Mega cisterna magna
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosures- Mega cisterna magna
- Mega-cisterna magna
- Megacisterna magna
- Retrocerebellar arachnoid pouch
- Enlarged cisterna magna
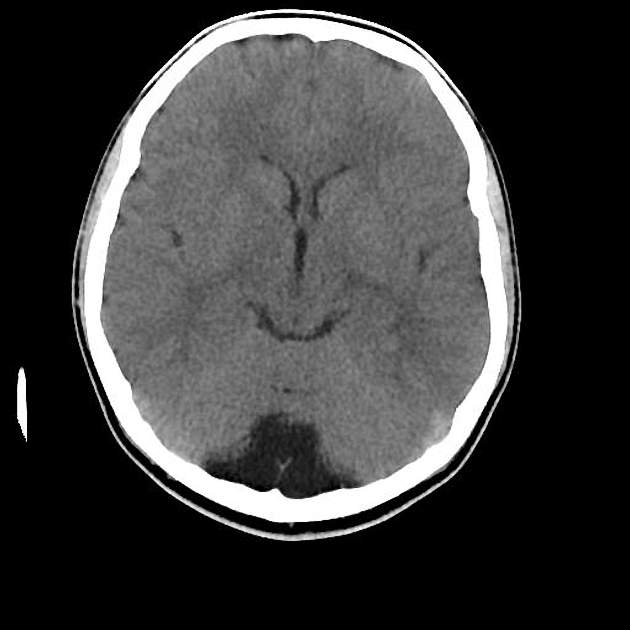
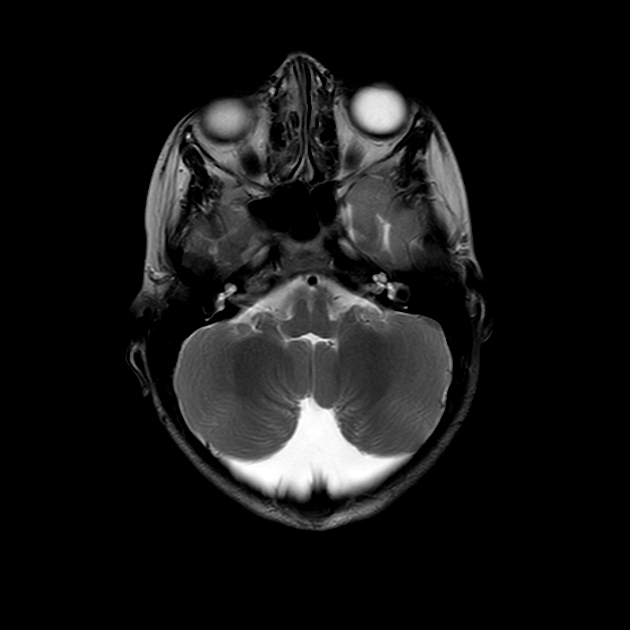
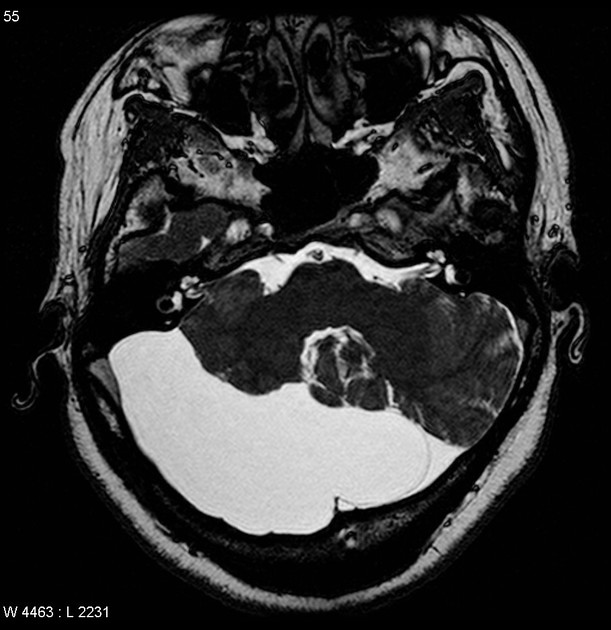
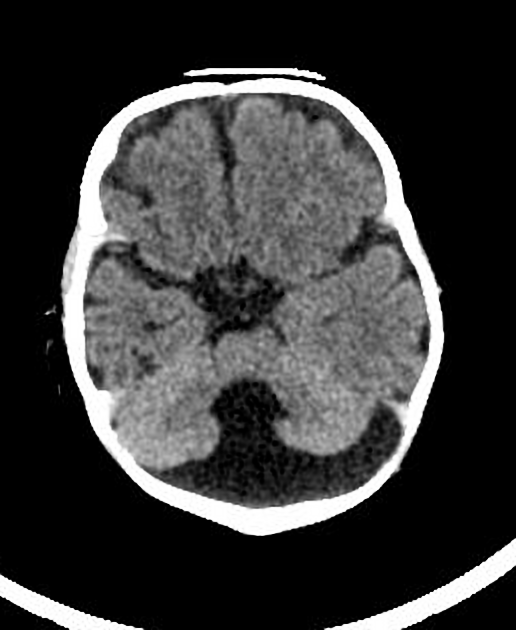
Mega cisterna magna refers to a normal variant characterized by a truly focal enlargement of the CSF-filled subarachnoid space in the inferior and posterior portions of the posterior cranial fossa. It is an incidental finding on neuroimaging, and no imaging follow up is necessary.
On this page:
Epidemiology
A mega cisterna magna is thought to occur in ~1% of all brains imaged postnatally. It constitutes 54% of all cystic posterior fossa malformations 4.
Associations
Especially if noted antenatally, a mega cisterna magna has been associated with:
infarction
inflammation/infection: particularly cytomegalovirus
chromosomal abnormalities: especially trisomy 18
In children, it has also been identified in association with autism spectrum disorder 9,10.
However, when a mega cisterna magna occurs as an isolated finding and the ventricles are normal it should be considered a variant of normal with no prognostic significance.
Clinical presentation
There are no specific symptoms related to this condition.
Pathology
Some authors have proposed that mega cisterna magna is a result of a delayed Blake pouch fenestration; when fenestration does not occur, it results in a Blake pouch cyst 6.
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
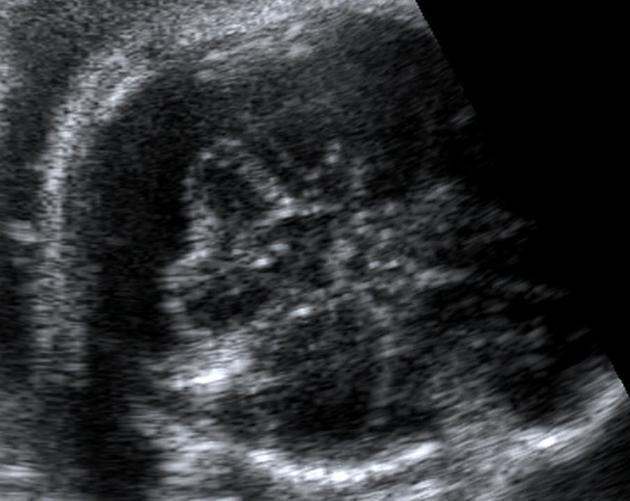
On antenatal ultrasound, mega cisterna magna refers to an enlarged retrocerebellar CSF space:
usually >10 mm (some consider up to 12 mm within normal limits)
septa may be seen within a mega cisterna magna, which are thought to be Blake pouch vestigial remnants 3
the vermis should be closely evaluated to exclude Dandy-Walker continuum abnormalities
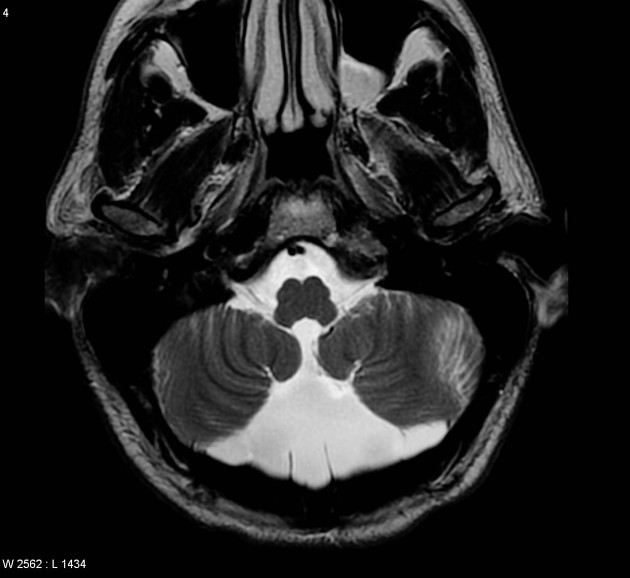
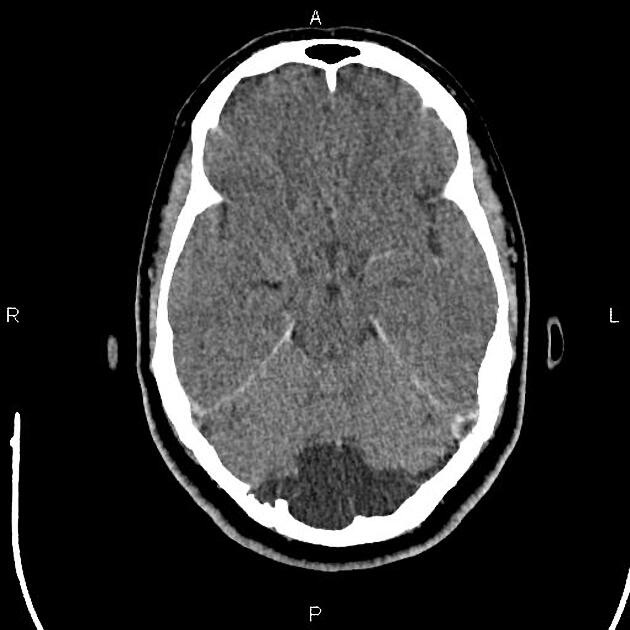
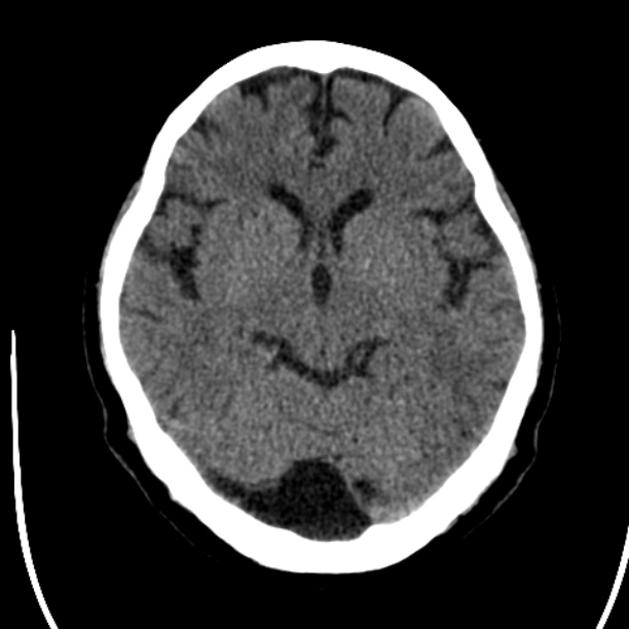
CT/MRI
Typically seen as prominent retrocerebellar cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) appearing space with a normal vermis, normal 4th ventricle, and normal cerebellar hemispheres. An enlarged cisterna magna usually measures >10 mm on midsagittal images. An enlarged posterior fossa can sometimes be present 6.
History and etymology
The term was coined by the Belgian neurosurgeon Richard Gonsette (1929-2014) 8 in 1962, in patients with cerebellar atrophy 7.
Differential diagnosis
Mega cisterna magna needs to be distinguished from other causes of an enlarged retrocerebellar CSF space:
arachnoid cyst: can be difficult to distinguish from a mega cisterna magna
epidermoid cyst: often shows a heterogeneous/dirty signal on FLAIR and restricted diffusion
Dandy-Walker malformation: vermis not intact
Blake pouch cyst: usually hydrocephalus is present
pilocytic astrocytoma: if very posterior and predominantly cystic; should contain a mural nodule
References
- 1. Epelman M, Daneman A, Blaser SI, Ortiz-Neira C, Konen O et al. Differential diagnosis of intracranial cystic lesions at head US: correlation with CT and MR imaging. Radiographics. ; 26(1): 173-96. doi:10.1148/rg.261055033 [pubmed citation]
- 2. Estroff JA, Scott MR, Benacerraf BR. Dandy-Walker variant: prenatal sonographic features and clinical outcome. Radiology. 1992; 185(3): 755-8. Radiology [pubmed citation]
- 3. Robinson AJ, Goldstein R. The cisterna magna septa: vestigial remnants of Blake's pouch and a potential new marker for normal development of the rhombencephalon. J Ultrasound Med. 2007;26 (1): 83-95. J Ultrasound Med (full text) - Pubmed citation
- 4. Kollias SS, Ball WS, Prenger EC. Cystic malformations of the posterior fossa: differential diagnosis clarified through embryologic analysis. Radiographics. 1993;13 (6): 1211-31. Radiographics (abstract) - Pubmed citation
- 5. Zimmer EZ, Lowenstein L, Bronshtein M et-al. Clinical significance of isolated mega cisterna magna. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2007;276 (5): 487-90. doi:10.1007/s00404-007-0369-6 - Pubmed citation
- 6. Bosemani T, Orman G, Boltshauser E, Tekes A, Huisman T, Poretti A. Congenital Abnormalities of the Posterior Fossa. Radiographics. 2015;35(1):200-20. doi:10.1148/rg.351140038 - Pubmed
- 7. Gonsette R, Potvliege R, Andre-Balisaux G, Stenuit J. Mega-cisterna magna: Clinical, radiologic and anatomopathologic study. Acta Neurol Psychiatr Belg. 1968. 68: 559-70
- 8. Sindic C, Edan G. Richard E Gonsette (1929-2014). (2015) Multiple sclerosis (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England). 21 (5): 540. doi:10.1177/1352458515572242 - Pubmed
- 9. Rochat MJ, Distefano G, Maffei M, Toni F, Posar A, Scaduto MC, Resca F, Cameli C, Bacchelli E, Maestrini E, Visconti P. Brain Magnetic Resonance Findings in 117 Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder under 5 Years Old. (2020) Brain sciences. doi:10.3390/brainsci10100741 - Pubmed
- 10. Erbetta A, Bulgheroni S, Contarino V et al. Neuroimaging Findings in 41 Low-Functioning Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Single-Center Experience. J Child Neurol. 2014;29(12):1626-31. doi:10.1177/0883073813511856 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Joubert syndrome
- Sonographic values in obstetrics and gynaecology
- Ritscher-Schinzel syndrome
- Fetal intracranial cystic lesions
- Edwards syndrome
- Enlarged posterior fossa 'CSF' space
- Vermian maturity assessment (approach)
- Cisterna magna
- Patau syndrome
- Diffuse cerebellar atrophy
- Dandy-Walker malformation
- Intracranial cystic lesions in the perinatal period
- Cerebellar hypoplasia
- Obstetric curriculum
- Intracranial epidermoid cyst
- Tegmentovermian angle
- Arachnoid cyst
- Blake's pouch cyst
- Paediatric curriculum
- Antenatal soft markers on ultrasound
- Diffuse cerebellar atrophy
- Mega cisterna magna
- Subependymal grey matter heterotopia
- Pituitary stalk interruption syndrome with subependymal grey matter heterotopia
- Mega cisterna magna
- Aicardi syndrome
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
- Agenesis of the corpus callosum with interhemispheric cyst
- Thanatophoric dwarfism
- Blake pouch cyst
- Ring-shaped lateral ventricular nodules (RSLVNs)
- Mega cisterna magna
- Arachnoid cyst of posterior fossa
- Mega cisterna magna
- Bilateral tonsillitis
- Arachnoid cyst
- Tuberous sclerosis - subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
- Dandy-Walker malformation
- Retrocerebellar cyst
- Scalp haemangioma
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway
Related articles: Pathology: Genitourinary
- obstetrics
-
first trimester
- ultrasound findings in early pregnancy
- embryo/fetus
- beta-hCG levels
- confirming intrauterine gestation
- pregnancy of unknown location (PUL)
- first trimester vaginal bleeding
- early structural scan
- aneuploidy testing
-
second trimester
- fetal biometry
- amniotic fluid volume
- fetal morphology assessment
- soft markers
- amnioreduction
- Doppler ultrasound
- nuchal translucency
- 11-13 weeks antenatal scan
- chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and amniocentesis
- other
- placenta
- placental anatomy
- placental developmental abnormalities
- placenta previa
- spectrum of abnormal placental villous adherence
- abnormalities of cord insertion
- abruptio placentae
- placental pathology
- vascular pathologies of placenta
- placental infections
- placental masses
- molar pregnancy
- twin placenta
- miscellaneous
-
first trimester
- gynecology
- acute pelvic pain
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterus
- ovaries
- ovarian follicle
- ovarian torsion
- pelvic inflammatory disease
- ovarian cysts and masses
- paraovarian cyst
- polycystic ovaries
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- post-hysterectomy ovary
- cervix
- fallopian tube
- other
- male genital tract
- prostate gland
- transrectal ultrasound
- prostate tumors
- infections of the prostate
-
prostatitis
- acute bacterial prostatitis
-
chronic prostatitis
- chronic bacterial prostatitis
- chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
- asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
- granulomatous prostatitis
- emphysematous prostatitis
- prostatic abscess
-
prostatitis
- benign prostatic hypertrophy
- cystic lesions of the prostate
- prostatic calcification
- prostatic infarction
- testes
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- testicular torsion
- orchitis
- testicular trauma
-
germ cell tumors of the testis
- testicular seminoma
-
non seminomatous germ cell tumors
- mixed germ cell tumor
- yolk sac tumor (endodermal sinus tumor)
- embryonal cell carcinoma
- choriocarcinoma
- testicular teratoma
- testicular epidermoid (teratoma with ectodermal elements only)
- burned out testis tumor
- sex cord / stromal tumors of the testis
- testicular cyst
- testicular lymphoma
- bilateral testicular lesion
- paratesticular lesions
- epididymis
- other
- polyorchidism
- cryptorchidism
- tubular ectasia of the rete testis
- cystadenoma of the rete testis
- testicular sarcoidosis
- testicular tuberculosis
- spermatic cord
- fibrous pseudotumor of the scrotum
- scrotal leiomyosarcoma
- testicular adrenal rest tumors (TARTs)
- tunica vaginalis testis mesothelioma
- splenogonadal fusion
- testicular vasculitis
- abnormal testicular Doppler flow (differential)
-
unilateral testicular lesion
- penis
- prostate gland
- KUB
- kidneys
- normal renal anatomy
- hydronephrosis
- urolithiasis
- renal masses
- renal cystic disease
- renal infection
- vascular
- trauma
- ureter
- normal ureter anatomy
- ureteral stricture
- ureteral dilatation
- ureteral anomalies
- ureteral tumors
- ureteral trauma
- other
- bladder
- kidneys






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.