Phrenic nerve
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Henry Knipe had no recorded disclosures.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yoshi Yu had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Yoshi Yu's current disclosures- Phrenic nerves
- Left phrenic nerve
- Right phrenic nerve
The phrenic nerve is a mixed motor/sensory nerve that courses through the neck and thorax to innervate the diaphragm.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Origin
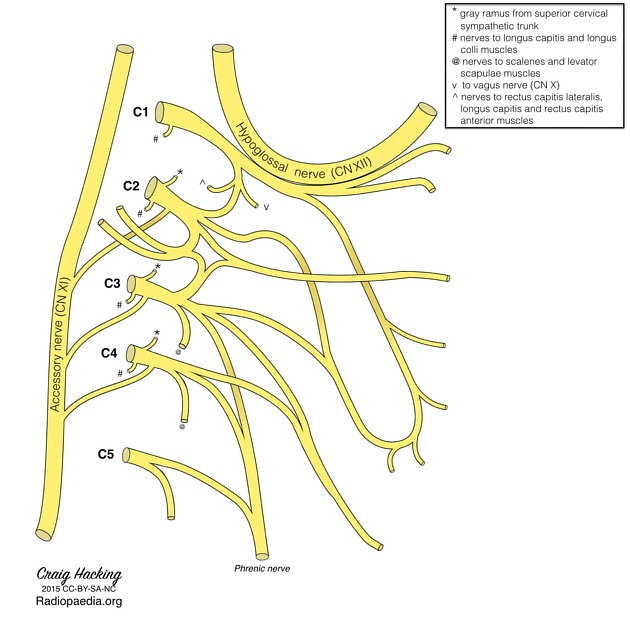
Arises from the ventral rami of the C3, C4 and C5 nerve roots, part of the cervical plexus.
Course
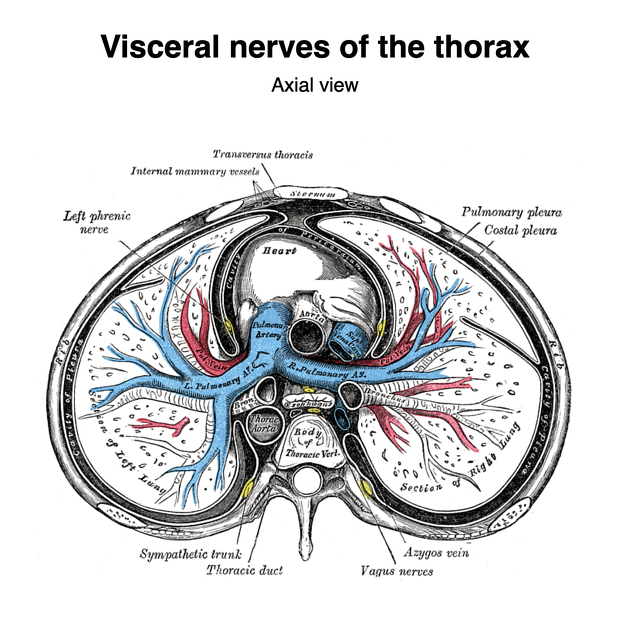
In the neck, the phrenic nerve lies on the anterior surface of the anterior scalene muscle, passes over the dome of the pleura and enters the thorax posterior to the subclavian vein. The right and left phrenic nerves have a different course in the thorax but as a general rule they descend as lateral as possible whilst keeping in contact with the mediastinal pleura. Both travel anterior to the hilum/bronchus on their respective side.
Left phrenic nerve
After entering the thorax posterior to the subclavian vein it descends lateral to origin of the left subclavian artery, arch of the aorta, left auricle and left ventricle (in contact with pericardium) before piercing the dome of the left hemidiaphragm to enter the abdominal cavity.
Right phrenic nerve
In contrast to the left phrenic nerve, the right is in contact with venous structures and descends lateral to the superior vena cava, right atrium and ventricle, and inferior vena cava before passing through the vena caval foramen to enter the abdominal cavity.
Within the abdominal cavity both the left and right phrenic nerves divide into three main branches - anterior, lateral and posterior. These course peripherally in a radial pattern.
Supply
The phrenic nerve is the sole motor supply to each hemidiaphragm. It also provides sensory supply to:
diaphragm (except the most peripheral diaphragm, which is supplied by intercostal nerves)
mediastinal pleura
central parts of diaphragmatic pleura and peritoneum
Blood supply
arterial supply: pericardiophrenic artery (branch of the internal thoracic artery)
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Variant anatomy
course anterior to the subclavian vein
course along the lateral border of the anterior scalene muscle
may pierce the anterior scalene muscle
accessory phrenic nerve (usually arising from the ansa cervicalis or subclavian nerve)
may receive additional branches from the cervical or brachial plexuses
may supply a branch to the subclavius muscle
Relations
Posterior: Scalenus anterior, 2nd part of subclavian artery (at root of neck)
Anterior: Sternocleidomastoid, inferior belly of omohyoid, internal jugular vein, transverse cervical artery, suprascapular artery, thoracic duct (for left phrenic only) subclavian vein (at base of neck)
Related pathology
Quiz questions
References
- 1. McMINN. Lasts Anatomy Regional and Applied. CHURCHILL LIVINGSTONE. (2003) ISBN:B0084AQDG8. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Bigeleisen PE. Anatomical variations of the phrenic nerve and its clinical implication for supraclavicular block. Br J Anaesth. 2003;91 (6): 916-7. doi:10.1093/bja/aeg254 - Pubmed citation
- 3. In Standring, S. (2016). Gray's anatomy: The anatomical basis of clinical practice.
Incoming Links
- Central tendon of diaphragm
- Accessory phrenic nerve
- Peritoneum
- Pericardiophrenic artery
- Thoracic duct
- Middle mediastinum
- Mediastinum
- Longus colli muscle
- Perivertebral space
- Brachial plexus
- Lesser diaphragmatic apertures
- Thyrocervical trunk
- Diaphragmatic apertures (mnemonic)
- Diaphragm
- Right atrium
- Pericardiophrenic vein
- Diaphragmatic apertures
- Sniff test
- Phrenic nerve paralysis
- Central control of respiration
Related articles: Anatomy: Thoracic
- thoracic skeleton[+][+]
- thoracic cage
- thoracic spine
- articulations
- muscles of the thorax[+][+]
- diaphragm
- intercostal space
- intercostal muscles
- variant anatomy
- spaces of the thorax[+][+]
- thoracic viscera[+][+]
- lower respiratory tract
-
heart
- cardiac chambers
- heart valves
- cardiac fibrous skeleton
- innervation of the heart
- development of the heart
- cardiac wall
-
pericardium
- epicardium
- epicardial fat pad
- pericardial space
- oblique pericardial sinus
- transverse pericardial sinus
-
pericardial recesses
- aortic recesses
- pulmonic recesses
- postcaval recess
- pulmonary venous recesses
- pericardial ligaments
- myocardium
- endocardium
-
pericardium
- esophagus
- thymus
- breast
- arterial supply of the thorax[+][+]
-
thoracic aorta (development)
-
ascending aorta
-
aortic root
- aortic annulus
-
coronary arteries
- coronary arterial dominance
- myocardial segments
-
left main coronary artery (LMCA)
- ramus intermedius artery (RI)
-
circumflex artery (LCx)
- obtuse marginal branches (OM1, OM2, etc))
- Kugel's artery
-
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
- diagonal branches (D1, D2, etc)
- septal perforators (S1, S2, etc)
-
right coronary artery (RCA)
- conus artery
- sinoatrial nodal artery
- acute marginal branches (AM1, AM2, etc)
- inferior interventricular artery (PDA)
- posterior left ventricular artery (PLV)
- congenital anomalies
- sinotubular junction
-
aortic root
- aortic arch
- aortic isthmus
- descending aorta
-
ascending aorta
- pulmonary trunk
-
thoracic aorta (development)
- venous drainage of the thorax[+][+]
- superior vena cava (SVC)
- inferior vena cava (IVC)
-
coronary veins
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- great cardiac vein
- middle cardiac vein
- small cardiac vein
- posterior vein of the left ventricle
- vein of Marshall (oblique vein of the left atrium)
- anterior cardiac veins
- venae cordis minimae (smallest cardiac veins or thebesian veins)
-
cardiac veins which drain into the coronary sinus
- pulmonary veins
- bronchial veins
- thoracoepigastric vein
- lymphatics of the thorax[+][+]
- innervation of the thorax
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia
-
deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- orbit
- ear
- paranasal sinuses
- upper respiratory tract
- viscera of the neck
- blood supply of the head and neck
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- embryological development of the head and neck






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.