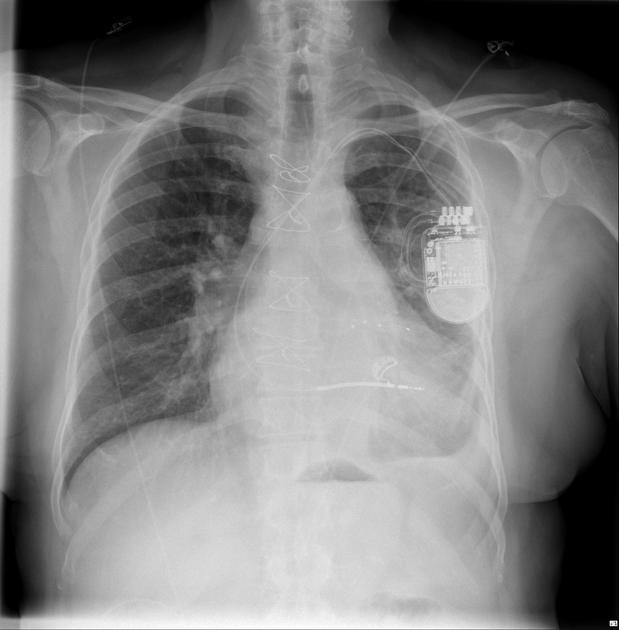
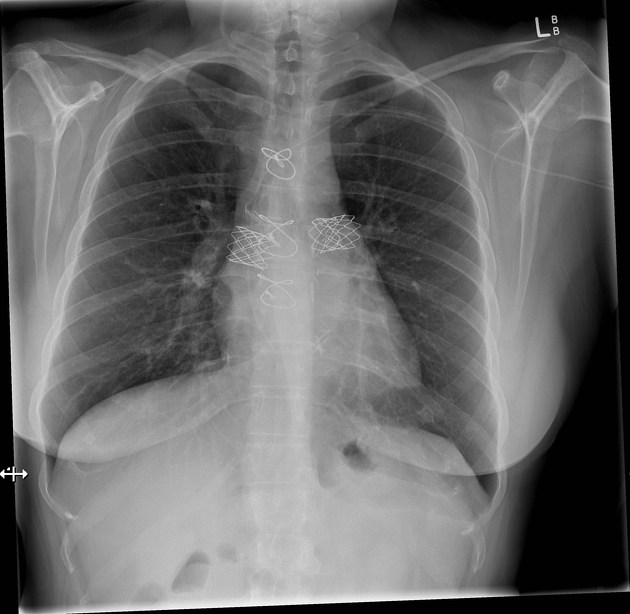
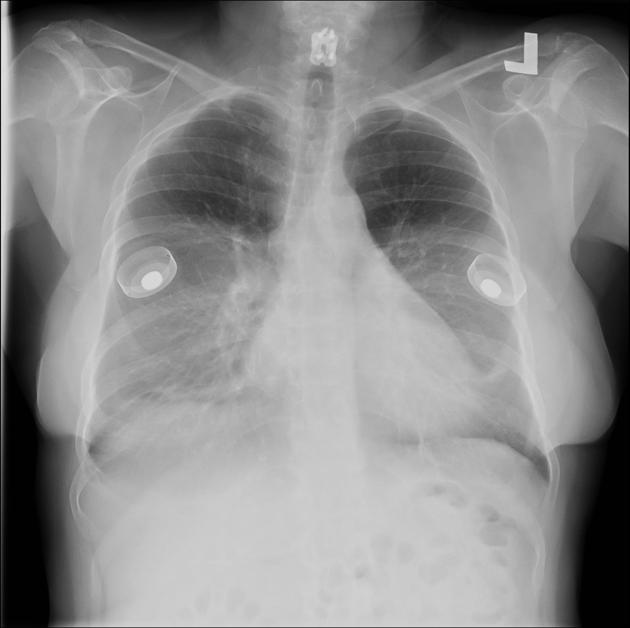
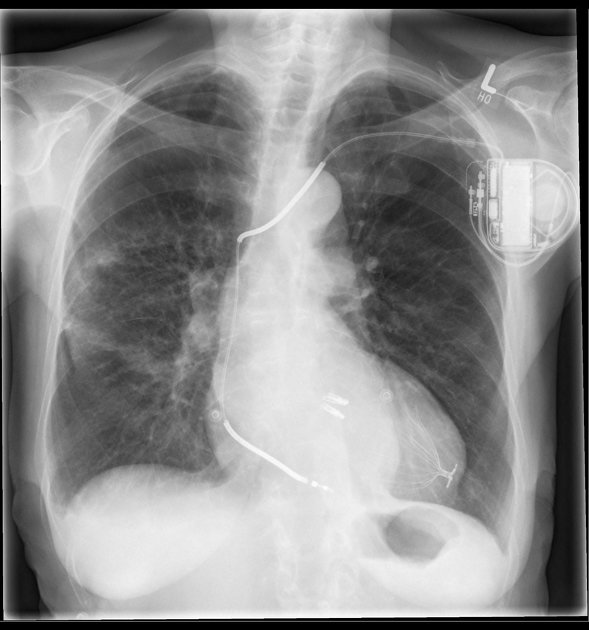
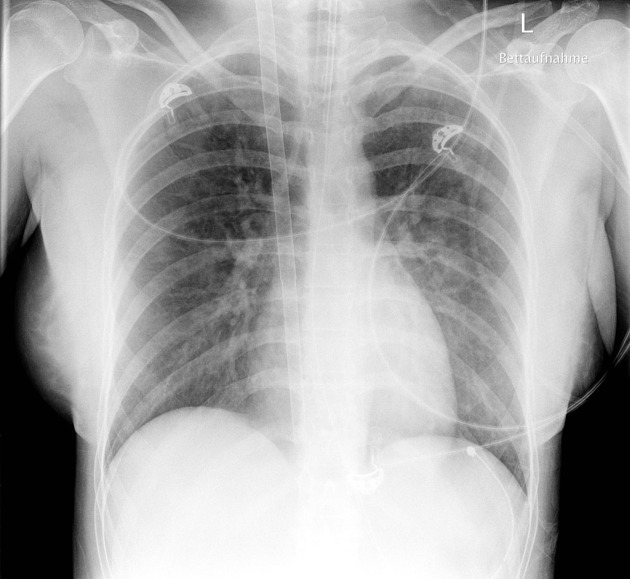
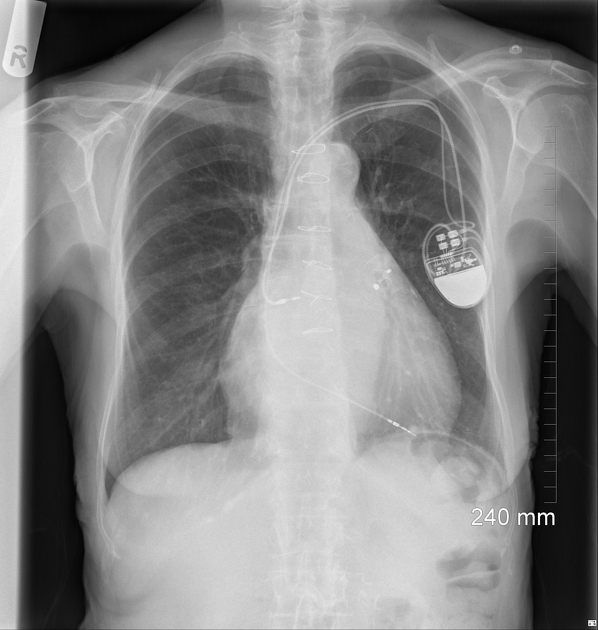
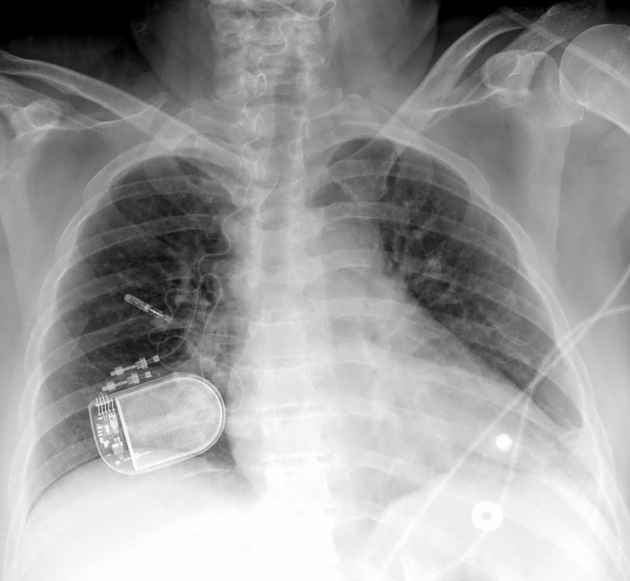
Cardiac devices
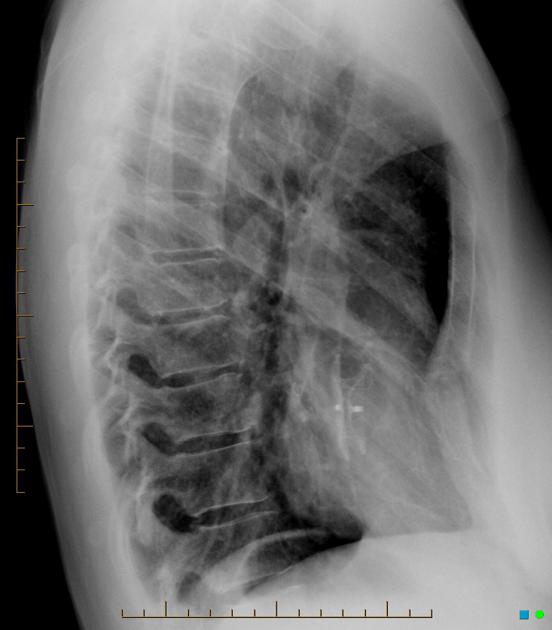
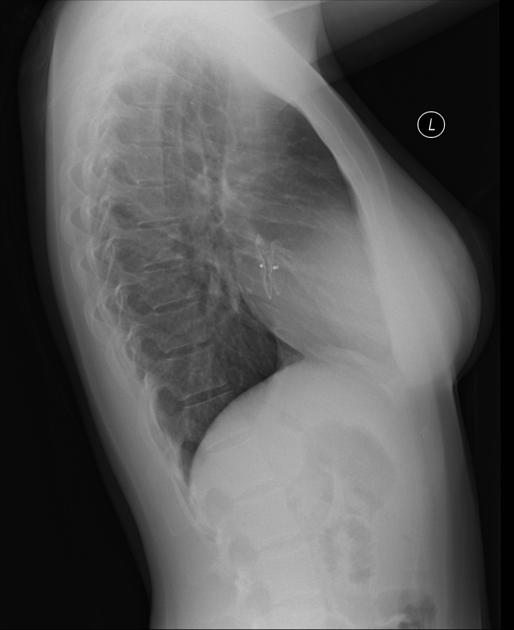
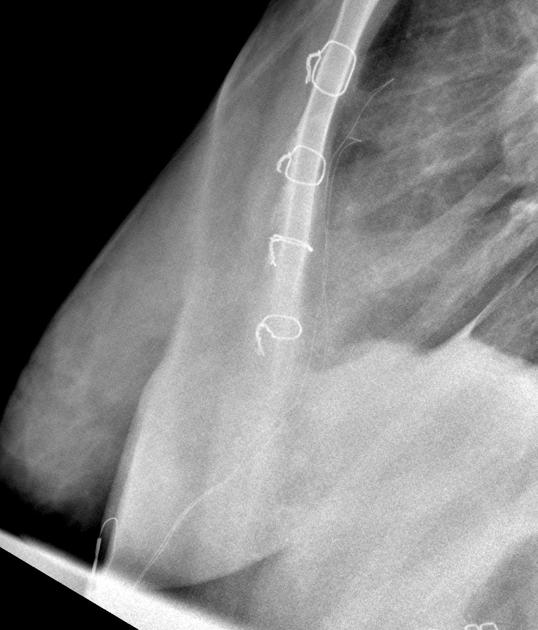
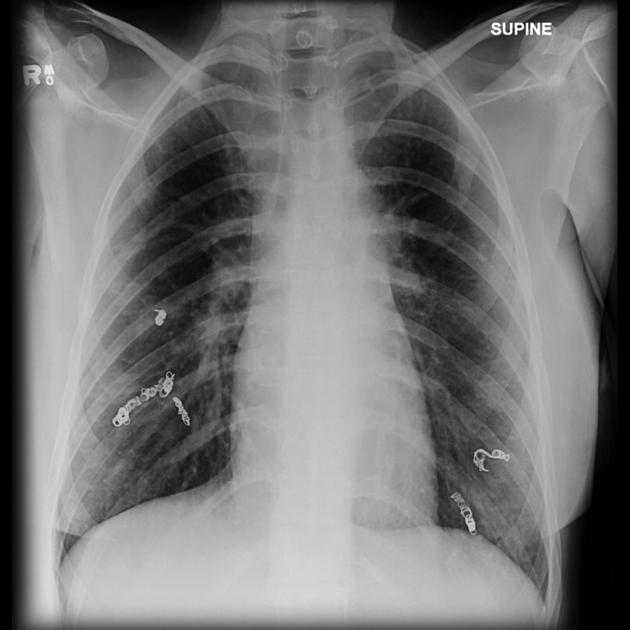
sternal wires, plates
-
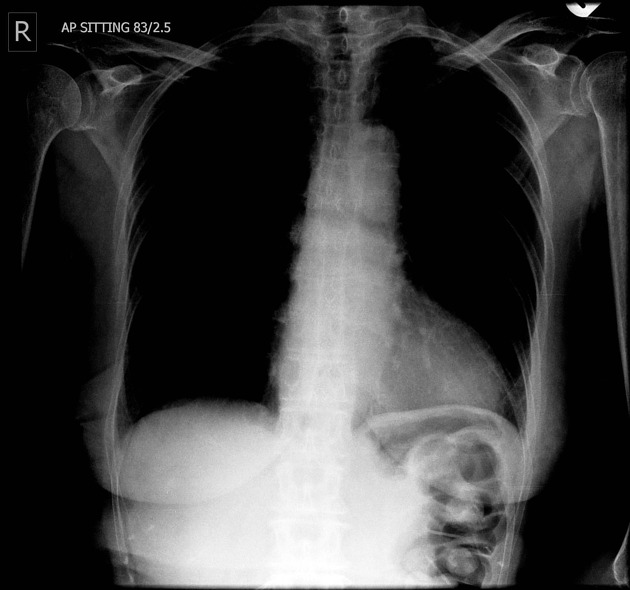
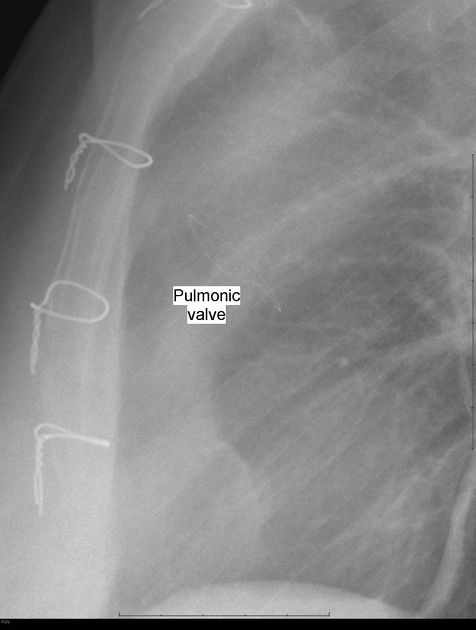
cardiac valve devices or replacements
-
circulatory assist devices
intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) (e.g. Impella®)
left ventricular assist device (LVAD) (e.g. TandemHeart percutaneous VAD)
atrial septal occlusion device (e.g. Amplatz closure device)
left atrial appendage closure devices (e.g. Watchman device)
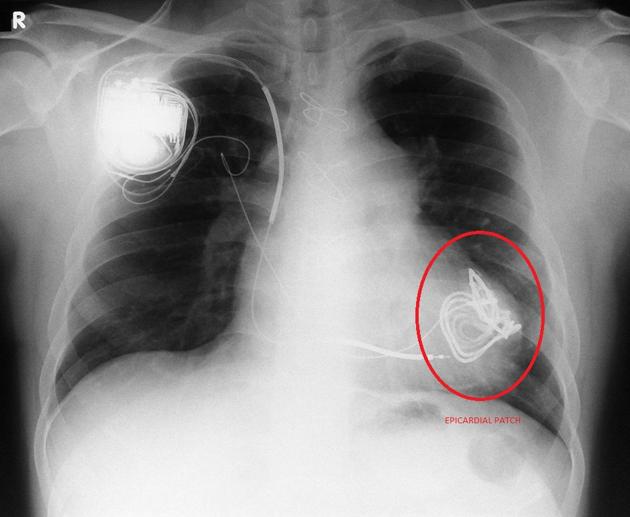
epicardial patch
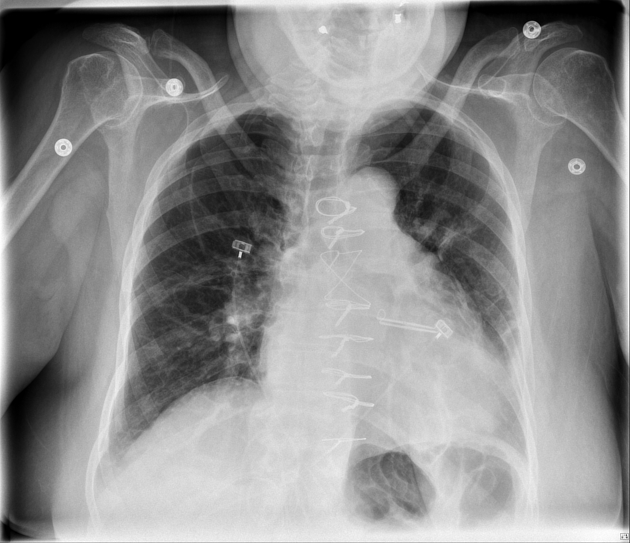
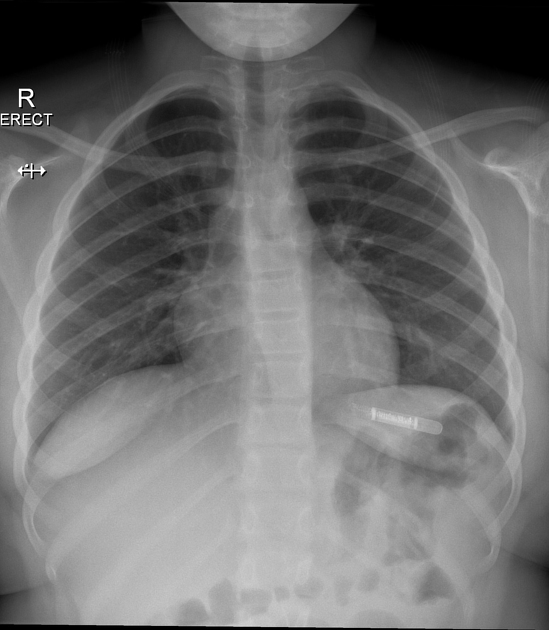
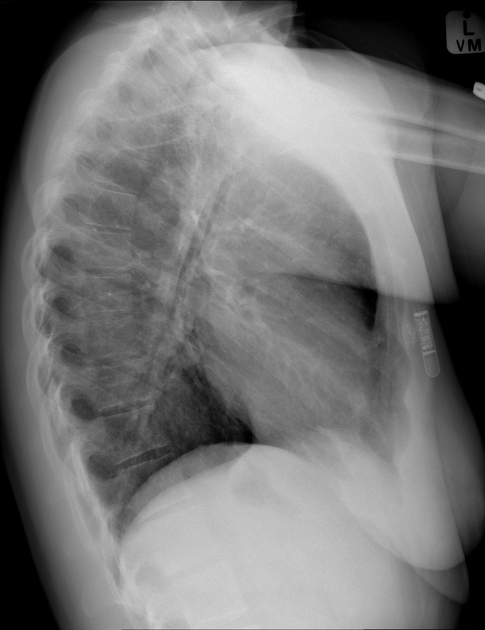
insertable loop recorder (e.g. Reveal LINQ)
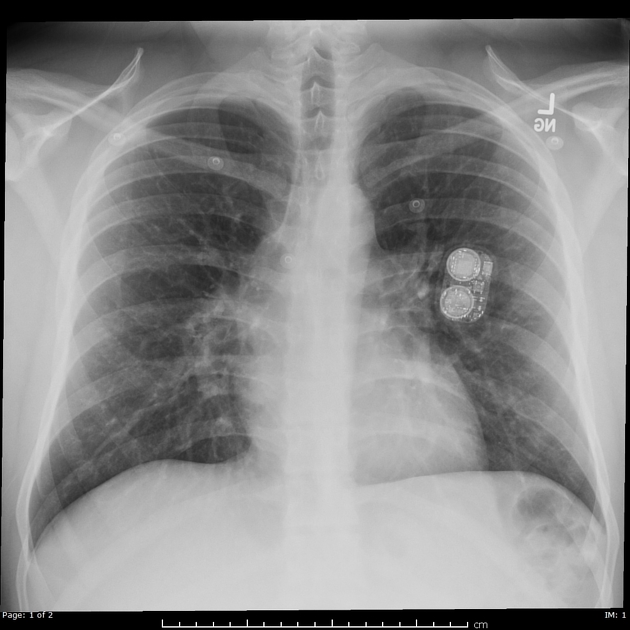
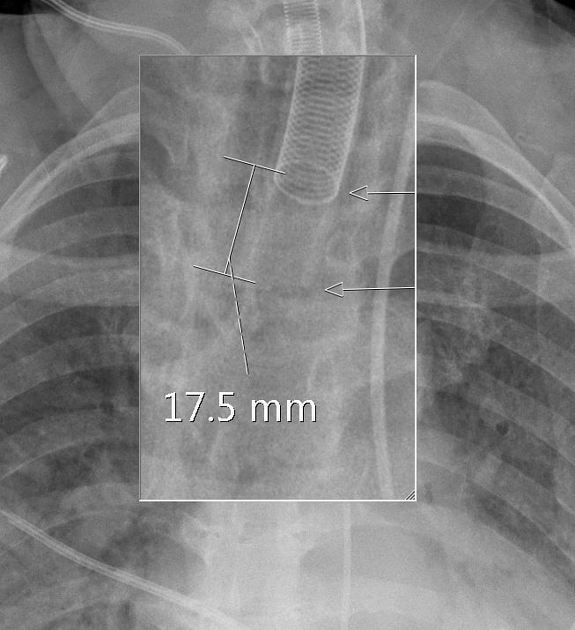
implantable pulmonary artery pressure monitoring device (e.g. CardioMEMS)
Miscellaneous
hypoglossal nerve stimulator (e.g. Inspire® device)
antibiotic spacer
vertebroplasty-related
spinal rods, transpedicular screws, disc spacers, interspinous spacers
surgical clips (e.g. following axillary nodal clearance)
-
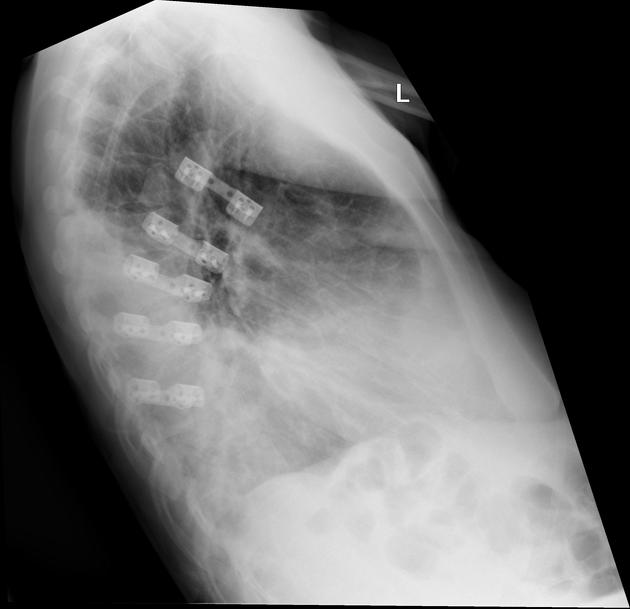
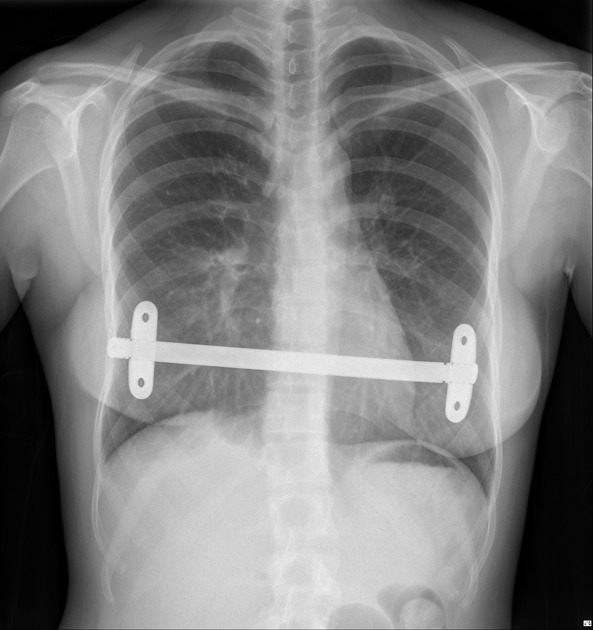
surgical chest bars























 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.